These are 3 infectious causes of new AV blocks.
What are chagas disease, lyme disease, and myocardial abscess?
This is the first line therapy for (stable) atrial flutter.
What is radiofrequency catheter ablation?
After an MI, bradycardia is most common if this coronary vessel was involved.
What is the right coronary artery (inferior MI)?
This is the optimal treatment for sinus tachycardia.
What is treating the underlying cause?
These are class 1 indications for permanent pacemaker placement. (Name 3)
What are:
Class 1:
Blocks) symptomatic Mobitz type 1, high-grade (advanced) AV block, Mobitz type 2, 3rd degree AV block, exercise-induced 2nd or 3rd degree AV block (w/out ischemia)
Brady) symptomatic bradycardia (including SSS and 2/2 required Rx), symptomatic chronotropic incompetence
?
This is the name of and treatment for this severe complication of high-grade or complete heart block.
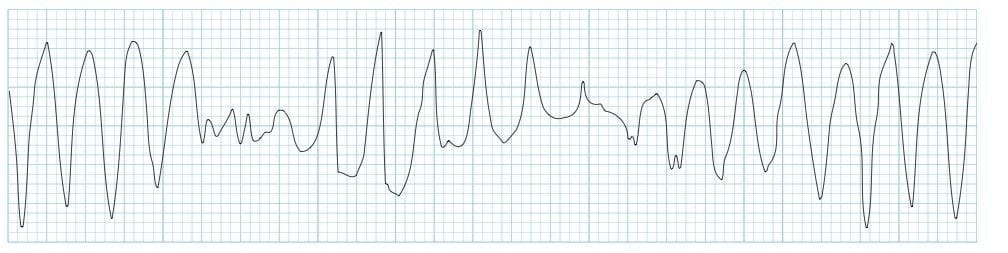
What is torsades de pointes and defibrillation plus magnesium sulfate IV (1-2g over 15 minutes, can follow with infusion)?
This is the treatment for unstable afib/flutter.
What is synchronized cardioversion?
Apart from beta blockers and CCBs, these are all medications that can commonly cause bradycardia. (name 3)
What are digoxin, donepezil, opioids, SSRIs, and TCAs?
This finding is the characteristic example used for Wolff-Parkinson-White pattern of AVRT.
What is a delta wave or slurred upstroke of the QRS complex?
Name the abnormality on this ECG:
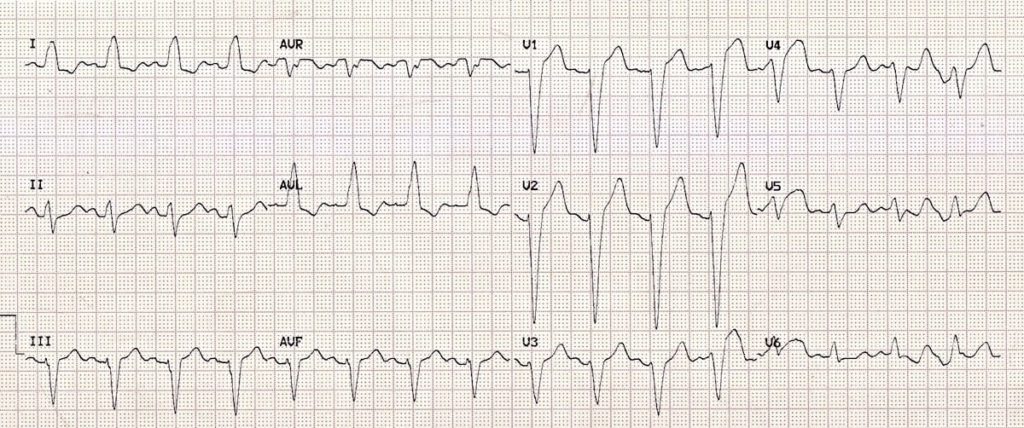
What is LBBB?
QRS >= 120ms
Dominant S wave in V1
Broad, monophasic R wave in lateral leads (I, aVL, and V5 - V6)
Absent Q waves in lateral leads
Prolonged R wave peak time (notched) >60ms in leads V5 - V6
?
This is defined as high-grade AV block.
What is the occurrence of >1 consecutively blocked P wave without the presence of third-degree block?
or
R-R interval containing non-conducted beats >= 2 x P-P interval?
These are 7 causes of atrial fibrillation.
What are:
PE/COPD
Ischemia
Rheumatic heart disease (mitral stenosis/regurg)
Anemia, alcohol, or age
Thyroid disease (hyperthyroidism)
Electrolytes, endocarditis
Sepsis, SSS
?
These can act as temporizing measures in a patient with symptomatic and persistent bradycardia.
What are atropine (1mg IV push q3min to 3mg), dopamine or epinephrine drip, or temporary cardiac pacing (transcutaneous, transvenous)?
This is the longest-term continuous monitoring option for patients with tachy/bradyarrhythmias.
