Cell division is also known as
Mitosis.
During _____________ the chromosomes are pulled to opposite ends of the cell.

Telophase
Cell division allows an organism to create more of itself without a partner or other gametes. This is called what?
Reproduction (asexual)
The enzyme that unzips the DNA double helix
This is the longest phase in the cell cycle.
Interphase
During _____________, the spindle fibers start to pull the chromosomes apart.

Anaphase?
Name the phases of the cell cycle in order.
Interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis
This phase of the interphase where the cell prepares for cell division by replicating its DNA
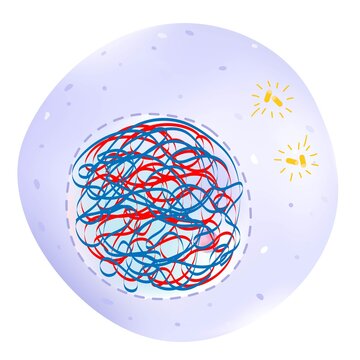
S Phase
The enzyme that builds complementary DNA bases.
DNA Polymerase
The cell cycle results in two genetically _________ daughter cells.
identical
During __________, the DNA condenses into chromosomes.
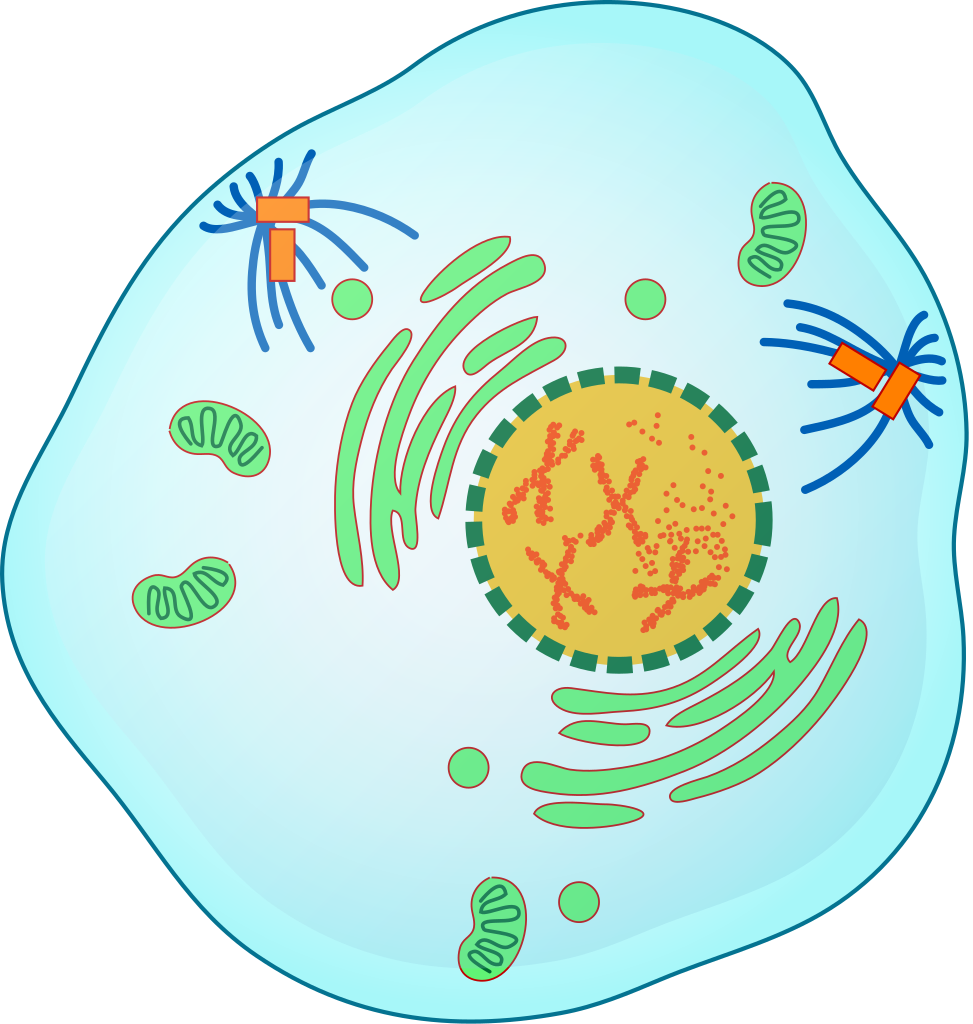
Prophase
True or false: metaphase comes after prophase.
What is true?
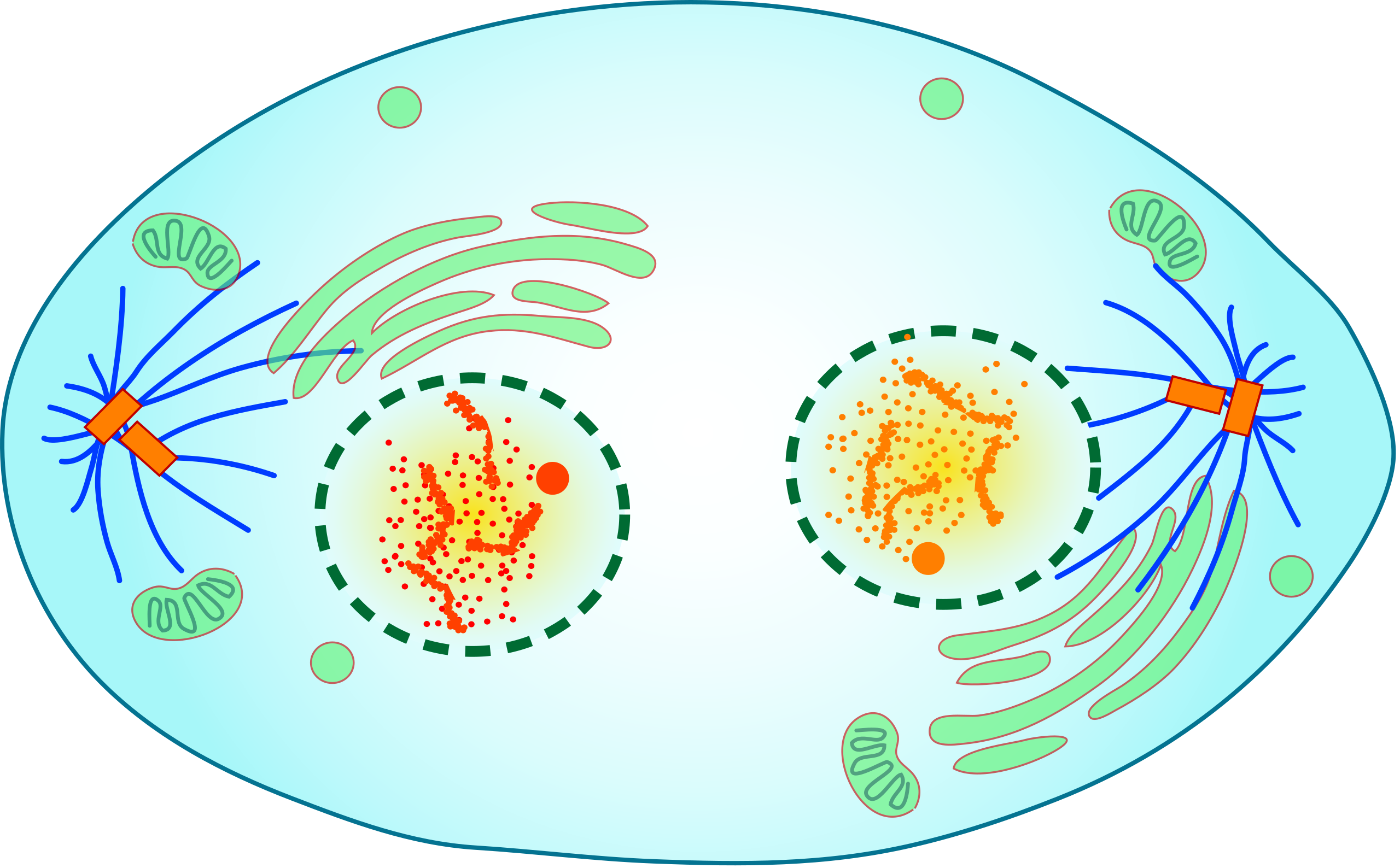
During telophase, this happens.
There are "two" nuclei forming at opposite ends of the cell.
What enzyme is responsible for helping DNA polymerase by telling it where to build with primer?
Primase
The part of the cell cycle where the cell grows, copies the DNA and organelles, and prepares to divide is called the ________________.
Interphase?
During ____________, the chromosomes line up along the center of the cell.

Metaphase?
During metaphase, the chromosomes do this.
What is line up along the center?

True or false: The centrioles are the "rope" that pulls the chromosomes and spindle is the anchor. They both work to help with cell division.
False
What is the enzyme that finishes DNA Replication by gluing together fragments of DNA
Ligase
Put the following stages of cell cycle in order.
3,6,1,4,2,5
List the phases of mitosis in order.
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
During prophase, this happens.
What is DNA condenses into chromosomes.

If a cell divides without stopping at checkpoints or skipping checkpoints it can possibly result in _______.
Cancer
Write the complementary DNA bases that would be across from A C T G C T A C on a DNA strand.
T G A C G A T G