This is the study of mechanisms of disease processes.
What is pathophysiology?
May also be worded as the study of functional alterations in human health because of an injury, disease, or syndrome.
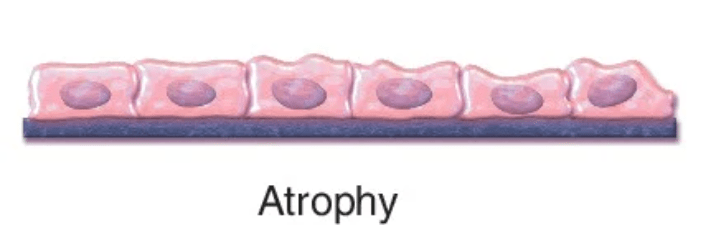
A 60-year-old client has had his leg in a cast for prolonged treatment of a tibia and fibula fracture. Name the condition the patient's gastrocnemius muscle may experience once the cast is removed.
What is atrophy?
A decrease in the functional demand on a cell prompts a decrease in cell size. This type of decrease often occurs when a limb is immobilized in a cast and active muscle movement is impaired.
Name these cells involved in innate immunity that work together with the adaptive immune system to initiate and direct continued protection from infection.
What are macrophages, neutrophils, and dendritic cells?
Figure: pH 7.25, PaCO2 55, HC03 25.
What is respiratory acidosis uncompensated?
Step 1 – pH 7.25 is Acidic
Step 2 – match PaCO2 with partner, PaCO2 is 55 = Acidic
Our HCO3 25 is WNL
Step 3 – Compensated or Uncompensated? No balance was found, so it’s Uncompensated
These are the specific actions a nurse takes to help a patient achieve their care goals.
What are nursing interventions?
This results from exposure to infection in the healthcare environment.
What is a nosocomial infection?
Name this organelle that is involved in cellular respiration and is linked to the development of oxidative stress.
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?

Name this disorder that results from excessive immune responses to allergens.
What is/are hypersensitivity reaction(s)?
Figure: pH 7.57, PaCO2 25, HCO3 22.
What is respiratory alkalosis uncompensated?
Step 1 – pH 7.57 is Base
Step 2 – match PaCO2 with partner, PaCO2 is 25 = Base
Our HCO3 22 is WNL
Step 3 – Compensated or Uncompensated? No balance was found, so it’s Uncompensated
List four primary nursing interventions for patients with a fluid overload diagnosis.
What is monitor fluid intake and output, encourage fluid restrictions, administer diuretics as ordered, and monitor for electrolyte imbalances and other side effects?
These are objective manifestations that can be measured.
What are signs?
True or False:
Treatment of chronic conditions associated with cerebral atrophy is targeted toward slowing neuronal injury and atrophy.
What is true?
The aim is to slow the neuronal injury and atrophy.
A client receiving intravenous ciprofloxacin for a diagnosis of pneumonia immediately developed a life-threatening anaphylaxis reaction. Name the category of the hypersensitivity reaction.
What is Type I, immediate hypersensitivity reaction?
Figure: pH 7.21, PaCO2 39, HCO3 19.
What is metabolic acidosis uncompensated?
Step 1 – pH 7.21 is Acid
Step 2 – match PaCO2 with partner, PaCO2 is 39 = WNL
Our HCO3 19 = Acid
Step 3 – Compensated or Uncompensated? No balance was found, so it’s Uncompensated
List the primary nursing interventions for patients with a dehydration diagnosis.
What are assessing fluid status, preventing further loss, and restoring hydration through oral or intravenous means per provider orders?
These are reportable indicators and considered to be manifestations because they are not directly observable.
What are the symptoms?
