A 16-year-old female presents to ED with a 2-day history of abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and right lower quadrant pain. Imaging and surgery confirmed appendicitis.
What is the appropriate initial antibiotic regimen including dose and max dose?
What is Ceftriaxone 50 mg/kg daily (Max: 2 g)
AND
Metronidazole 30 mg/kg daily (Max: 1500 mg)
What is the most common cause of seizures in children?
What is fever?
What is the minimum age for the influenza vaccine?
What is 6 months?
You are called to help treat an infant with severe symptomatic bradycardia (HR <60/min) associated with respiratory distress. The bradycardia persists despite the establishment of an effective airway, oxygenation, and ventilation.
What is the first drug you should administer and dose?
What is Epinephrine? 0.01 mg/kg (0.1 mL/kg of the 0.1 mg/mL concentration) IV/IO every 3-5 minutes (max dose single 1 mg)
What is the mechanism of deferoxamine?
Binds to ferric iron to produce ferrioxamine complex that is excreted in urine
Deferoxamine therapy 15 mg/kilogram/hour IV
A one-week-old term neonate presents to RCH ED with fever, lethargy, and decreased appetite. Lumbar puncture with decreased glucose and increased white count. The resident orders gentamicin and ampicillin for suspected meningitis.
Is this treatment appropriate and what organisms are associated with bacterial meningitis in this age group?
NO, Ampicillin and ceftazidime for better CSF penetration
Ampicillin 300 mg/kg/day IV div q6h AND Ceftazidime 50 mg/kg/dose IV q8h
GBS, E. coli, Listeria monocytogenes
In the management of TBI, what is the CPP target?
What is the formula?
What is a CPP target is between 40 to 50 mmHg?
What is CPP = MAP - ICP?
Kochanek PM, Tasker RC, Carney N, et al. Guidelines for the Management of Pediatric Severe Traumatic Brain Injury, Third Edition: Update of the Brain Trauma Foundation Guidelines, Executive Summary. Neurosurgery. 2019;84(6):1169-1178. doi:10.1093/neuros/nyz051
A 5-year old kid was admitted to ED following a dog bite to the nose. The provider orders ketamine for sedation for laceration repair.
What are some appropriate counseling points to provide parents prior to the procedure regarding the potential side effects of ketamine?
What is Nystagmus, shivering, light blotchy rash, increased blood pressure, and laryngospasm?
Probable SVT, What is the drug of choice? Dose and MOA?
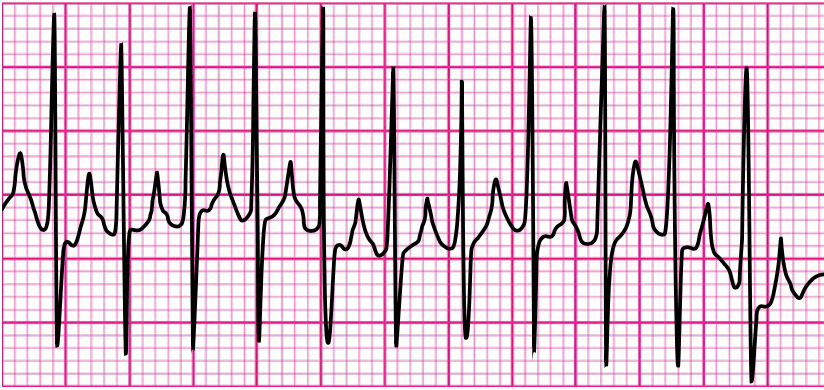
What is Adenosine 0.1 mg/kg IV/IO rapid push (max 6 mg); then 0.2 mg/kg IV/IO rapid push (max 12 mg)?
MOA: Blocks conduction through the AV node
17-year old male presents with reported ingestion of triple C with hallucinations and gait abnormalities. Tachycardia with all other vitals within normal limits.
Name this ingestion?
What is Dextromethorphan?
