What is the longest phase in the cell cycle?
Interphase
Two identical daughter cells
What phase do chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell?
Metaphase
What is the first phase of mitosis?
Prophase
What stage is this cell?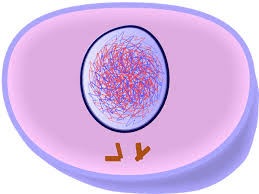
Interphase
What happens to the nuclear membrane during prophase?
It dissolves, freeing the chromosomes
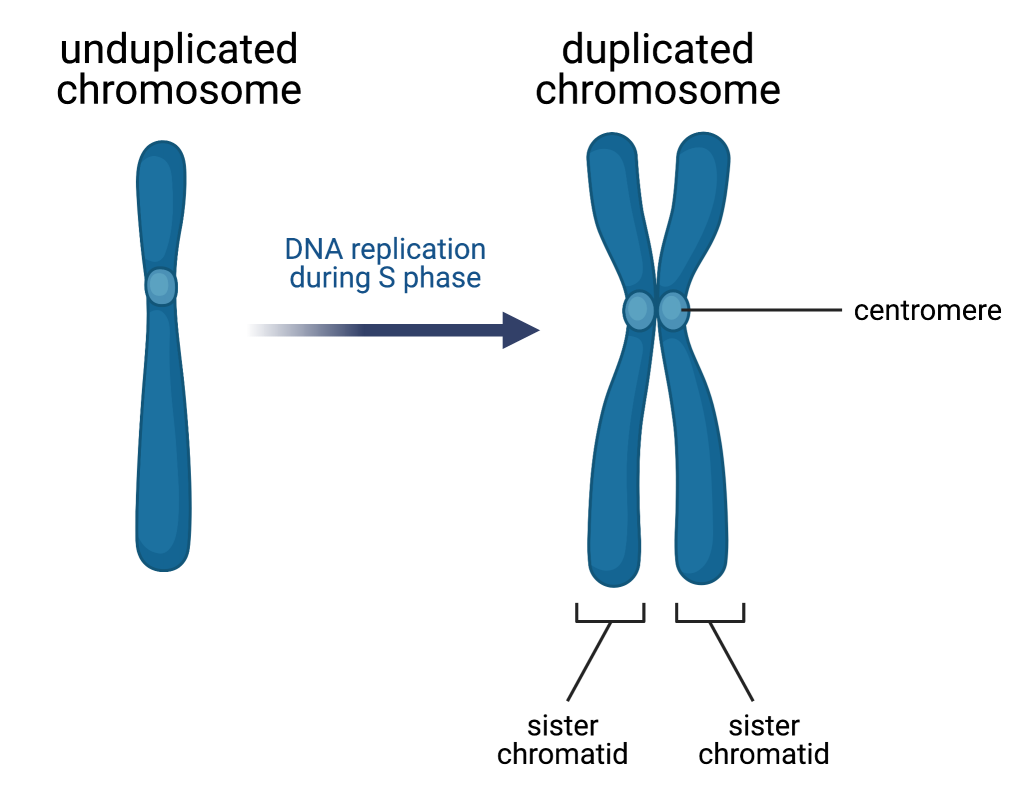
What is the significance of the centromere?
It is the point where sister chromatids are attached.
What happens to DNA during prophase?
It condenses and becomes visible
Which two cells represents anaphase?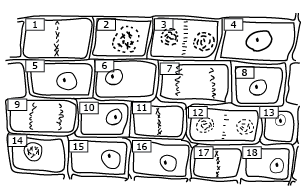
7 and 9
What stage is this cell? 
Anaphase- sister chromatids pulled apart to opposite ends of the cell
Which letter represents mitosis of the cell cycle?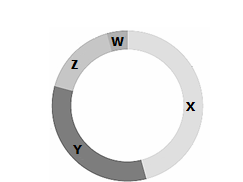
W
Define "chromatin"
uncoiled, loose DNA
What happens if a checkpoint fails?
When an animal cell begins to pinch in the middle during telophase, what is that area called?
Cleavage furrow
What happens to a cell if a checkpoint detects a flaw in the DNA?
Apoptosis- programmed cell death
What process MUST take place before mitosis can occur properly?
DNA replication
What is the role of the M checkpoint?
Checks that sister chromatids are correctly attached to spindle finers/microtubules
What forms in a plant cell during telophase?
Cell Plate (beginnings of a cell wall)
What is the purpose of the G1 checkpoint?
Evaluates the integrity of the DNA, checking for damage. Checks to see if cell has grown enough.
Which cell is at the latest stage of mitosis?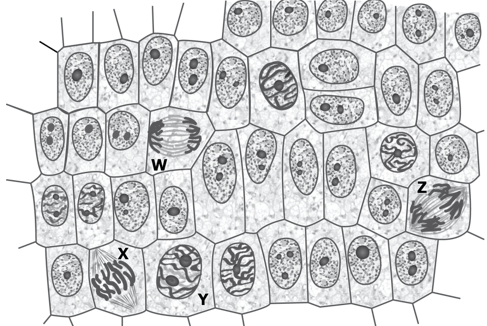
If a cell has 46 chromosomes in G1 (normal cell), how many chromosomes will it have after cytokinesis?
46, cell division ends with two identical daughter cells
Place these in correct sequence
A-Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
B- DNA condenses into chromosomes
C-Sister chromatids move to opposite sides of the cell
B, A, C
What phase does a cell enter after cytokinesis?
G1 of interphase
What structure plays a role in cell division but is only found in animal cells?
Centriole
During G1 phase a normal cell has 46 chromatids, how many chromatids will it have after S phase?
96- chromatids