Looked at thin slices of cork under a microscope
Who is Robert Hooke?
What does a prokaryotic cell lack that a eukaryotic cell has?
nucleus
Another name for the mitochondria is the powerhouse of the cell. The function of the mitochondria is to:
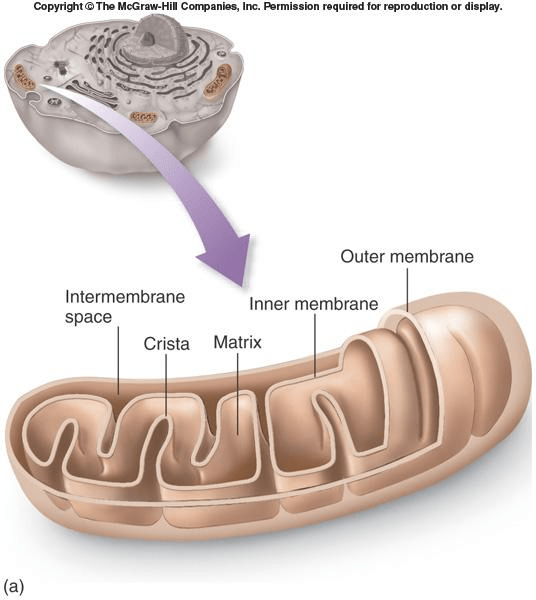
produce ATP Energy
