Cellular Respiration
Cellular Respiration
How do we derive energy from glucose?
Cellular Respiration
Explain glycolysis.
In glycolysis, glucose—a six-carbon sugar—undergoes a series of chemical transformations. In the end, it gets converted into two molecules of pyruvate, a three-carbon organic molecule. In these reactions, ATP is made, and NAD+ is converted into NADH.
What is oxidative phosphorylation?
The process of the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis.
What is ATP synthase?
ATP synthase is a protein that pumps protons through a membrane that produces ATP.
_____ is the energy currency.
ATP
What is the basic formula for cellular respiration? What does energy in the formula stand for?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 -----> 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
Energy stands for heat (thermal energy) and the 30-32 ATP molecules produced.
Explain pyruvate oxidation.
Each pyruvate from glycolysis goes into the mitochondrial matrix—the innermost compartment of mitochondria. There, it’s converted into a two-carbon molecule bound to Coenzyme A, known as acetyl CoA. Carbon dioxide is released and NADH is generated.
What happens during the electron transport chain?
In the electron transport chain, electrons are passed from one molecule to another, and energy released in these electron transfers is used to form an electrochemical gradient.
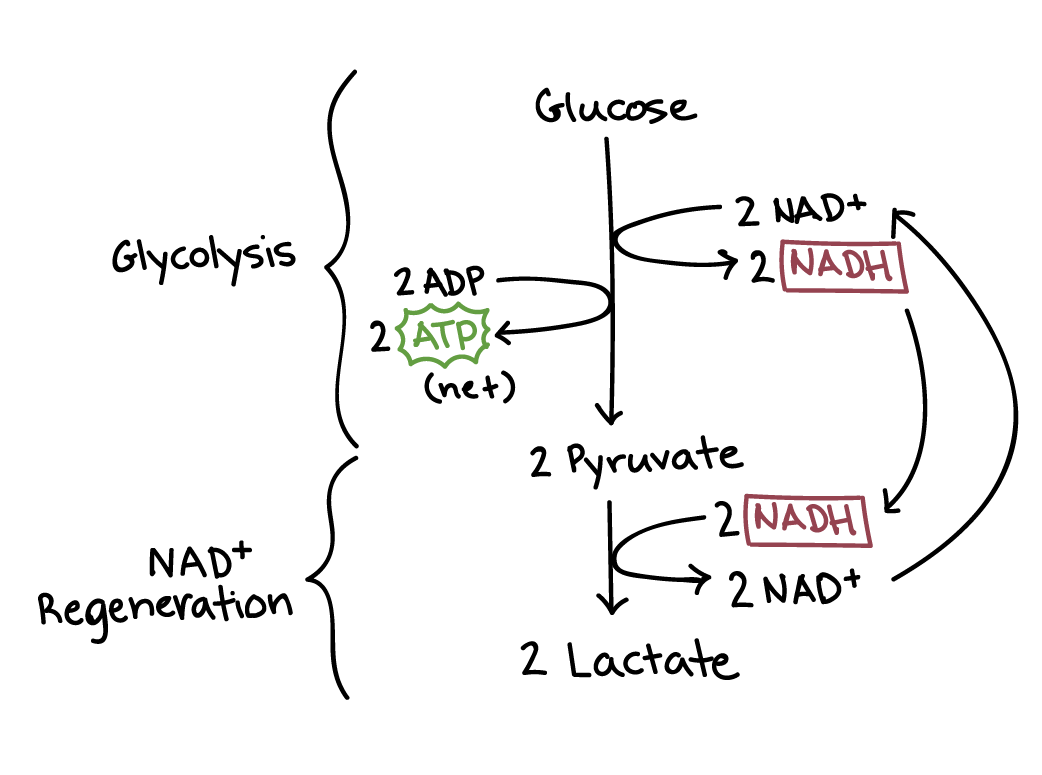
Draw a diagram of lactic acid fermentation.
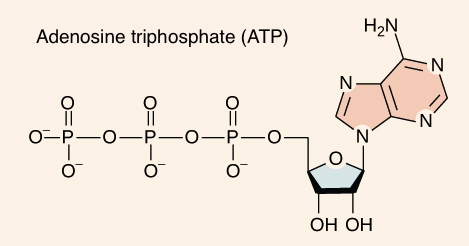
Draw an ATP molecule.
What are the stages of cellular respiration? What are the inputs and outputs of each?
Glycolysis; 1 glucose; 2 pyruvate, 2 ATP, 2 NADH
Pyruvate Oxidation; 2 pyruvate; 2 Acetyl CoA, 2 CO2, 2 NADH
Citric Acid Cycle; 2 Acetyl CoA; 4 CO2, 2 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2
Oxidative Phosphorylation; 10 NADH, 2 FADH2; 26-28 ATP
Explain the citric acid cycle.
