men: 13.5 to 17.5 g/dL; women 12.0 to 15.5g/dL
what is hemoglobin?
Records electrical impulses of the heart to determine rate, rhythm of heart, site of pacemaker, and presence of injury at rest.
What is an electrocardiogram?
this rhythm contains all P, QRS, and T
What is sinus rhythm?
another term medically used for heart attack
What is Myocardial infarction?
digoxin is typically used for patients to treat heart failure and abnormal heart rhythms, when typically should the nurse hold the medication and notify the provider?
What is a heart rate of less than 60bpm?
Major carriers of hemoglobin in the blood.
what is red blood cell (RBC)?
used to evaluate size, shape, and position of structures and movement within the heart
What is an echocardiogram?
This rhythm is likely to be seen when client’s rate is too low & symptomatic (syncope, dizziness, hypotension), treatment may be initiated with atropine (increases heart rate).
What is sinus bradycardia?
List at least one diagnostic lab for a patient suspected with MI
BNP, CK-MB, troponin
this class of medication helps treat fluid retention (edema) and swelling that is caused by congestive heart failure, liver disease, kidney disease, or other medical conditions. It works by acting on the kidneys to increase the flow of urine
What are diuretics? (i.e. furosemide/lasix, spironolactone)
low levels may indicate prolonged infection or bone marrow suppression
What is leukopenia (low white blood cells)?
What is cardiac catheterization?
0.06-0.10 seconds is the normal range for which part of the ECG
What is QRS interval?
this Rhythm is irregular, has Quivering of the atria and NO defined “P” wave, patient will likely be on a blood thinner (i.e. pradaxa, warfarin/coumadin, eliquis)
What is atrial fibrillation?
What is atrial fibrillation?
may indicate polycythemia vera, malignancy, or rheumatoid arthritis
What is thrombocytosis/elevated platelets?
this lab to evaluate heart failure to test natriuretic peptides
normally natriuretic peptides promote urine excretion, relax blood vessels, lower blood pressure, and reduce the heart's workload.
What is BNP?
B-type natriuretic peptide
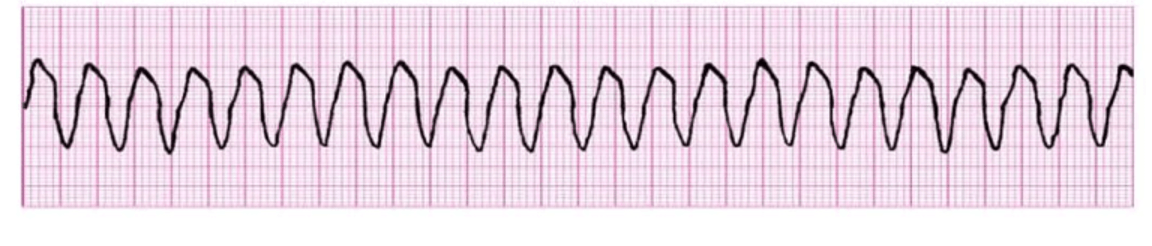
What is Ventricular Tachycardia?
for this situation the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet body’s demand and is typically related to congestion and increased pressure, this is a gradual progression
What is heart failure?
this cardiac medication class blocks calcium from entering muscle cells of heart and arteries; decrease strength in heart contractions; dilate arteries.
Widening of the arteries causes a decrease in blood pressure and reduces the heart’s workload.
What are calcium channel blockers?
the normal value 5,000 to 10,000 cells/mm³
What is White blood cell count?
These lab levels may elevate within 4-6 hours after MI, peak within 10-24 hours, and return to normal within 10 days.
What is Troponin?
0.12 to 0.20 seconds is the normal range for this part of the ECG
What is PR interval?
A BNP was performed for this patient with Shortness of breath with activity or when lying down, Fatigue and weakness, Swelling in the legs, ankles and feet, Rapid or irregular heartbeat.
What is heart failure?
this class of medication may be prescribed after a MI leading to a reduction in myocardial oxygen consumption and increasing the threshold to myocardial ischemia
block effects of epinephrine (adrenaline) on cardiovascular system.
Intended responses: decreased heart rate, force of heart contraction, workload of heart; lowered BP
what are beta blockers?