Relative quantitative measurement of radio density used by radiologists in the interpretation of computed tomography (CT) images.
Hounsfield units

Identify the liver
Patient presents with fever, abdominal pain, and jaundice. AST and ALT are elevated. Decreased albumin. Anti-HAV IgM are present. CT presents hepatomegaly, decreased attenuation around the portal system and at the hepatic hilum. What is the most likely pathology of this patient?
Hepatitis
You are forced at gunpoint to inoculate yourself with a hepatitis virus. Taking into account their prognosis, which virus would you choose?
A. HepA
B. HepB
C. HepC
HepA, because it's an acute infection that resolves on its own.
HepB and C infections are chronic and are the leading causes of hepatocellular carcinoma
What is the full name of the current RCM?
How many segments does the liver have?
9

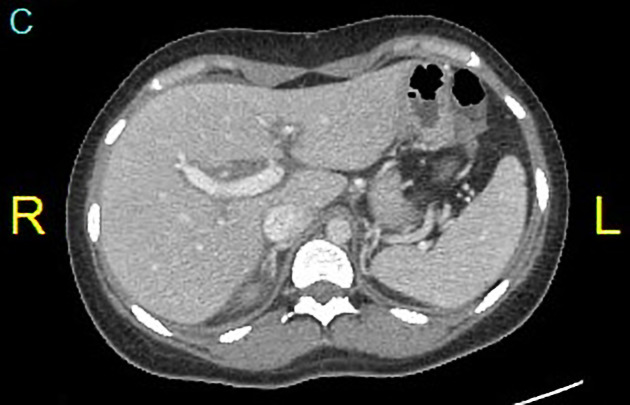
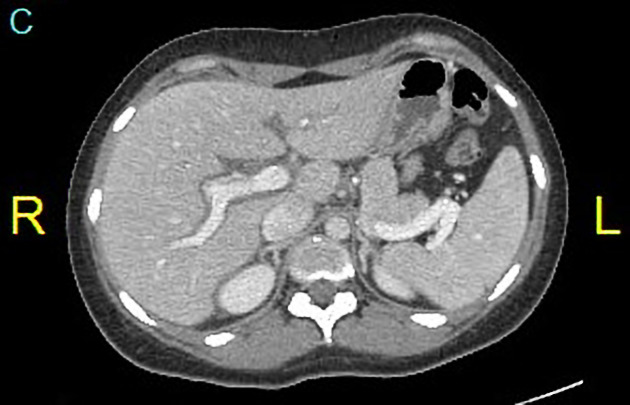
What are two abnormalities seen in this plain axial CT of the abdomen?
1. Hepatomegaly
2. Spleenomegaly
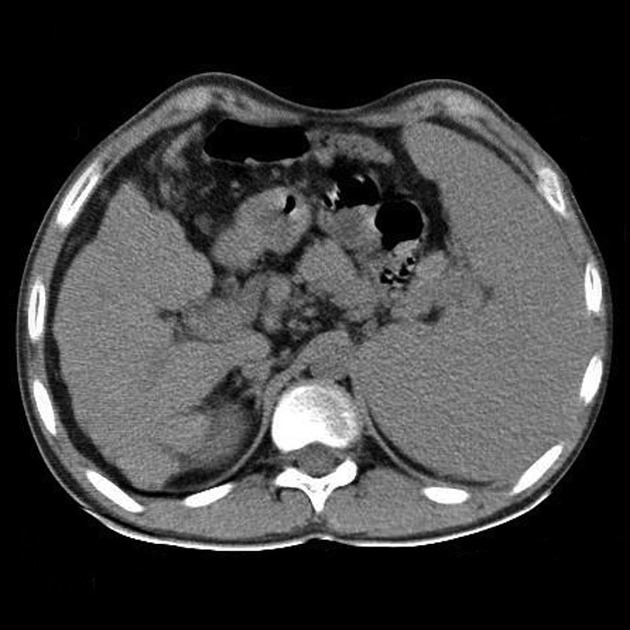
Patient came to you with fever, right upper quadrant abdominal pain, and jaundice. Abdominal ultrasonography also shows biliary dilatation.