The acetyl CoA made in the last step combines with a four-carbon molecule and goes through a cycle of reactions, ultimately regenerating the four-carbon starting molecule. ATP, NADH, and FADH2 are produced, and carbon dioxide is released.
What happens in chemiosmosis?
In chemiosmosis, the energy stored in the gradient formed by the electron transport chain is used to make ATP.
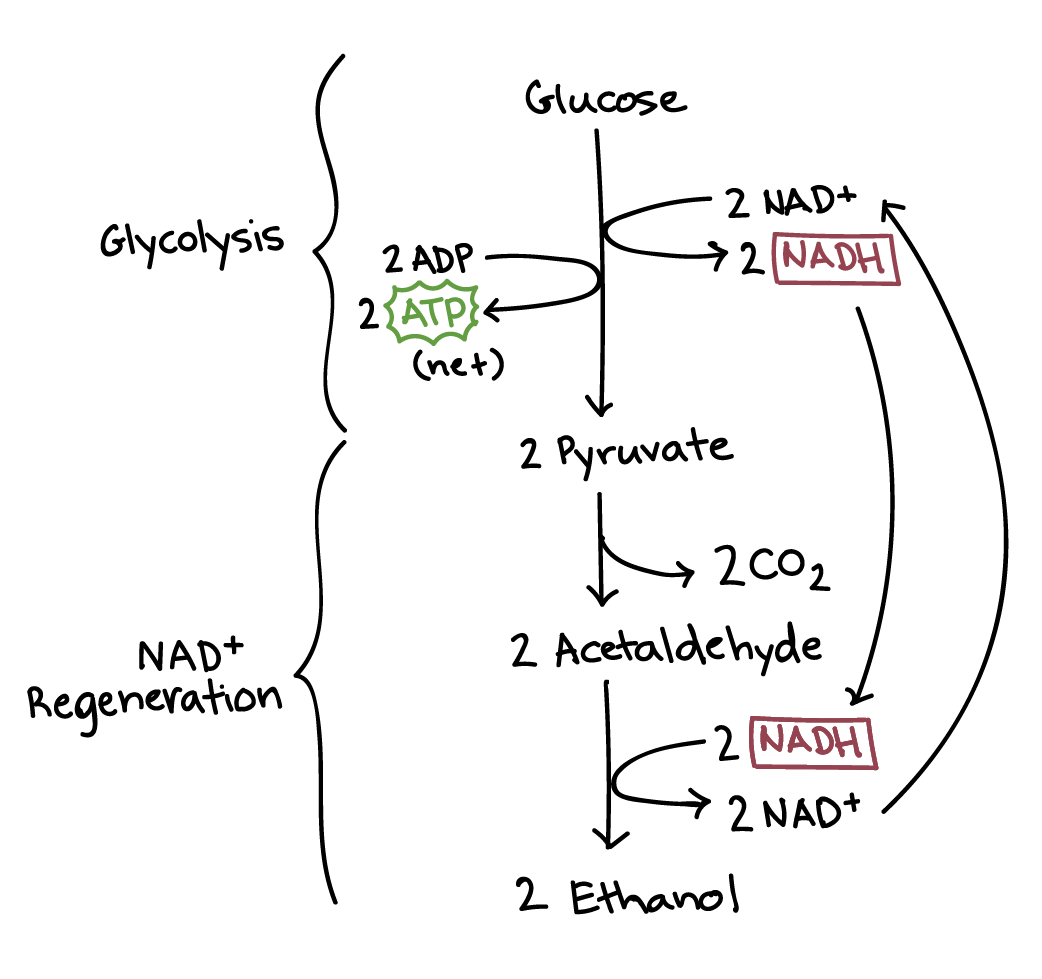
Draw a diagram of alcoholic fermentation.
Cyanide poisoning is a type of poisoning caused by exposure to certain cyanide-containing compounds, such as hydrogen cyanide or cyanide salts. Inhalation or consumption of these compounds can cause histotoxic hypoxia, a condition in which cells are no longer able to take up or utilize oxygen during cellular respiration. As a result, ATP production during respiration is significantly reduced.
What is the best explanation for how cyanide causes histotoxic hypoxia?
Cyanide inhibits the transfer of electrons to the final acceptor in the electron transport chain.
The final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain is oxygen. By inhibiting the transfer of electrons to oxygen, cyanide shuts down the electron transport chain, halting ATP synthesis and causing histotoxic hypoxia
What happens when oxygen is not present? What kind happens in yeast? What kind happens in humans?
Fermentation
Alcoholic Fermentation
Lactic Acid Fermentation
Explain oxidative phosphorylation.
The NADH and FADH2 made in other steps deposit their electrons in the electron transport chain, turning back into their "empty" forms (NAD+ and FAD). As electrons move down the chain, energy is released and used to pump protons out of the matrix, forming a gradient. Protons flow back into the matrix through an enzyme called ATP synthase, making ATP. At the end of the electron transport chain, oxygen accepts electrons and takes up protons to form water.
