Uterine Size & Position
Uterine Size & Position
The arrow is indicative of about how many weeks gestation.
What is 20 weeks?
Uterus is at level of umbilicus.
What is 120 - 160bpm?
What does gravida mean?
What is the number of total pregnancies?
18 weeks gestation
What is 2nd trimester?
What does the acronym PIH mean?
What is pregnancy induced hypertension?
PIH is hypertension that presents after 20 weeks gestation and has no other associated symptoms.
What is cystitis?
What is preeclampsia?
This vaccine can be given as early as age 9 to protect against cervical cancers.
What is HPV vaccine?
CDC recommends routine vaccination of preteens at ages 11 or 12 years. The vaccination series can be started at age 9 years. HPV vaccine may be given at the same time as other vaccines.
The 9-valent HPV vaccine protects against HPV types 16 and 18, which cause about 66% of cervical cancers and most other HPV-attributable cancers in the United States, and five additional cancer-causing types, which account for about 15% of cervical cancers. It also protects against HPV 6 and 11, which cause most anogenital warts.
What is treatment and name of the condition that is characterized by premature separation of the placenta from the uterus, causing uterine pain and severe vaginal bleeding?
What is placental abruption. Treatment is prompt deliver.
Prompt cesarean delivery is usually indicated if placental abruption plus any of the following is present:
Maternal hemodynamic instability
Nonreassuring fetal heart rate pattern
Term pregnancy (≥ 37 weeks); preterm delivery possibly necessary if the mother or fetus is at risk of severe morbidity or mortality
At how many weeks gestation can fetal heart tones be heard?
What is 9 - 12 weeks?
What does LMP mean?
What is last menstrual period?
How many weeks gestation is considered term?
What is 37 - 42 weeks gestation?
nonstress test (NST)
What is 3rd trimester?
A normal NST requires 2 accelerations of fetal heart rate in 20 minutes of up to 15 bpm from the baseline heart rate for a duration of 15 seconds and the absence of declerations.
What is stage 2?
What are leiomyomas (uterine fibroids)?
Diagnosis is by pelvic examination, ultrasonography, or other imaging studies. Treatment of patients depends on symptoms and desire for fertility and preferences regarding surgical treatments. Treatment may include estrogen-progestin contraceptives, progestin therapy, tranexamic acid, and surgical procedures (eg, hysterectomy, myomectomy).
The two types of hypertension classifications during pregnancy.
What is Chronic and Gestational?
hronic: BP is high before pregnancy or before 20 weeks gestation. Chronic hypertension complicates about 1 to 5% of all pregnancies.
Gestational: Hypertension develops after 20 weeks gestation (typically after 37 weeks) and remits by 6 weeks postpartum; it occurs in about 5 to 10% of pregnancies, more commonly in multifetal pregnancy.
Ceftriaxone 500mg IM and Aizthromycin 1g po OR Ceftriaxone 50mg and Doxycycline 10mg BID x 7 days
What is the treatment for gonorrhea and chlamydia?
This condition lasts 2 days to 2 weeks and is characterized by relatively mild symptoms of trouble sleeping, crying and decreased appetite that do not interfere with daily activities.
What is postpartum blues?
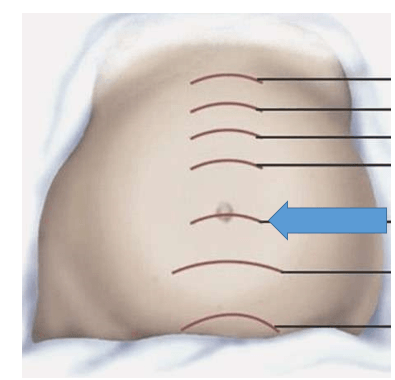
The arrow is indicative of about how many weeks gestation?
What is 12 weeks?
What is quickening?
What is the range, in weeks, considered as premature?
What is 20 - 36 weeks gestation?
4 weeks of gestation
What is 1st trimester?
The triad of hypertension, edema and proteinuria
What is preeclampsia?
The condition seen in the this image characterized when ectopic endometrial tissue infiltrates the myometrium.
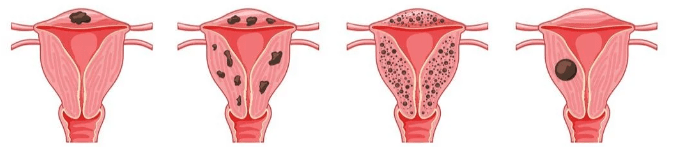
What is uterine adenomyosis?