What is an implanted loop recorder?
These are the indications for cardiac resynchronization therapy in a patient with heart failure. (4 things)
What are:
1) Symptomatic HF with LVEF <35%
2) on optimized GDMT
3) LBBB
4) QRS >= 150ms
?
These are the definitions for the two kinds of 2nd degree AV blocks.
What is intermittent p waves not followed by QRS complexes plus either:
Mobitz type 1 = increasing PR interval
or
Mobitz type 2 = unchanging PR intervals
?
These are the AHA guideline recommendations for anticoagulation in a stable afib patient considering cardioversion.
What is being on anticoagulation for at least 3 weeks prior and 4 weeks post cardioversion?
This initial evaluation should be done for all patients with suspected bradycardia. (4 generic things)
What is a detailed history, ECG, med review, labs (lytes + mag, TSH)?
Name this rhythm.
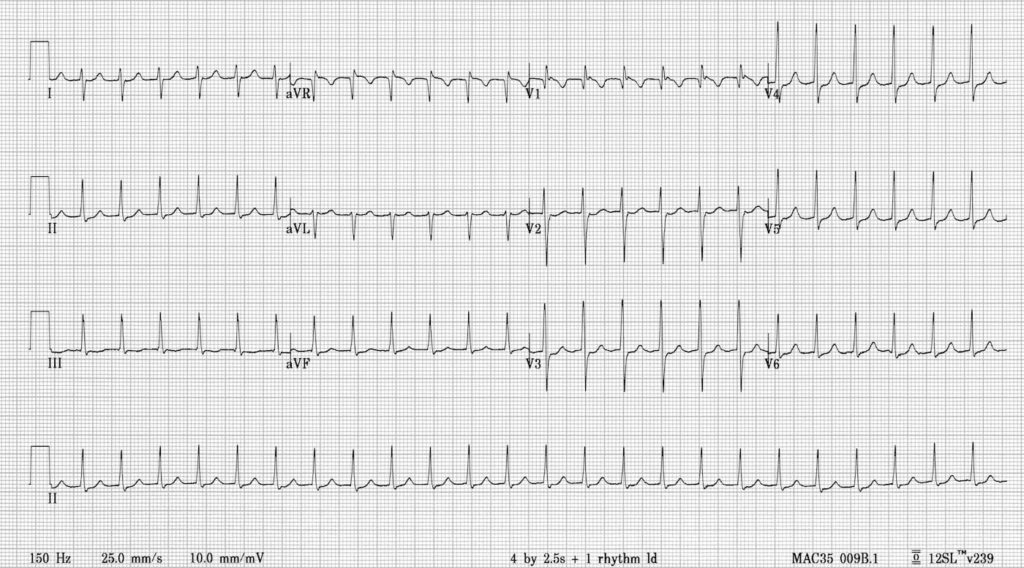
What is AVNRT?
See the pseudo S wave in the inferior leads due to RP interval being so short the P wave is buried within the QRS complex.
These criteria can help identify ST segment changes suggestive of infarction in patients with LBBB.
What are the Sgarbossa criteria?
Any of:
1) Concordant ST elevation ≥ 1 mm in ≥ 1 lead
2) Concordant ST depression ≥ 1 mm in ≥ 1 lead of V1-V3
3) Proportionally excessive discordant STE in ≥ 1 lead anywhere with ≥ 1 mm STE, as defined by ≥ 25% of the depth of the preceding S-wave
Name this arrhythmia and the definition of the arrythmia.
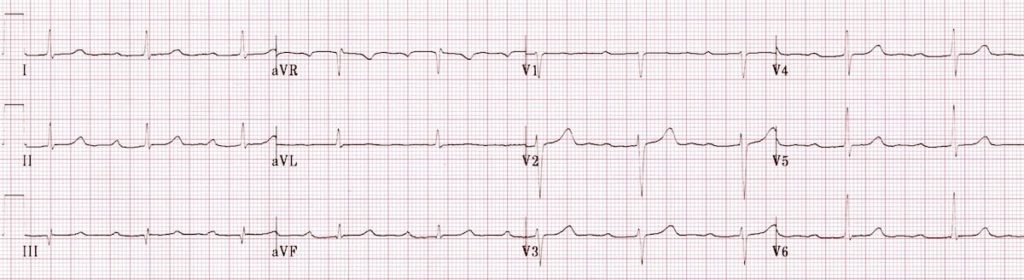
What is 1st degree AV block with bradycardia, based on HR <60 and PR >200ms?
These are 4 cases where rhythm control might be superior to rate control in patients with atrial fibrillation.
What are:
1) patients <50 years old (70 y.o.?)
2) recent-onset afib
3) high symptom burden
4) high risk for adverse events related to afib (concurrent HF, decreased hospitalization and mortality)
Originally based on AFFIRM trial findings, rate control was superior but more recent studies show ablation (CASTLE-AF, CABANA) or rhythm control (EAST-AFNET 4) could be superior.
