An autoimmune condition that requires the monitoring of glycated hemoglobin ("A1C")
What is type 1 diabetes?
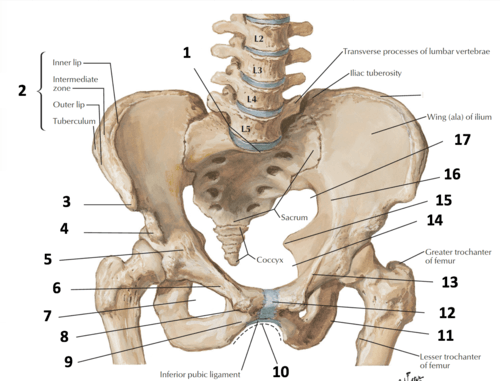 Number 6
Number 6
superior pubic ramus
The number of patients who need treatment in order to avoid adverse reaction.
Number Needed to Treat
A heart rate of less than 60bpm
What is Bradycardia?
The amount of sharpness on a film
radiographic contrast
Range of motion between 15-20 degrees
What is normal Lumbar Lateral Flexion?
This disturbance in growth causes cells to grow in a completely disorganized manner
When using the Snellen Eye Chart, we are assessing this cranial nerve.
What is the Optic Nerve (II)?
A type of data that is used when measuring a rating of pain
What is Ordinal data?
Takes up 1/3 of the cardiac cycle; when the AV valves are closed and the SL valves are open
What is Systole?
The 5 radiodensities from least to most radiodense
1. Air
2. Fat
3. Water
4. Bone
5. Metal
Stage 1 Hypertension
What is systolic 130-139 OR diastolic 80-89
During parasitic infection, this type of white blood cell predominates
What are eosinophils?
This mixed cranial nerve is responsible for taste of the back third of the tongue and the action of swallowing.
IX: Glossopharyngeal
The gold standard in the hierarchy of evidence
What are Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses?
The site of greatest water reabosorption
What is the large intestine?
A femoral angle of less than 120 degrees.
Coxa Vara
This type of lesion causes flaccid paralysis and an absent deep tendon reflex
What is Lower Motor Neuron Lesion
This type of antibody is the most abundant in circulation
What is IgG?
Muscles of the Rotator Cuff
SITS
supraspinatus
infraspinatus
teres minor
subscapularis
A longitudinal measure of acute illness
What is incidence?
Secreted by the Zona Glomerulosa and triggers reabsorption of sodium and potassium
aldosterone
This patient has this rare abnormality
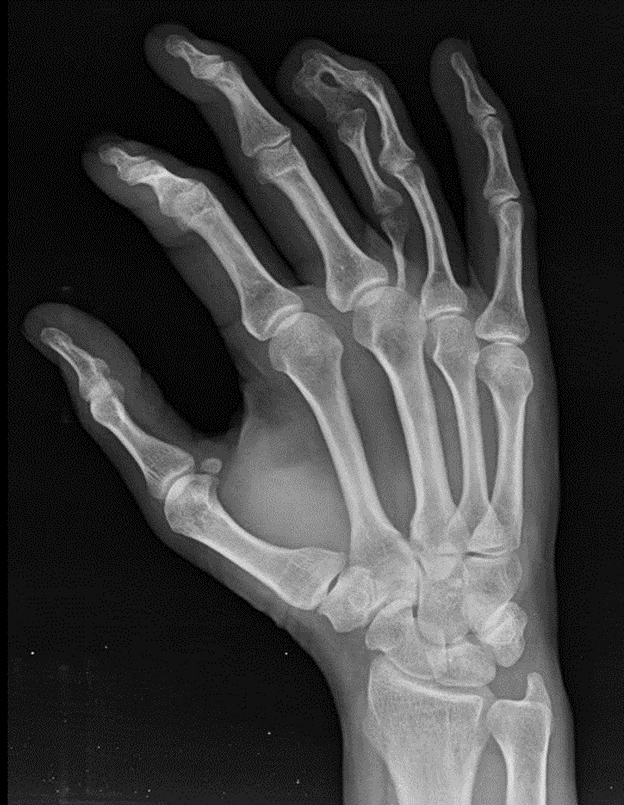
polysyndactyly
The nerve supplying the Facet Joint
What are vitamins, minerals and enzymes?