Uterine adenomyosis is the presence of endometrial glands and stroma in the uterine musculature. Symptoms include heavy menstrual bleeding, dysmenorrhea, and pelvic pain. Diagnosis is with a pelvic examination that detects a diffusely enlarged uterus and with transvaginal ultrasonography or MRI. Treatment is hormonal medications or hysterectomy.
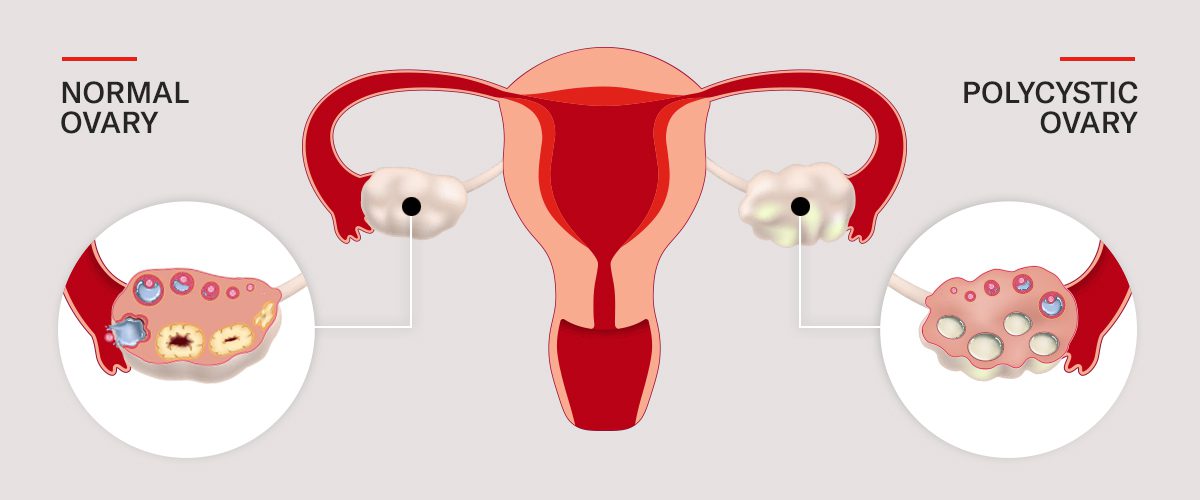
This condition is characterized by signs of androgen excess (acne, hirsutism) and insulin resistance.
What is polycystic Ovary Syndrome?
Treatment:
Usually estrogen/progestin contraceptives or progestins
Sometimes metformin or other insulin sensitizers
Management of hirsutism and, in adult women, long-term risks of hormonal abnormalities
Infertility treatments in women who desire pregnancy
Treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome aims to
Manage hormonal and metabolic abnormalities and thus reduce risks of estrogen excess (eg, endometrial hyperplasia) and androgen excess (eg, diabetes, cardiovascular disorders)
Relieve symptoms
Treat infertility
What is group B streptococcus?
Penicillin G 5 million units intravenous is administered as a loading dose, followed by 2.5 to 3 million units every 4 hours during labor until delivery[1]. Ampicillin is a reasonable alternative to penicillin G if penicillin G is unavailable[1]. Ampicillin is administered as a 2 gm intravenous loading dose followed by 1 gm intravenous every 4 hours during labor until delivery[1].
This condition is usually diagnosed within the first 3 months of pregnancy is characterized by: +pregnancy test, hyperemesis, abdominal swelling, vaginal bleeding, and absent FHTs.
What is a hydatidiform mole (molar pregnancy)?
Gestational trophoblastic disease is classified as hydatiform moles or gestational trophoblastic neoplasias:
Hydatiform moles are benign placental tumors with malignant potential. They consist of proliferations of villous trophoblasts. They are further classified as complete or partial moles.
Gestational trophoblastic neoplasias are malignant placental tumors. These tumors include postmolar gestational trophoblastic neoplasia (gestational trophoblastic neoplasia that develops after a molar pregnancy), placental-site trophoblastic tumor, epithelioid trophoblastic tumor, choriocarcinoma, and invasive mole.
Hydatidiform moles are most common among women < 17 or > 35 years old and those who have previously had gestational trophoblastic disease.