The function of the nucleolus is to:
make ribosomes
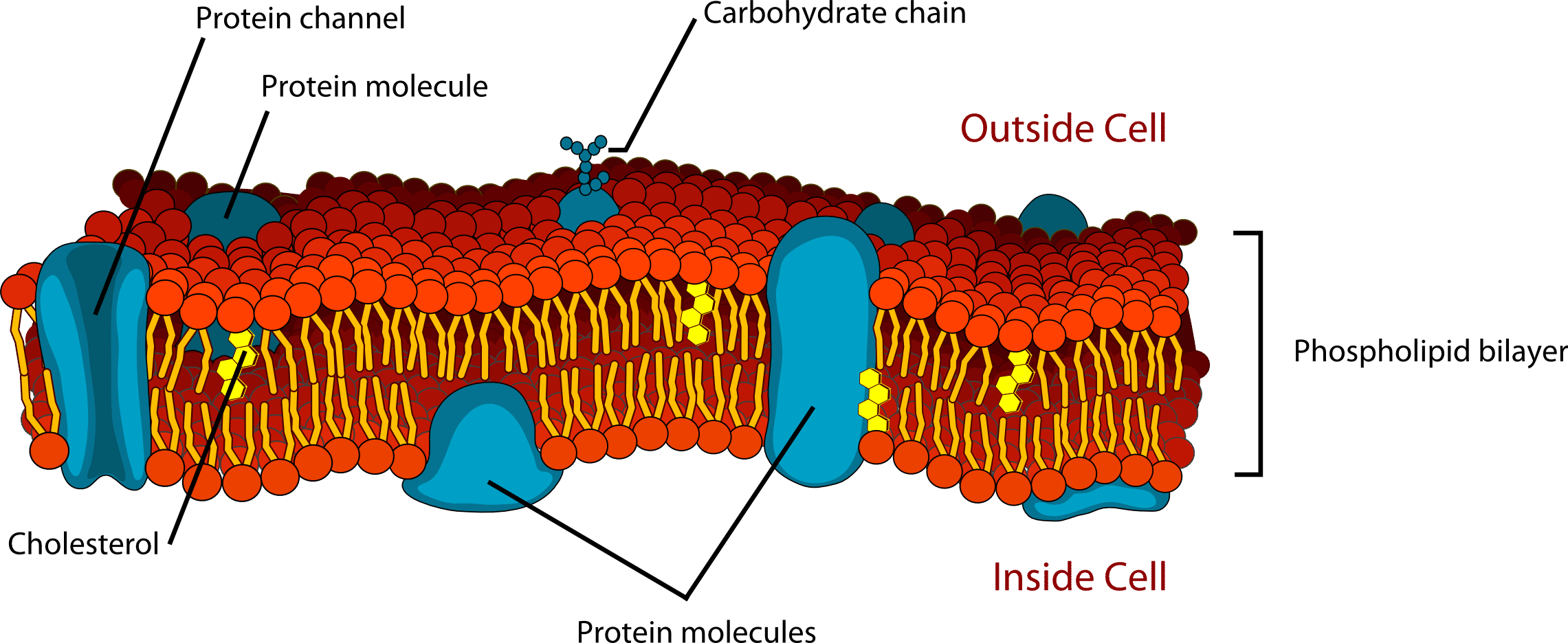
The plasma membrane is made up primarily of a bilayer of

phospholipids
The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
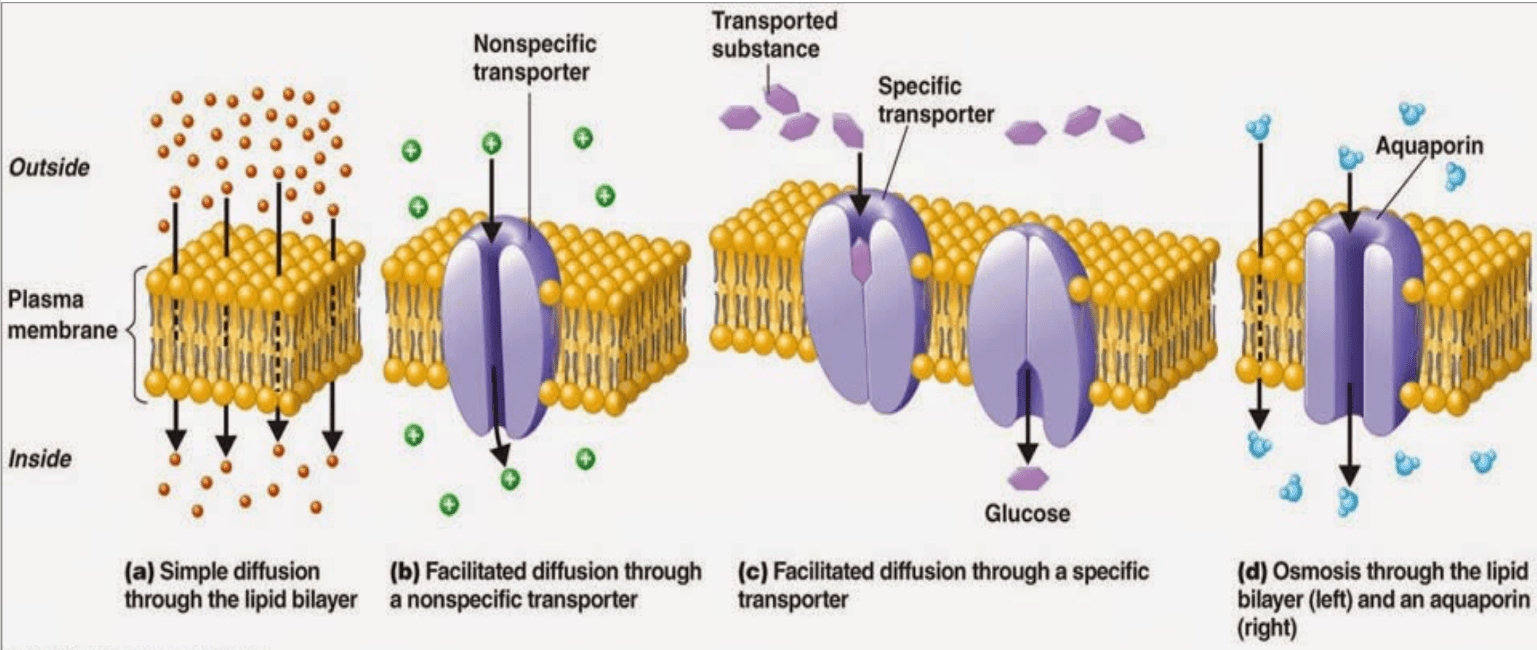
Passive Transport
What cellular transport did this cell model demonstrate?
