What are the 2 atrioventricular valves in the heart?
Tricuspid and Mitral
Which of the following structures carries oxygenated blood?
A) Pulmonary arteries
B) Pulmonary veins
C) Superior vena cava
D) Inferior vena cava
B. Pulmonary Veins
A heart rate of 56 bpm is indicative of what condition?
Bradycardia
Bradycardia = <60 bpm
Tachycardia = >100 bpm
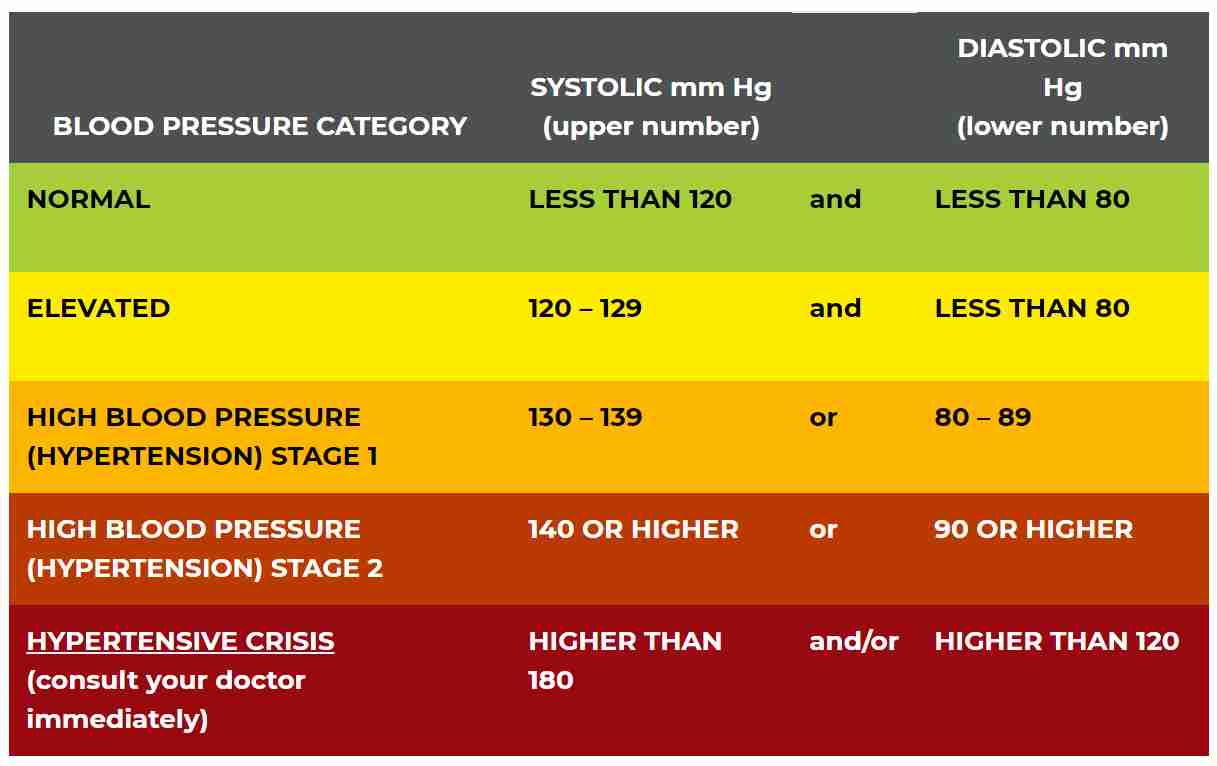
A patient presents with a blood pressure of 128/78. What blood pressure category is this patient in?
Elevated
Sudden dyspnea, with sharp chest pain, hemoptysis and a positive D–dimer test?
1. Pneumonia
2. Pneumothorax
3. Pulmonary Embolus
4. Pulmonary edema
3. Pulmonary Embolus
The atrioventricular node can beat at what range (in beats/minute)?
40-60 bpm
The (upper/lower) ribs have a bucket handle motion while the (upper/lower) ribs have a pump handle motion.
