The sodium-potassium pump moves sodium ions outside the cell and potassium ions inside the cell.
What type of transport is this an example of?
Active Transport
The reason cells move substances in and out
To maintain homeostasis, release waste, and/or transmit molecules to other parts of the body
What does the term "selectively permeable" mean?
only letting some things through
The molecule that active transport uses to move large molecules against the concentration gradient
ATP
Inside of cell : 75% salt, 25%water
Outside of cell: 70% salt, 30% water
Which way does water move and what is the name of the solution ?
Into cell
hypotonic
What is the difference between active and passive transport?
Active requires energy (ATP) and goes against the concentration gradient
What type of cell transport is represented by moving molecules from high to low concentration gradient?
Passive Transport
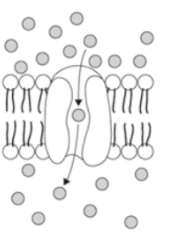 The image shows the process of __(1)__ across the cell membrane to maintain cellular __(2)__.
The image shows the process of __(1)__ across the cell membrane to maintain cellular __(2)__.
molecule transport and homeostasis
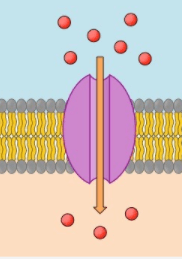 The type of transport is shown in the diagram
The type of transport is shown in the diagram
Facilitated Diffusion
When there is a higher SOLUTE concentration inside the cell than outside the cell, what type of solution is it?
hypotonic
The type of transport is shown in the picture
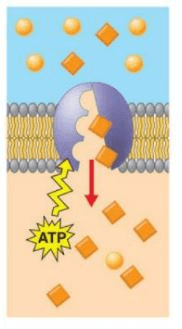
Active Transport
When a cell surrounds a large amount of waste with a cell membrane and moves it outside the cell?
Exocytosis
The heads of a phospholipid are ___________, meaning they are attracted to water.
hydrophilic
The organelle responsible for the production of energy (ATP) for your cell
Mitochondria
The main function of the cell membrane
To control what substances enter and exit the cell
__________ is the diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane.
What is Osmosis?
Description of substances that CAN move across the cell membrane
small and non-polar
What are the three types of passive transport?
Diffusion
Facilitated diffusion
Osmosis
What cellular transport did this cell model demonstrate?
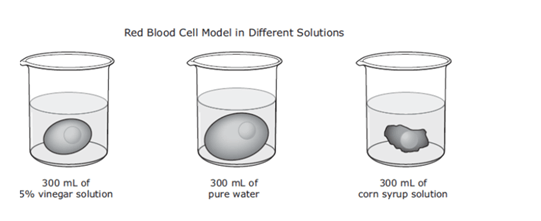
Osmosis (movement of water in/out of cell)?
Your teacher sprays an air freshener, and it slowly spread throughout the classroom This was an example of what type of transport?
Diffusion, passive transport
The substance moved during OSMOSIS
WATER
During transport water will move in what direction?
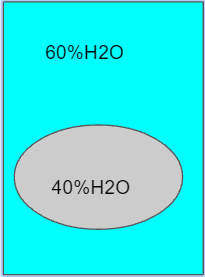
What is INTO the cell?
Why can glucose diffuse across the membrane?
The size of the molecules
Carbon dioxide moving out of the body into the blood cells is an example of what type of transport?
Diffusion, passive transport
The structure that makes facilitated diffusion different from other types of passive transport
channel protein
The gradual change in the concentration of a substance within a given volume
Concentration gradient
List three of the five main parts of a cell membrane.
Phospholipids, Channel Proteins, Carrier Proteins/Protein Pumps, Cholesterol, Carbohydrates
If the inside of a cell contains 55% solute and the outside is composed of 25% solute, what direction will water move and what will happen to the cell?
Water will move into the cell causing it to burst if it an animal cell or become turgid if it is a plant cell
What macromolecule is responsible for moving molecules into and out of the cell?
Proteins
An egg is placed in a hypotonic solution, what will happen to the egg after 24hours
The egg will swell, gaining mass (weigh) as water moves into the egg