Relative Risk is ...
Relative Risk is the ratio of the probability of an event occurring in the exposed group versus the probability of the event occurring in the non-exposed group.
ODDS RATIO is defined as...
Odds Ratio - Measure of how strongly an event is associated with exposure.
OR = (odds of the event in the exposed group) /
(odds of the event in the non-exposed group)
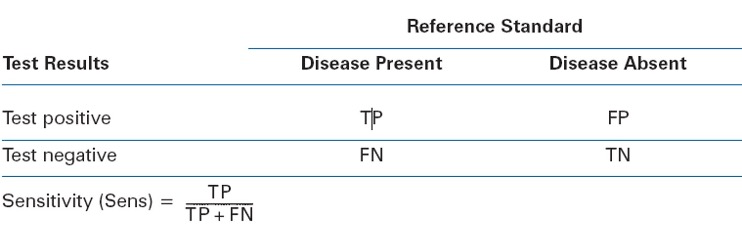
Sensitivity of a test is...
Sensitivity indicates how well a test identifies individuals who actually have the disease (true positives)
The ACCORD Trial
Intenssive vs Conservative Blood Sugar Control for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Using evidence to change therapy - discussion with specialist
AECOPD - antibiotic therapy
Relative Risk Reduction is defined as
Relative Risk Reduction is the difference between the event rate rates in elative terms.
A way to express how much a treatment or intervention decreases the risk of an event compared to a control group.
Positive Predictive Value is ...
Positive Predictive Value reflects the probability that a positive test result is actually correct (true positives out of all positive results).

The COURAGE Trial
"Optimal Medical Therapy with or without PCI for Stable Coronary Disease"
(Initial Treatment of Stable Coronary Artery Disease)
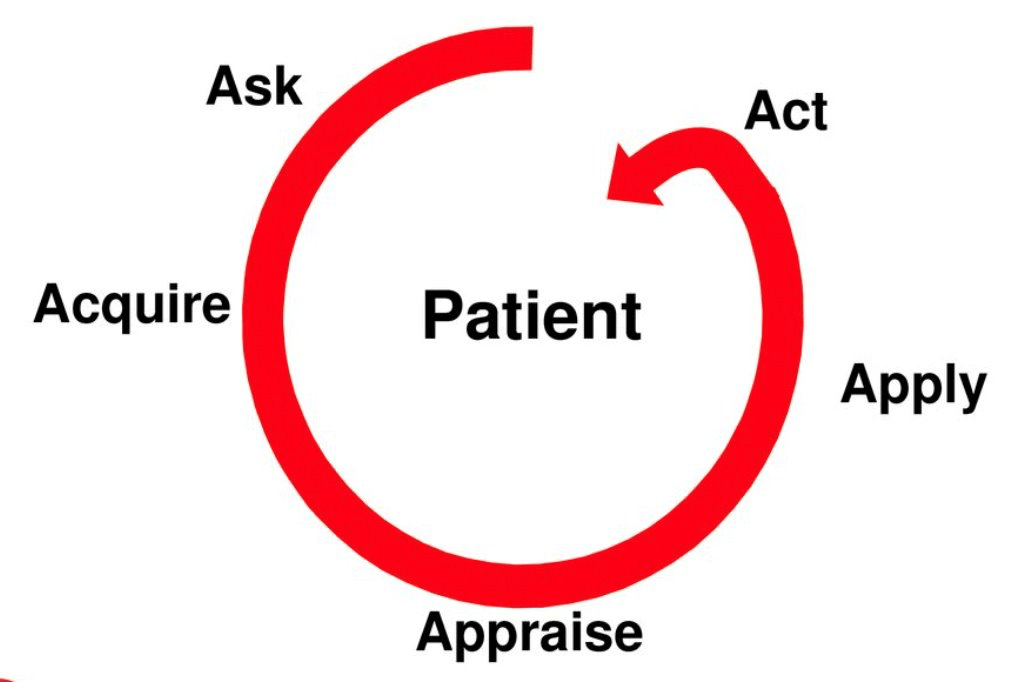
3 key steps in the process of evidence based clinical practice
How can you decribe Allocation Concealment
Hides the sorting of trial participants into treatment groups so that this knowledge cannot be exploited.
Adequate allocation concealment serves to prevent study participants from influencing treatment allocations for subjects.
Probability of target condition being present before results of diagnostic test are known is called
EARLY GOAL-DIRECTED THERAPY COLLABORATIVE GROUP STUDY
Early Goal-Directed Therapy in Sepsis
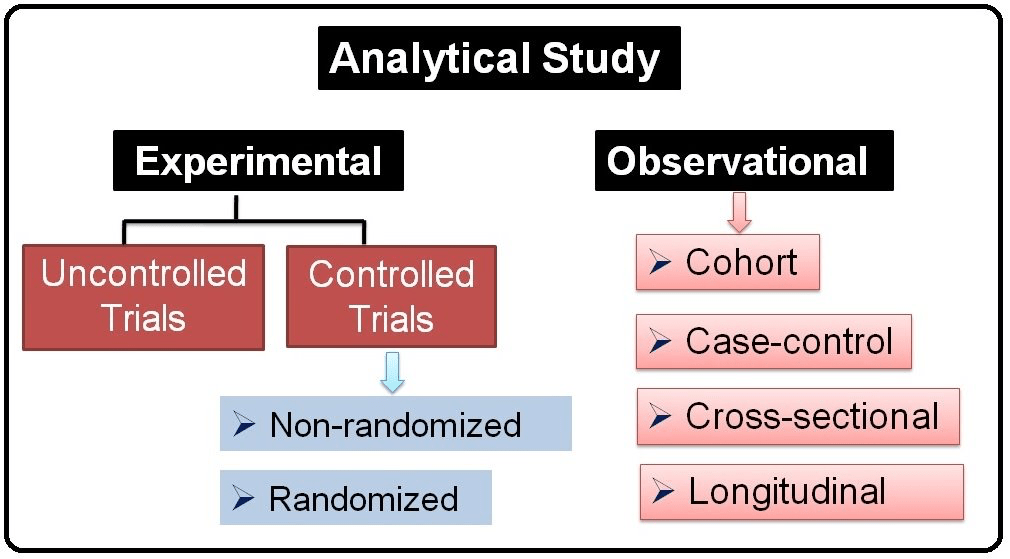
One type of observational study is called
How do you call the difference in the event rates between control and experimental group
Absolute Risk Reduction (ARR)
Probability that a given test result would be expected in a patient with (as opposed to without) disorder of interest is called
Likelihood Ratio (LR) 
THE DIAMOND TRIAL
Step-Up versus Step-Down Therapy for Dyspepsia
This is what makes Randomized Controlled Trials special
- Avoid selection bias
- Handle confounding
Main limitations of observational designs
Number of patients who would have to receive the treatment for 1 of them to experience the adverse effect
Number Needed to Harm (NNH)
A tool that helps healthcare professionals make diagnostic and therapeutic decisions at the bedside is called
Clinical Decision Tool
The MRC Spine Stabilization Trial
Surgery versus Rehabilitation for Chronic Low Back Pain