The hydrophobic ends of the phospholipid are __________.
What are the tails?
The type of protein used in active transport.
What is a protein pump?
True or False: Passive transport requires energy.
False!
True or false: Active transport requires energy in the form of ACT?
False!
Active transport requires energy in the form of ATP
This type of transport does not require ATP.
What is passive transport?
The following image best represents ________.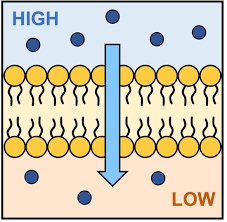
What is simple diffusion?
What is passive transport?
The hydrophilic ends of the phospholipid are ___________.
What are the heads?
The type of protein used in passive transport.
What is a protein channel?
What type of passive transport requires a protein channel?
What is "facilitated diffusion?"
In active transport, molecules move from an area of _______ to _________ concentration.
What is low to high?
What type of diffusion would a glucose molecule likely use to get into the cell?
[hint: formula = C6H12O6]
What is facilitated diffusion?
The following is best described as ___________ transport.
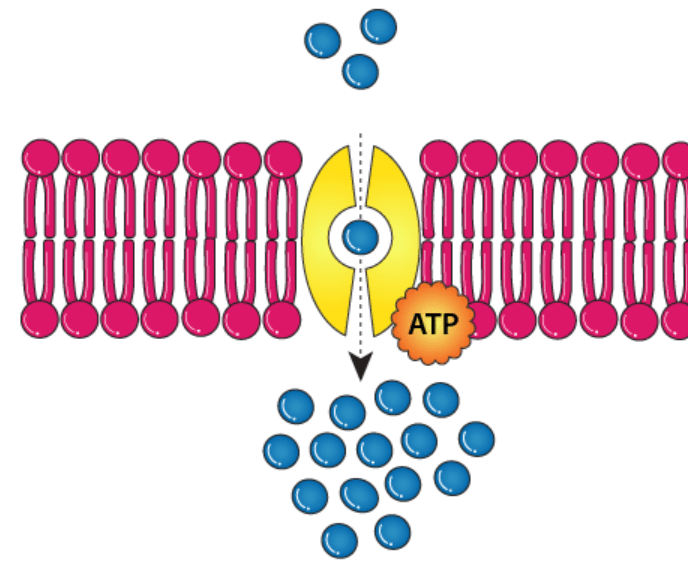
What is active transport?
Phospholipids form a ________ to make up the majority of the cell membrane.
What is bi-layer?
The types of molecules that need a protein transporter (e.g., channel or pump), are generally __________ , _________, or both.
What are large and charged (ions) ?
Which type of passive transport does not require a protein?
What is "simple diffusion?"
A protein __________ is needed for active transport.
What is a protein pump?
The diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide across the cell membrane happens through this process.
[Both are small and nonpolar]
What is simple diffusion?
The following can best be described as ______________ diffusion.
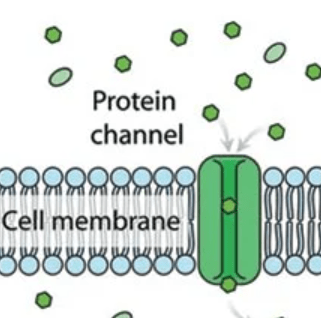
What is facilitated diffusion?
In this process, water moves across a selectively permeable membrane.
What is osmosis?
This type of diffusion requires transport proteins but no energy
What is facilitated diffusion?
When molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. (General term)
What is diffusion?
Name one example from class of active transport.
What is the Na+/K+ pump?
When molecules reach equal concentrations on both sides of a membrane, this has been reached.
What is equilibrium?
Draw a picture of passive transport on the board. Label where the high/ low concentration is as well as the direction of movement. Explain why it is either simple of facilitated diffusion.
Graded in person.
The cell membrane is described as this type of barrier because it allows some substances through but not others.
What is selectively permeable (or semi-permeable)?
A protein which goes all the way through the membrane is called a ___________, while a protein that only interacts with the inside or outside of the membrane is called a ______________.
What is a
-Transmembrane/ membrane spanning protein
-Peripheral/ surface protein?
Name one example from class of a protein channel. [Multiple answers accepted]
-Na + leakage channel
-K+ leakage channel
-gated channels (e.g., glucose channel in the packet)
In ___________ transport molecules most along the concentration gradient, while in ____________ transport molecules move against the gradient.
What is passive and active transport?
The ________ mosaic model describe the heterogeneity and movement of the cell membrane.
What is the fluid mosaic model?
Draw a picture of active transport on the board. Label where the high/ low concentration is as well as the direction of movement. Include ATP in your drawing (if relevant)
Graded in person.