1. Lower
2. Upper
Which wave denotes ventricular repolarization?
A. P wave
B. R wave
C. T wave
D. U wave
C. T wave
P wave: Atrial depolarization
R wave: Ventricular Depolarization
T wave: Ventricular Repolarization
U wave: Repolarization of Purkinjee fibers
Which one of the following is a sign indicative of left
sided heart failure?
A. Jugular distention
B. Pulmonary Rales
C. Hepatomegaly/ splenomegaly
D. Peripheral edema
B. Pulmonary Rales
Patient has a balloon-like presentation of the alveoli with blebs on the surface of the lung. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. COPD
B. Chronic Bronchitis
C. Asthma
D. Emphysema
D. Emphysema
The volume of blood ejected out of the left ventricle into systemic vasculature per minute is called...?
Cardiac Output (CO) or (Q)
What is the normal range of pH in the blood?
7.35-7.45
What would indicate a transmural myocardial infarct?
A. Prolonged PR interval
B. Shortened PR segment
C. ST depression
D. ST elevation
D. ST elevation
ST elevation = Transmural MI
ST depression = Ischemia
Which of the following is NOT a feature of Tetralogy of Fallot?
A. Ventricular Septal Defect
B. Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
C. Right Ventricular Hypertrophy
D. Overriding Aorta
B. Left ventricular hypertrophy
Bronchophony findings -sounds like a clear 99 on a lobe. Which pathology is it?
1. Pneumonia
2. Pneumothorax
3. Obesity
4. Hemothorax
1. Pneumonia
Which of the following is the action of the parasympathetic system on the heart?
a. Vasodilates the coronary arteries
b. Negative Chronotropic effects
c. Positive ionotrophic effects
d. Stimulates cardio-acceleratory center in medulla
b. Negative chronotrophic effects
The parasympathetic system vasoconstricts the coronary arteries, elicits negative chronotrophic and ionotrophic effects, and stimulates the cardio-inhibitory center of the medulla
A patient was asked to count to 15 and took 3 breaths. What grade would the physical therapist give this patient on the dyspnea scale?
a. Level 0
b. Level 1
c. Level 2
d. Level 3
C. Level 2
Ability to count to 15 in a 7.5-8 second time span:
Level 0: On a single breath
Level 1: Requires 2 breaths
Level 2: Requires 3 breaths
Level 3: Requires 4 breaths
Level 4: Unable to count
What is this ECG strip depicting? (Hint: A diagnosis with 2 types)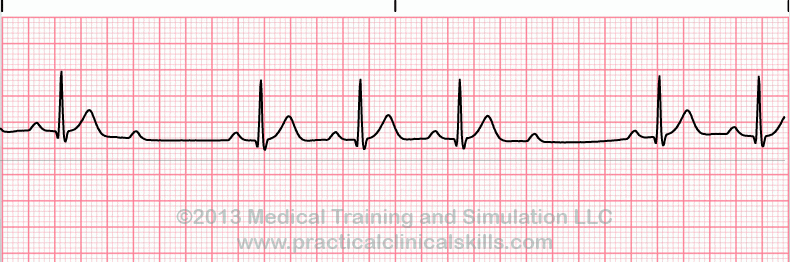
Second Degree AV block Type II/Mobitz II
Characteristics:
Fixed PR interval, 2-4 P waves followed by a QRS complex, pattern maintained
A patient with pericarditis presents with elevated intracardiac pressures, reduced SV and limited ventricular diastolic filling. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Cor pulmonale
B. Cardiac tamponade
C. Pericardial effusion
D. Myocarditis
B. Cardiac tamponade
FEVI/ FVC ratio is 90% with hypoxemia what does it indicate?
A. Normal respiratory status
B. Obstructive lung disease
C. Restrictive lung disease
D. Cannot determine the respiratory status
C. Restrictive lung Disease
They have trouble getting air in so the FEVI/FVC ratio would be normal or higher. Since there is difficulty getting air in, there is a decreased surface area for gas exchange, therefore hypoxemia