Pictured in blue is the nerve distribution for this nerve
Median Nerve
This is used to create an effect size when outcome measures are different.
What is Standardized Mean Difference?
This hormone inhibits the effects of growth hormone.
What is Somatostatin?
Klippel-Feil
Cervical Extension ROM
What normally has 50-70 degrees of motion
A type of necrosis that causes the extremities to become ischemic
What is gangrenous necrosis?
Your external rotator muscles
PGOGOQ
piriformis
Gemellus superior
obturator internus
gemellus inferior
obturator externus
quadratus femoris
Used in Retrospective Case Controlled studies when the item of interest is Risk Factor.
What is Odds Ratio?
The 4 Signs of Addison's Disease
1. anorexia
2. weight loss
3. weakness
4. hypotension
According to Sandoz, this is where Passive ROM ends
An autoimmune disorder that decreases the production of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone and Thyrotropin-releasing Hormone
What is Graves' Disease?
These muscles are involved in glenohumeral medial rotation.
subscapularis, teres major, pec major, latissimus dorsi & anterior deltoid
The probability of patient's with a NEGATIVE screening test that do NOT have the disease
What is Negative Predictive Value?
The path of a drop of blood beginning from the right atrium
RA > Tricuspid valve > RV > pulmonary semilunar valve > pulmonary trunk > pulmonary arteries > lung > pulmonary veins > LA > bicuspid (mitral) valve > LV > aortic semilunar valve > aorta > systemic vessels > inferior vena cava & superior vena cava > back to RA
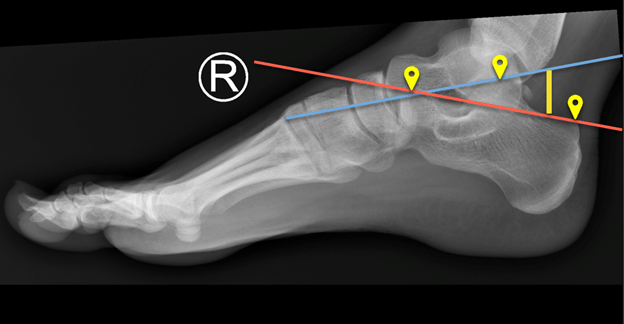 This measurement is used to assess whether or not a patient has a calcaneal fracture.
This measurement is used to assess whether or not a patient has a calcaneal fracture.
Bohler's Angle
O (MP3) PPQRSTFID ADLs
What is the abbreviation for:
Onset
Mechanism of Injury
Progression
Prior Hx of same complaint
Prior care of same complaint
Palliative
Provocative
Quality of Pain
Radiating Characteristics
Site
Timing
Frequency
Intensity
Duration
Activities of Daily Living
An adrenocortical condition caused by an adrenal tumor that increases aldosterone production
What is Conn's Disease?
Which 2 cranial nerves are tested using the Corneal Reflex?
V: trigeminal & VII: facial
Used when measuring whether or not 1 group of students has improved testing scores after a session of tutoring versus another group of students who takes the same test without a tutoring session.
What is a 1-tail, paired t-test?
On labs, this condition will show: decreased potassium, increased sodium, and low renin
What is Primary Hyperaldosteronism
- most commonly Conn's Syndrome
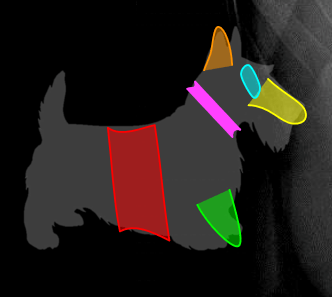
These structures form a "Scotty Dog"
Orange = superior articular process
Green = inferior articular process
Blue = eye
Yellow = transverse processes
Pink = pars interarticularis
Red = laminae
Boundaries of the IVF
1. superior/inferior pedicle
2. superior/inferior vertebral body
3. z joint capsule
4. posterior aspect of the IVD