Why do you perform ct scan on these cases?
Abdominal computed tomography (CT) can be performed as an adjunct to investigate co-existing pathologies such as hepatic/pancreatic tumors, metastasis, or hepatic abscess
The gallstones shown below are probably made of...
A. Calcium
B. Bilirubin
C. Cholesterol
C. Cholesterol stones are hypoattenuated to the surrounding bile. Calcium stones are hyperattenuated. The rest are most likely to appear isoattenuated.
% alcohol of Ginebra San Miguel gin 
40%
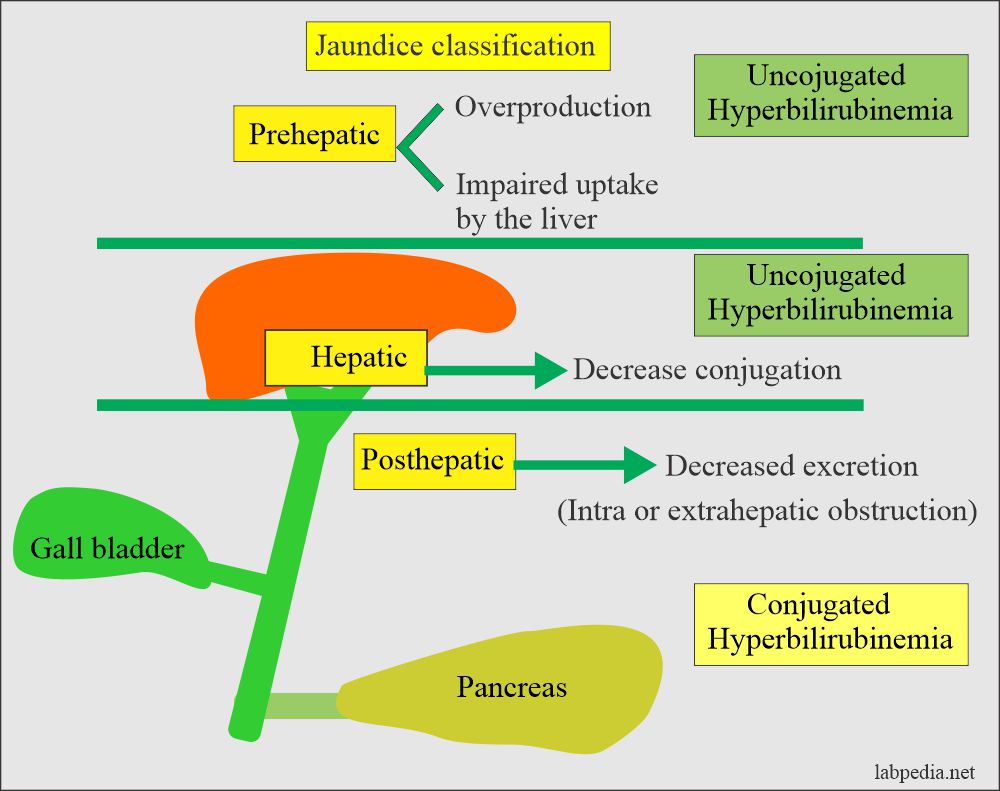
2 types of hyperbilirubinemia
conjugated and unconjugated
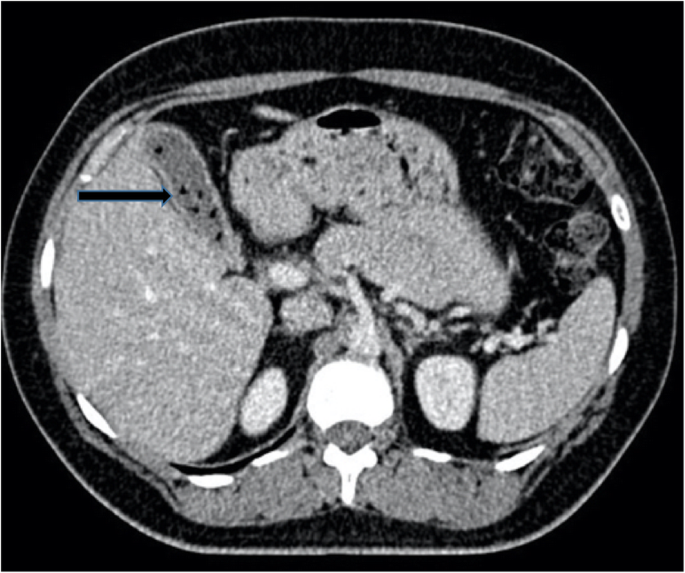
What are the two abnormalities seen on this CT scan that point to acute viral hepatitis?
