Name the two major structural components of the cell membrane.
What are Phospholipids and Proteins?
The organelle responsible for the production of energy (ATP) for your cell
What is the Mitochondria?
The main function of the cell membrane
What is to control what substances enter and exit the cell?
__________ is the diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane.
What is Osmosis?
Description of substances that CAN move across the cell membrane
What are small and non-polar?
What cellular transport did this cell model demonstrate?
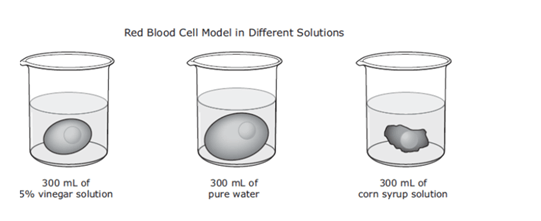
What is Osmosis (movement of water in/out of cell)?
The air freshener your teacher sprayed is an example of diffusion. This was an example of what type of transport?
What is passive transport?
The substance moved during OSMOSIS
What is WATER?
During transport water will move in what direction?
What is INTO the cell?
Water moves into a cell when the solution surrounding the cell is
What is Hypotonic?
What type of cell transport is represented by a high to low concentration gradient?
Passive Transport
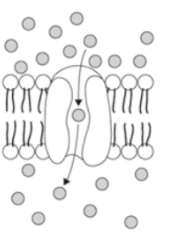 The image shows the process of __(1)__ across the cell membrane to maintain cellular __(2)__.
The image shows the process of __(1)__ across the cell membrane to maintain cellular __(2)__.
What are molecule transport and homeostasis?
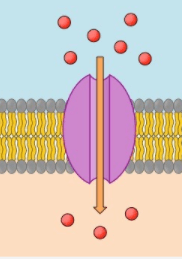 The type of transport is shown in the diagram
The type of transport is shown in the diagram
What is Facilitated Diffusion?
The are of higher SOLUTE concentration where water will exit the cell through osmosis
What is OUTSIDE the cell?
The type of transport is shown in the picture
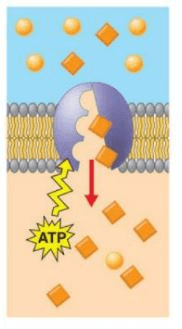
What is Active Transport?
The sodium-potassium pump is a form of active transport that moves sodium ions outside the cell and potassium ions inside the cell. Why is energy needed for active transport?
2. Ions are moving Low to High (against the concentration gradient)
The reason cells move substances in and out
What is maintain homeostasis, release waste, and/or transmit molecules to other parts of the body?
The area of higher concentration when it is likely that a substance will move from outside the cell to inside the cell
What is OUTSIDE?
The molecule that active transport uses to move large molecules against the concentration gradient
What is ATP?
Four major types of active transport?
What are pumps, cotransport, endocytosis, and exocytosis?
What is a CHANNEL PROTEIN?
The gradual change in the concentration of a substance within a given volume
What is CONCENTRATION GRADIENT?
Where there is higher SOLUTE concentration leading to water entering the cell through osmosis
What is INSIDE the cell?
The direction substances move during active transport
What is AGAINST the CONCENTRATION GRADIENT?
Water will move OUT of a cell when the surrounding solution is______________
What is HYPERTONIC?