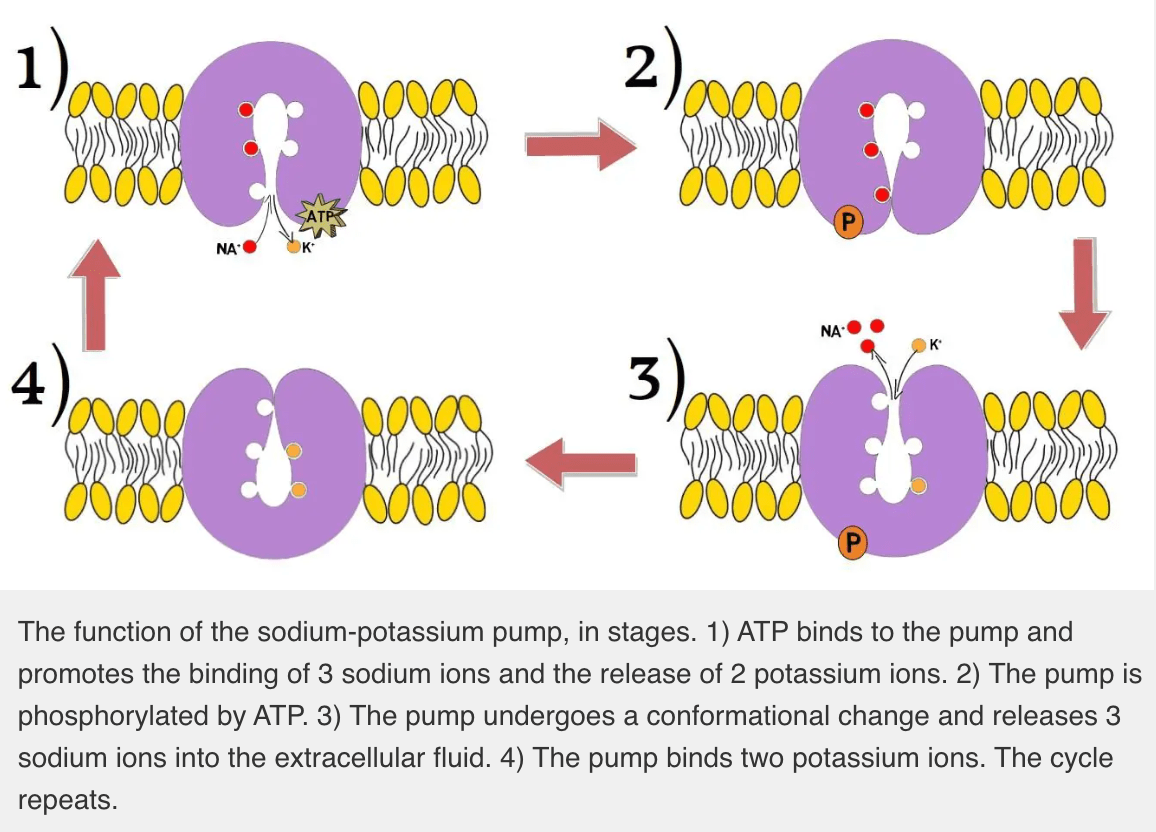
Name this critical pump vital for maintaining homeostasis by regulating two essential ions inside and outside of the cells.
What is the sodium-potassium pump (aka Na+/K+ ATPase)?
A client receiving intravenous self-autologous blood transfusion for a surgical procedure of a total knee arthroplasty immediately developed a Type II, antibody-mediated reaction. Name the etiology and mechanism of injury.
What is IgG or IgM-mediated? And what is action against normal "self" antigens; organization and lysis of cells?
Figure: pH 7.48, PaCO2 36, HCO3 28.
What is metabolic alkalosis uncompensated?
Step 1 – pH 7.48 is Base
Step 2 – match PaCO2 with partner, PaCO2 is 36 = WNL
Our HCO3 28 = Base
Step 3 – Compensated or Uncompensated? No balance was found, so it’s Uncompensated
List the nursing actions needed for a hypersensitivity I reaction.
What are stopping the infusion if there is one, maintaining airway, assisting with breathing, and chest compressions if needed (ABCs) support, as well as medication administration?
The dynamic steady state that the body strives to achieve every day.
What is homeostasis?
The nurse is caring for a 68-year-old male patient with infectious tuberculosis, newly admitted to the medical-surgical unit from the emergency department. The patient's history includes Alzheimer's disease, heart failure, and Bartter syndrome. Name what the nurse suspects the patient's underlying conditions to be caused by.
What is a disruption in the membrane transport?
A 28-year-old client presents for her outpatient appointment with a visible butterfly rash to her face, and complaints of flank, groin, and bilateral hand pain. Name the disorder you immediately suspect.
What is systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), a type III hypersensitivity reaction?
Figure: pH 7.45, PaCO2 46, HCO3 27.
What is respiratory acidosis compensated?
Step 1 – pH 7.45 is WNL
Step 2 – match PaCO2 with partner, PaCO2 is 46 = Acidic
Our HCO3 27 = Base
Step 3 – Compensated or Uncompensated? Balance was found, so it’s compensated
List the primary nursing interventions for patients with Reed-Sternberg cells.
What are administering medications, managing chemotherapy side effects, preventing infections, and offering emotional support?