What is the longest phase of the cell cycle?
Interphase
What are the stages of mitosis in order?
PMAT
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
What is label F?
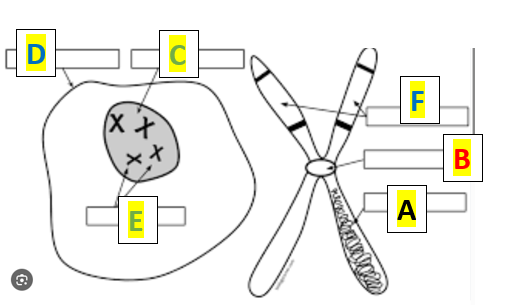
chromatids
Question: Which type of biomolecule regulates the cell cycle by controlling its timing?
A) Carbohydrates
B) Proteins
C) Lipids
D) Nucleic Acids
Proteins
Malignant or benign, which one means cells are non-cancerous?
benign
200 Points
What are the three phases within Interphase? This will need to be placed in order.
G1, S, G2
During which phase of interphase does the cell replicate its DNA?
S phase (Synthesis phase)
During which phase of mitosis do the chromosomes align in the middle of the cell?
Metaphase
What is Label C?
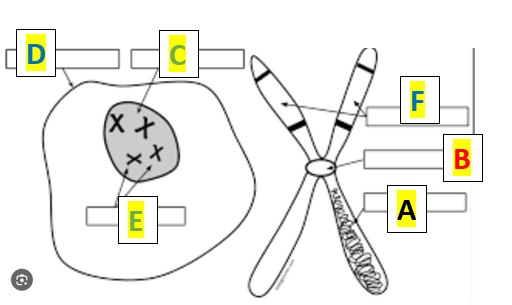
Nucleus
How many major checkpoints regulate the cell cycle?
3
Which cell don't respond to the signals that regulate the cell cycle, and grow/divide really quickly
Cancer cells
400 Points
What is the longest phase of the cell cycle?
Interphase
What are the two main stages of the M phase in eukaryotic cells?
Mitosis and Cytokinesis
Which structure is responsible for pulling apart the sister chromatids during mitosis?
Spindle fibers
What phase of this mitosis is does this illustration represent?
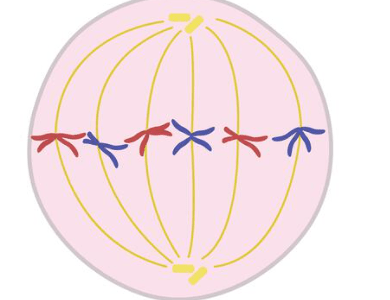
Metaphase
One thing a cell might do if it reaches a checkpoint and things are NOT going the way they're supposed to
What is die/apoptize, fix the mistake, or keep on going anyway (cancerous)?
Which type of tumor is more dangerous because it invades healthy tissues and can spread to other parts of the body?
Malignant
600 Points
How many chromosome pairs does a human have?
Which pairs are somatic cells?
Which pair/pairs are gamete cells?
23, 1-22, 23
What is the purpose of the G2 phase in the cell cycle?
A) The cell grows and performs normal functions
B) The cell divides its cytoplasm into two daughter cells
C) The cell prepares for mitosis by producing needed organelles like ribosomes and mitochondria
D) The cell’s DNA is copied
The cell prepares for mitosis by producing necessary organelles such as ribosomes and mitochondria
What happens during telophase in mitosis?
A) Chromosomes condense and spindle fibers form
B) Sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell
C) The nuclear membrane reforms around each set of chromosomes, and the cell begins to split
D) DNA replication occurs
The nuclear membrane reforms around each set of chromosomes, and the cell begins to split
Which phase of mitosis does this illustration represent?
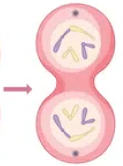
telophase
What happens if a checkpoint isn’t met?
The cell enters into a dormant/ resting phase (G0)
When cancer spreads from one place in the body to a different place.
What is Metastasis?
800 Points
Name and draw a picture of the first phase of the cell cycle and list the three stages (in order) within this phase.
Interphase
G1, S, G2
Question: How does mitosis ensure that daughter cells are genetically identical to the parent cell?
A) It duplicates and evenly divides chromosomes, ensuring each daughter cell gets an identical set of DNA
B) It randomly distributes chromosomes, leading to genetic diversity
C) It fuses the two daughter cells into one large cell
D) It allows uncontrolled cell growth
Mitosis ensures genetic consistency by precisely aligning and separating duplicated chromosomes so that each daughter cell receives an identical set of DNA.
In this phase of mitosis, you can see two new nuclei begin to form, and the original cell is starting to become two.
What is telophase (or cytokinesis)?
What is A in the illustration below:
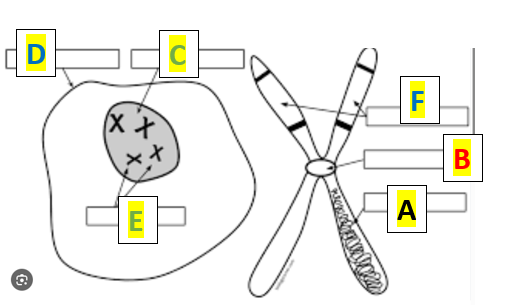
DNA
Which biomolecule regulates the cell cycle?
Proteins
Which of the following is NOT a known cause of cancer?
a. Carcinogens
b. Stem cells
c. Radiation
d. Viruses
Stem cells
1000 Points, what does DNA stand for? (YOU MUST ACCURATLEY PRONOUNCE the name correctly!
Deoxynucliec Acid