This unique scenario can present as false bradycardia either on monitoring (EKG or continuous) or on pulse check.
What is bigeminy?
Can identify the pseudobradycardia via auscultation or close examination of the EKG.
This is the name of this arrythmia.
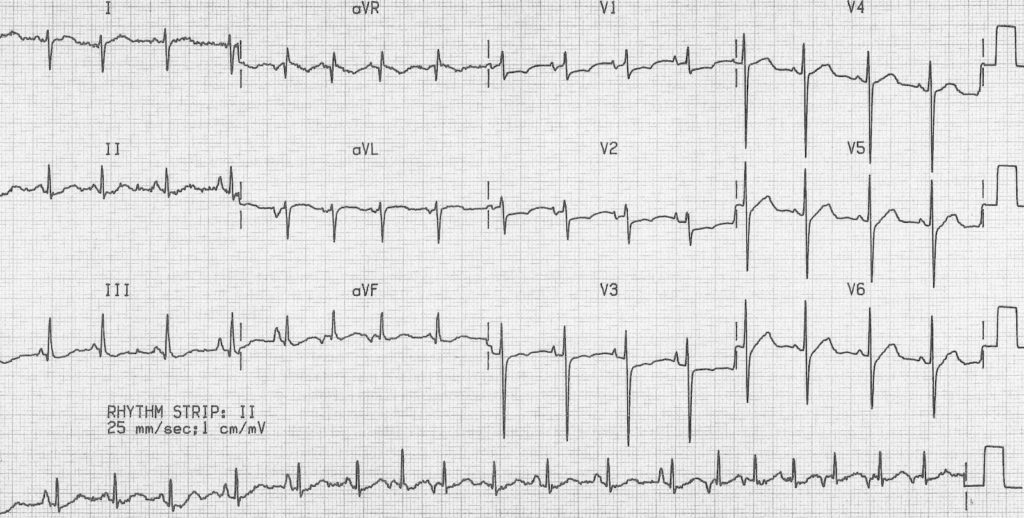
What is Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia?
At least 3 different P-wave morphologies, HR >100, variable PR, PP, and RR intervals, isoelectric baseline between P waves.
The patient with this ECG showing atrial tachycardia with a high-grade 2nd degree AV block likely received an overdose of this medication.
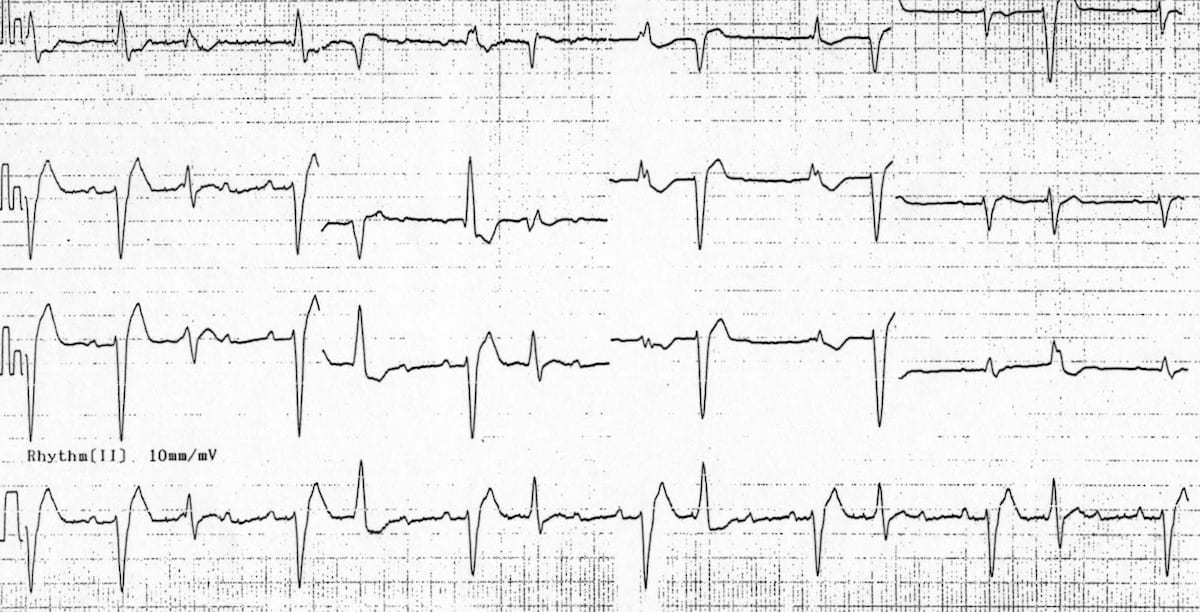
What is digoxin?
Digoxin toxicity can produce various arrythmias but the "classic" ECG shows atrial tachycardia, PVCs, scooped or sagging ST depressions, flattened/inverted biphasic T waves, and a shortened QT interval.