D-isomer of codeine at appropriate doses binding of sigma opioid receptors in the medulla.
In overdose the active metabolite, dextrorphanol inhibits NMDA receptors leading to similar neurobehavioral effects to ketamine and PCP including hallucinations, “out of body” sensation, and dissociation.
DXM also inhibits adrenergic NT reuptake in the PNS and CNS--> tachycardia, HTN, diaphoresis
A ten-month-old (10 kg) infant presents to ED with a three-day history of fever increased fussiness, decreased appetite, and reported pulling on the right ear
What is the likely diagnosis and treatment?
What is Acute otitis media – amoxicillin 80-90 mg/kg daily in two divided doses for 10 days?
10-year old male (32 kg) presents to ED actively seizing. EMS reports administering 10 mg of intranasal Versed en route. The patient has IV access, What drug and dose should the administer immediately?
Levetiracetam (Keppra) 60 mg/kg IV (MAX 4500 mg/dose) over 5 minutes
A 6-year old (20 kg) boy went to the ED after being stung by a bee. The patient initially had pain and swelling, but then developed SOB and wheezing on arrival. The physician orders epinephrine. What is the appropriate dose, concentration, and route?
What is epinephrine 0.15 mg IM thigh
1 mg/mL concentration
10-29 kg: 0.15 mg IM thigh
>30 kg: 0.3 mg IM thigh
Name the first-line treatment option and dose in the treatment of persistent bradycardia with AV block?
What is Atropine 0.02 mg/kg IV/IO (minimum dose 0.1 mg) max 0.5 mg ?
MOA: Increases AV conduction by blocking acetylcholine. Used in bradycardia caused by increased vagal tone or primary AV block.
Theo, a 4-year-old boy arrives at RCH ED after getting into grandmas medicine cabinet and eating some of her daily chewable aspirin. On arrival, Theo's pH is 7.29, CO2 33 mmHg, HCO3 14, Na 140, and Cl 110.
Indicating an anion gap metabolic acidosis
What is the antidote?
What IV sodium bicarbonate? (Goal serum pH above 7.4, urine pH 7.5-7.8)
A 1-month old infant diagnosed with Influenza in the ED.
What dose of Tamiflu is indicated and what is the mechanism of action?
What is 3 mg/kg/dose twice daily
MOA:
Inhibits influenza virus neuraminidase. The enzyme known to cleave the budding viral progeny from its cellular envelope attachment point (neuraminic acid) just prior to the release
What is the first-line therapy for ICP control?
What is the mechanism?
Hypertonic saline 3% bolus 2 – 5 mL/kg over 10-20 minutes followed by 0.1-1 mL/kg infusion
Creation of osmotic gradient that draws cerebral edema fluid form brain
What are the primary pathways of metabolism of acetaminophen?
What metabolism pathway is responsible for the conversion to NAPQI?
What substrate is replaced in the treatment of acetaminophen overdose?
What are sulfation and glucuronidation?
What is CYP450?
What is glutathione?
You are in an active code with a 40 kg patient in Vfib. He has been defibrillated, had 2 min CPR, and was defibrillated again. Epi was given and CPR resumed. What medication should the pharmacist anticipate next?
What is Amiodarone IV/IO 5 mg/kg OR Lidocaine IV/IO 1mg/kg?
Daisy a 16-year-old female presents to RCH ED with c/o increased HR and dizziness. The patient reports that she has not been feeling well for the past couple of days and last saw her provider about a week ago. PMH: Migraines
In the process of completing her med reconciliation, you notice she recently had a dose increase of one of her home medications and think this could possibly be causing her symptoms.
Name this class of medication?
What are Tricyclic antidepressants?
-Central and peripheral antagonism of muscarinic receptors causes an anticholinergic syndrome
-Blocking fast sodium channels--> arrhythmias
-Antagonist activity at alpha leads to a decrease in preload and vascular resistance