Bradycardia
What is Slow heart rate?
Blood vessels branching from the aorta to carry oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle.
What is Coronary Arteries?
Patent
What is Open?
Gaseous waste found in expelled air. Carried in the veins
What is Carbon Dioxide?
Rapid Heart Rate
What is Tachycardia?

What is Electrocardiogram (ECG)?
Medication used to strengthen the heart rate
What is Digitalis?

Phleborrhexis
What is Rupture of a vein?
This tissue in the right atrium starts the heartbeat
What is Sinoatrial Node?
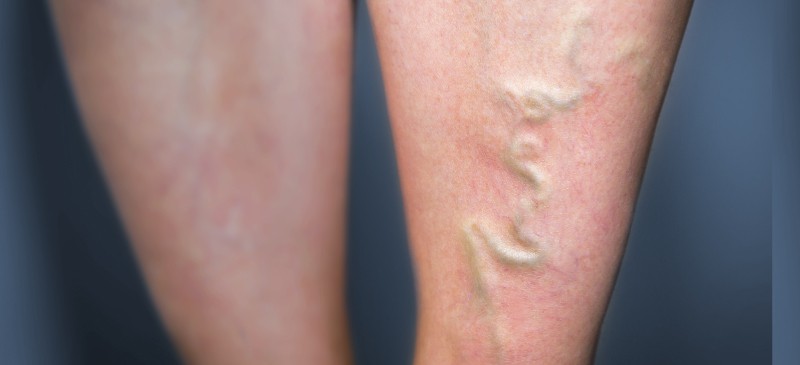
Right leg is normal veins & Left leg is inflamed veins
What is Phlebitis?
Barlow Syndrome is an example of
What is Mitral Valve Prolapse?
Pericardium
What is membrane sac that encloses the heart?
Patient gets admitted to the hospital with a blue tint to their skin and lips caused from hypoxia (low oxygen)
What is Cyanosis?
Mr.Jones has just recovered from his first heart attack, the doctor has prescribed him a medication to protect his heart from a second heart attack.
What is Beta Blocker?
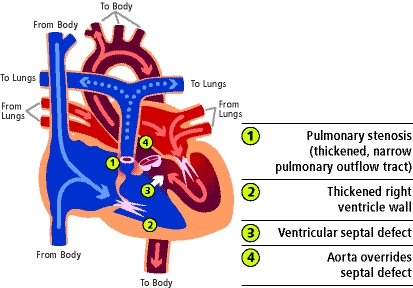
4 things that are wrong within the heart
What is Tetralogy of Fallot?
A patient with hypertension is prescribed this medication in order to cause dilation of the blood vessel, making it easier for the heart to pump blood through the vessels
What is Calcium Channel Blocker?
What is Cardiomyopathy?
Patient is admitted due to an hemorrhagic stroke (bleeding in the brain) after some examination an artery in the brain has ruptured, ballooning and weakening of the artery caused this rupture
What is an Aneurysm?
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/mediastinum/iwJHKUPTpBQAhEq9cWHw_Mediastinum.png)
This cavity holds holds all these organs
What is Mediastinum?

These are different ECGs of different hearts, each has an unusual electrical pattern some examples of this condition include; flutter, heart block, fibrillation, and premature ventricular contractions (PVC's)
What is Cardiac Arrhythmia?