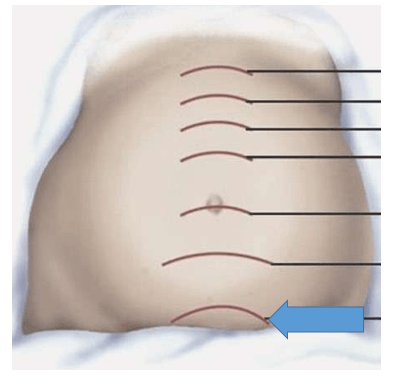
The arrow is indicative of approximately how many weeks gestation?
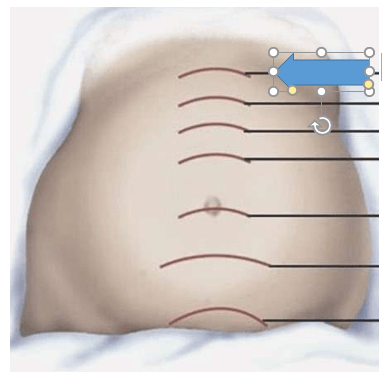
What is 36 - 40 weeks?
What does B-hCG stand for?
What is beta human chorionic gonadotropin?
B-hCG is a hormone produced during pregnancy.
What does parity mean?
What is the total number of deliveries?
Amniocentesis
What is 2nd trimester?
A 29-year-old is 24 weeks gestation has an elevated glucose of 152 after a 50-g challenge. The 3-hour glucose tolerance test revels: fasting 92, 1 hour 201, 2 hour 180, 3 hour 138. What is the best diagnosis?
What is gestational diabetes?
What is pyelonephritis?
This test should be ordered for all women of child bearing age who complains of abdominal pain.
What is a urine pregnancy test?
Recommended for women age 30 - 65 as part of cervical screening.
What is Pap and HPV co-testing?
- he human papillomavirus (HPV) test checks cells for infection with high-risk HPV types that can cause cervical cancer.
- The Pap test (also called a Pap smear or cervical cytology) collects cervical cells so they can be checked for changes caused by HPV that may—if left untreated—turn into cervical cancer. It can find precancerous cells and cervical cancer cells. A Pap test also sometimes finds conditions that are not cancer, such as infection or inflammation.
- The HPV/Pap cotest uses an HPV test and Pap test together to check for both high-risk HPV and cervical cell changes.
This is an obstetric emergency where the anterior fetal shoulder becomes stuck on the maternal pubic symphysis, delaying the birth of the baby's body?
What is shoulder dystocia?
Once shoulder dystocia is recognized, extra personnel are summoned to the room, and various maneuvers are tried sequentially to disengage the anterior shoulder:
The woman’s thighs are hyperflexed to widen the pelvic outlet (McRoberts maneuver), and suprapubic pressure is applied to rotate and dislodge the anterior shoulder.
What presentation is this?
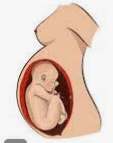
What is breech presentation?
Breech presentation is when the fetus is in longitudinal lie with buttocks or lower extremity entering the pelvis first.
What does EDC mean?
What is estimated or expected date of confinement?
What does the acronym PROM mean?
What is Premature Rupture of Membranes which is the rupture of the amniotic membranes before the onset of labor at or beyond 37 weeks of gestation.
AFP
What is 2nd trimester?
Elevated levels of Alpha-fetoprotein indicate increase risk of neuro tube defects (spinal cord defect, anencephaly).
What does the acronym HELLP syndrome stand for?
What is Hemolysis, Elevated Liver enzymes and Low Platelets?
What is Staphylococcus aureus?
Mastitis and treated with:
Dicloxacillin 500 mg orally every 6 hours for 7 to 10 days
For women allergic to penicillin, cephalexin 500 mg orally 4 times a day or clindamycin 300 mg orally 3 times a day for 10 to 14 days
Erythromycin 250 mg orally every 6 hours is used less frequently.
This condition is a medical emergency and is characterized by hypertension, proteinuria and unexplained general seizures.
What is eclampsia.
This condition is characterized by the classic triad of dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia and infertility but could also include dysuria and dyschezia.
What is endometriosis?
Diagnosis is by direct visualization and sometimes biopsy, usually via laparoscopy. Imaging studies (transvaginal ultrasound, MRI) are useful in diagnosing more advanced cases (eg, endometriosis involving the ovary [endometrioma]). Treatments include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, medications to suppress ovarian function and endometrial tissue growth, surgical ablation and excision of endometriotic implants, and, if disease is severe and no childbearing is planned, hysterectomy alone or hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy.
This condition lasts more than 2 weeks and is characterized by severe symptoms of sleeping all day, crying and decreased appetite which interfere with daily activities.
What is postpartum depression?