The organelle where photosynthesis occurs
What is the chloroplast?
What alcohol/ethanol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation?
The model describing the structure of the cell membrane
What is the Fluid Mosaic Model?
When one solution has more solute than another
What is hypertonic?
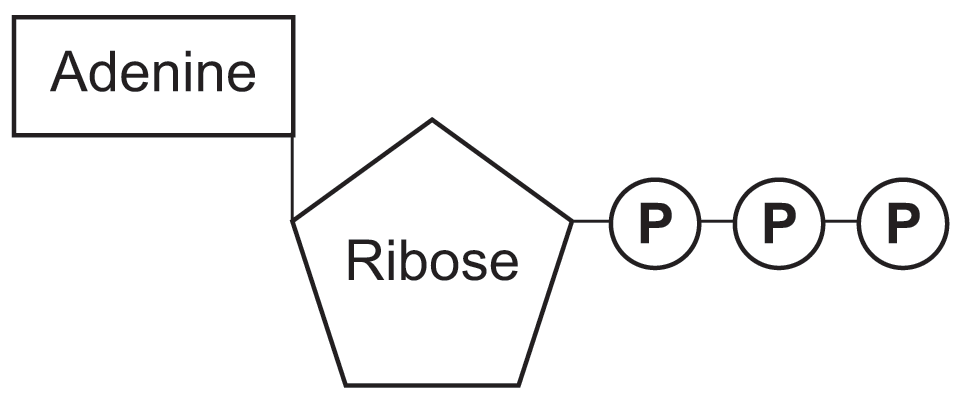
What is ATP?
The reactants of photosynthesis
What are Light, carbon dioxide, and water
The products of cellular respiration
carbon dioxide, water, and ATP
A membrane that allows some material to go through it.
What is a semi-permeable membrane
When one solution has less solute than the other
What is hypotonic?
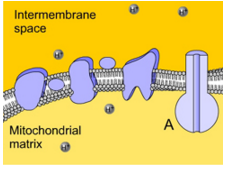
What is ATP synthase?
The products of photosynthesis
The first step of cellular respiration, where glucose is broken down into pyruvate
What is glycolysis?
The molecule that makes up the majority of the cell membrane's lipid bilayer
What is a phospholipid?
The movement of a solute across a membrane from high concentration to low concentration
What is diffusion?

What are cells in a hypertonic solution?
The first reaction of photosynthesis, using light and H2O to create ATP, NADPH, and O2 waste
What is the light-dependent reaction?
The second step of cellular respiration, where pyruvate is broken down to fill the hydrogen/electron carriers NADPH and FADH2
What is the Krebs Cycle?
The proteins embedded in the cell membrane that allow facilitated diffusion to occur
What are transport proteins?
The movement of a solute from low concentration to high concentration by using energy
What is active transport?

What is a cell in a hypotonic solution? or What is lysed?
The second reaction of photosynthesis, using CO2, ATP, and NADPH to create C6H12O6(glucose) with ADP and NADP+ as byproducts.
The third step of cellular respiration, where electrons and hydrogen ions are used to generate the most ATP
What is the Electron Transport Chain?
A state of balance inside a cell that the cell membrane exists to maintain
The movement of water across a membrane
What is osmosis?

What is a thylakoid (one)? What is a granum(group)?