1. Hepatomegaly
2. Periportal halo tracking
Periportal halo or periportal collar sign is a zone of low attenuation seen around the portal vein on contrast enhanced CT. Periportal haloes may occur around the central portal veins or their peripheral branches.
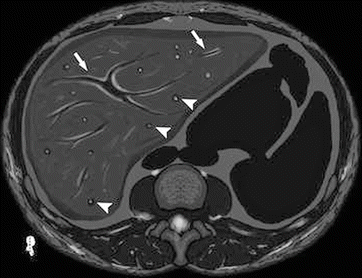
Patient presents with mild to moderate upper abdominal pain, weight loss, early satiety, and a palpable mass in the upper abdomen.
May also presents with hypocalcemia, Erythrocytosis and diarrhea.
What will you usually observe in the ct of this patient?
Computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen typically demonstrates a liver mass and free intraperitoneal blood
Explain the pathophysiology of post-hepatic jaundice
3 key ingredients of absinthe?
Wormwood, anise, fennel
Charcot's Triad?
Fever
Jaundice
Right upper quadrant pain
Describe the arrowhead and arrow in this figure
On contrast-enhanced helical CT scan, choledocholithiasis is represented as central density (arrowhead) surrounded by hypoattenuating ampulla of Vater (arrow). In this particular scan, stone is seen as heterogeneous with center showing lower density.
Patient came to you presenting with jaundice. CBC indicates anemia with increased reticulocyte count that is not explained by recent bleeding or recent correction of iron or other nutrient deficiency, or other causes. Patient also has High LDH and bilirubin.
Chronic condition of this pathology may present on CT as?
marrow reconversion and/or splenomegaly
Which of these is not like the other?
A. Beta Thalassemia
B. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
C. Wilson Disease
D. Lead poisoning
C. Wilson Disease, because the rest are prehepatic causes of jaundice
Beta Thalassemia, PNH, and lead poisoning lead to hemolytic anemia
Wilson Disease pathophysiology: Genetic defect impairs copper transport, secretion into the bile --> copper overload in liver --> hepatic fibrosis --> cirrhosis
Country of origin of the first document to describe cancer?

Egypt
Identify three diseases that cause unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia
Identify the pathology of this patient.
CT
Acute cholangitis is is typically a clinical diagnosis with imaging performed to determine if there is evidence of:
intrahepatic and/or extrahepatic duct dilatation (indicating obstruction/stasis)
bile duct wall thickening or focal outpouchings
cholelithiasis/choledocholithiasis
Patient with a known case of Wilson disease (hepato-lenticular degeneration) was referred for evaluation of an abdominal mass. His non-contrast CT of the abdomen may show features of?
macronodular liver cirrhosis, relative sparing of the caudate lobe, and moderate splenomegaly
How should hepatocellular carcinoma appear in a CT scan with triphasic contrast for liver biopsy to be unnecessary?
The mass should enhance vividly during late arterial (~35 seconds) and then washes out rapidly, becoming indistinct or hypoattenuating in the portal venous phase, compared to the rest of the liver.

Radiological hallmarks of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Typical vascular pattern of HCC as observed in a 67-year old patient with histology proven HCC. Liver lesion in the right hepatic lobe observed in a cirrhotic patient. The lesion is presenting a typical HCC vascular pattern with arterial hyperenhancement (left images) and venous wash-out (right images) visible both in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (upper row) and computed tomography (CT) (lower row).
This animal's bile is considered the “king” of animal biles both in ancient times and currently in the Orient.
Bear bile
