name this rhythm
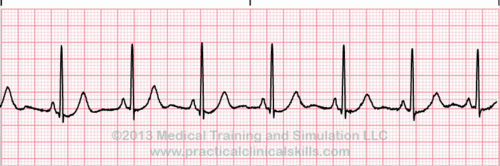
A patient in asystole is likely to receive which of the following drug treatments? SATA
a. levophed
b. Cardizem
c. epinephrine
d. atropine
The purpose of arterial lines are to: SATA
a.Obtain frequent arterial blood gases
b.infuse meds
c.monitor CVP
d. monitor BP cont.
A & D
what happens when the O2 demands exceeds supply?
ischemia occurs
if a client throws PVCs, what do you check?
With this rhythm you have to take the apical pulse for a full minute
Atrial Fibrillation
Indication:
VF and pulseless VT unresponsive to CPR and a vasopressor
Adult Dosage:
VF and pulseless VT: first dose 300 mg IV/IO push
Second dose: 150 mg IV/IO push if necessary
amiodarone
A client in the ICU has an elevated pulmonary artery wedge pressure. What should be included in this client's plan of care?
I&O
An intravenous analgesic frequently administered to relieve chest pain associated with MI is:
A.Meperidine hydrochloride
BHydromorphone hydrochloride
CMorphine sulfate
DCodeine sulfate
c
What is a major problem related to ADL changes after having a MI?
depression
Name this rhythm
*Clinical associations: Physiologic or psychological stressors (i.e., exercise, fever, pain, hypotension, hypovolemia, anemia, hypoxia, hypoglycemia, myocardial ischemia, heart failure, hyperthyroidism, anxiety, and fear
Sinus Tachycardia
3 clinical situations for V Tach Tx
unconscious/ no pulse: V fib
unstable: cardioversion
stable/ symptomatic: drugs Procainmide, amiodarone, and sotalal
A Nurse obtains the following results: PAS 34mm Hg, PAD 21 mmHg, PAWP 16mmHg, CVP 12mmHg. Which of the following conditions support these values?
Heart Failure, Pulmonary HTN
You note in the patient's chart that the patient recently had a myocardial infarction due to a blockage in the left coronary artery. You know that which of the following is true about this type of blockage?
A blockage in the left coronary artery causes the least amount of damage to the heart muscle.
B. Left coronary artery blockages can cause anterior wall death which affects the left ventricle.
C. Left coronary artery blockage can cause posterior wall death which affects the right ventricle.
D. The left anterior descending artery is least likely to be affected by coronary artery disease.
B
FILL IN THE BLANK
-------- decreases CVP?RA, PAWPlasix
Name the 5 Steps in the Rhythm Analysis
rhythm, rate, p: QRS ratio, PR interval, QRS width
What is the drug given for symptomatic bradycardia? dose? and why is it given?
Atropine 0.5mg IVP up to 3.0; bc you need tp speed up bradycardia
patient is experiencing reduced afterload. The nurse realizes that causes of reduced afterload include:
: Select all that apply.
1. Sepsis
2. Mitral stenosis
3. Reduced circulating blood volume
4. Vasodilator medications
5. Myocarditis
1& 4
A patient is admitted with chest pain to the ER. The patient has been in the ER for 5 hours and is being admitted to your unit for overnight observation. From the options below, what is the most IMPORTANT information to know about this patient at this time?
A. Troponin result and when the next troponin level is due to be collected
B. Diet status
C. Oxygen saturation
D. CK result and when the next CK level is due to be collected
A.
door to needle time for PCI?
and door to needle time for Fibrinolytic?
within 90mins
within 30 mins
The nurse obtains a 6-second rhythm strip and charts the following analysis: atrial rate 70, regular; ventricular rate 40, regular; QRS 0.04 sec; no relationship between P waves and QRS complexes; atria and ventricles beating independently of each other. Which of the following would be a correct interpretation of this rhythm strip?
Third-degree heart block
The patient in pulseless ventricular tachycardia is defibrillated twice and received appropriate meds given per ACLS protocol. The following rhythm is now present.( NSR) What should the nurse do next?
1. Continue monitoring and observing the patient for PVCs.
2. Place the patient on a maintenance lidocaine infusion.
3. Realize that the patient has been successfully converted to NSR.
4. Check the patient for a pulse and continue CPR if one is not present.
4
A patient's systemic vascular resistance (SVR) has dangerously decreased. The nurse would expect to administer which medications?
1.Furosemide (Lasix) and dopamine
2. Nitroprusside and furosemide (Lasix)
3. Dopamine and norepinephrine (Levophed)
4. Nitroglycerin and digoxin (Lanoxin)
3
A client is wearing a continuous cardiac monitor, which begins to sound its alarm. A nurse sees no electrocardiogram complexes on the screen. The first action of the nurse is to:
Sudden loss of electrocardiogram complexes indicates ventricular asystole or possible electrode displacement. Accurate assessment of the client and equipment is necessary to determine the cause and identify the appropriate intervention.
he nurse has just received change-of-shift report about these four patients. Which patient should the nurse assess first?
a.
A 38-year-old who has pericarditis and is complaining of sharp, stabbing chest pain
b.
A 45-year-old who had an MI 4 days ago and is anxious about the planned discharge
c.
A 51-year-old who has just returned to the unit after a coronary arteriogram and PCI
d.
A 60-year-old who has a scheduled dose of atenolol (Tenormin) 25 mg PO due
Correct Answer: C
Rationale: After PCI, the patient is at risk for bleeding from the arterial access site for the PCI, so the nurse should assess the patient immediately. The other patients also should be assessed as quickly as possible, but assessment of this patient has the highest priority