Does oxidative phosphorylation need oxygen? If so, why?
Yes; oxygen sits at the end of the electron transport chain, where it accepts electrons and picks up protons to form water. If oxygen isn’t there to accept electrons, the electron transport chain will stop running, and ATP will no longer be produced by chemiosmosis.
What is anaerobic respiration?
This is when organism use an inorganic molecule other than O2, such as sulfate, as a final electron acceptor for an electron transport chain.
Where does the citric acid cycle happen?
Mitochondrial Matrix
What are the two electron carriers in cellular respiration? What is the process called when one of these electron carriers gains or loses electrons (include full name and common name)?
NAD+ and FAD
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
Redox Reaction
Draw a diagram of the steps of cellular respiration.
Include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
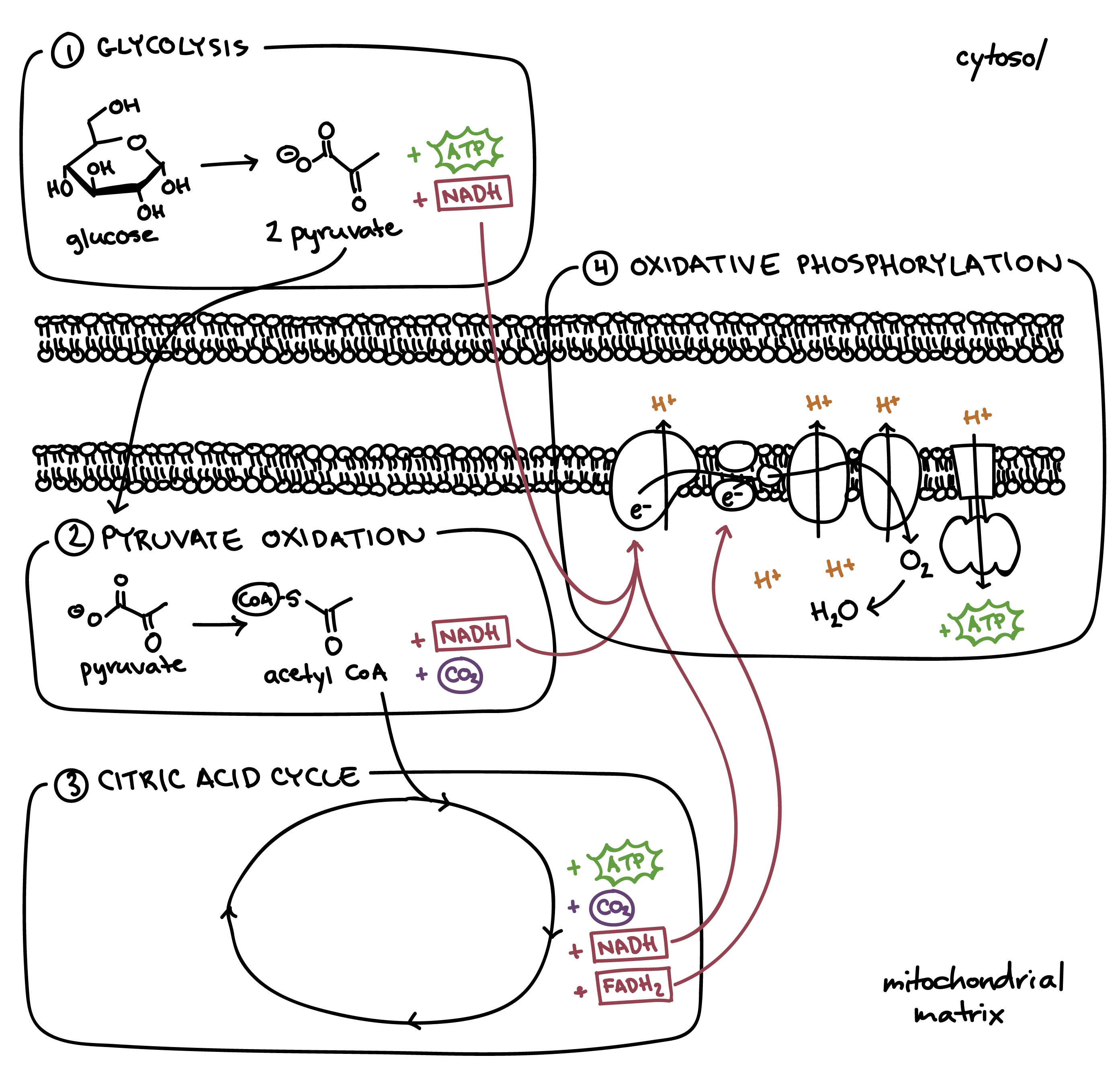
Draw a diagram of oxidative phosphorylation.

This question doesn't belong in this category, but I didn't have anywhere else to put it.
Where does glycolysis happen?
Cytosol
Where does oxidative phosphorylation happen?
Inner Membrane of the Mitochondria