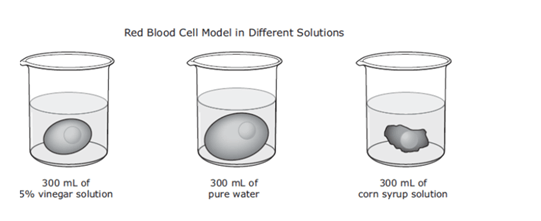
Osmosis (movement of water in/out of cell)
What is cell theory?
all organisms are made up of one or more cells, all the cells are the basic unit of life, all cells come from preexisting cells.
What cell type is classified as a prokaryotic cell.
bacteria
Sites of Protein Synthesis. (Where are proteins made)?
What is the ribosomes?
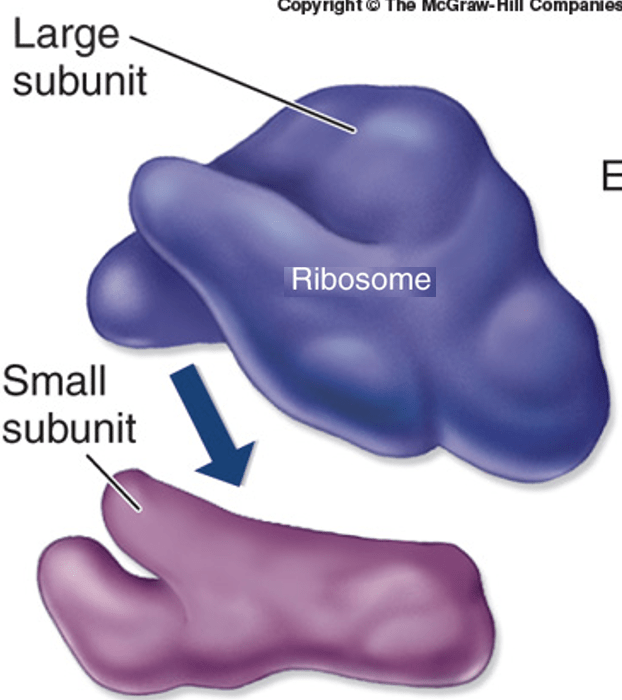
What is the lysosome?
Breaking down old cells parts is the job of this organelle
The phospholipid bilayer that forms the inner layer

Hydrophobic tail
Cellular drinking, or bringing liquid into the cell is this type of endocytosis
pinocytosis
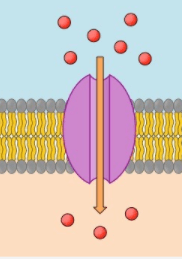
The type of transport is shown in the diagram
Facilitated Diffusion
Which scientists concluded animals are made of cells?
Schwann
What cell type is classified as a eukaryotic cell.
plants, animals, fungi, and protists
The function of the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
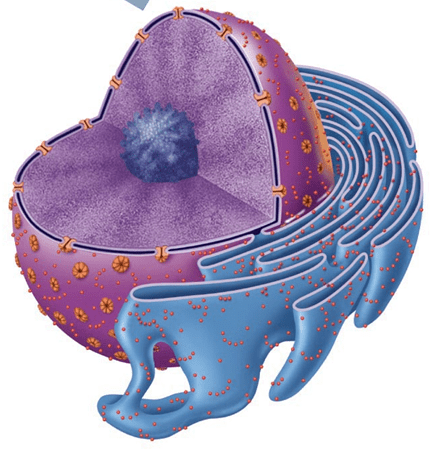
transport materials around the cell
Microfilaments, Microtubules, and intermediate filaments are part of this supportive cell structure
What is the cytoskeleton?
This protein regulates the movement of hydrophilic molecules through membrane.
Transport Protein, Channel Protein, and Integral Protein
Cellular eating, or bringing a solid material into the cell is this form of endocytosis
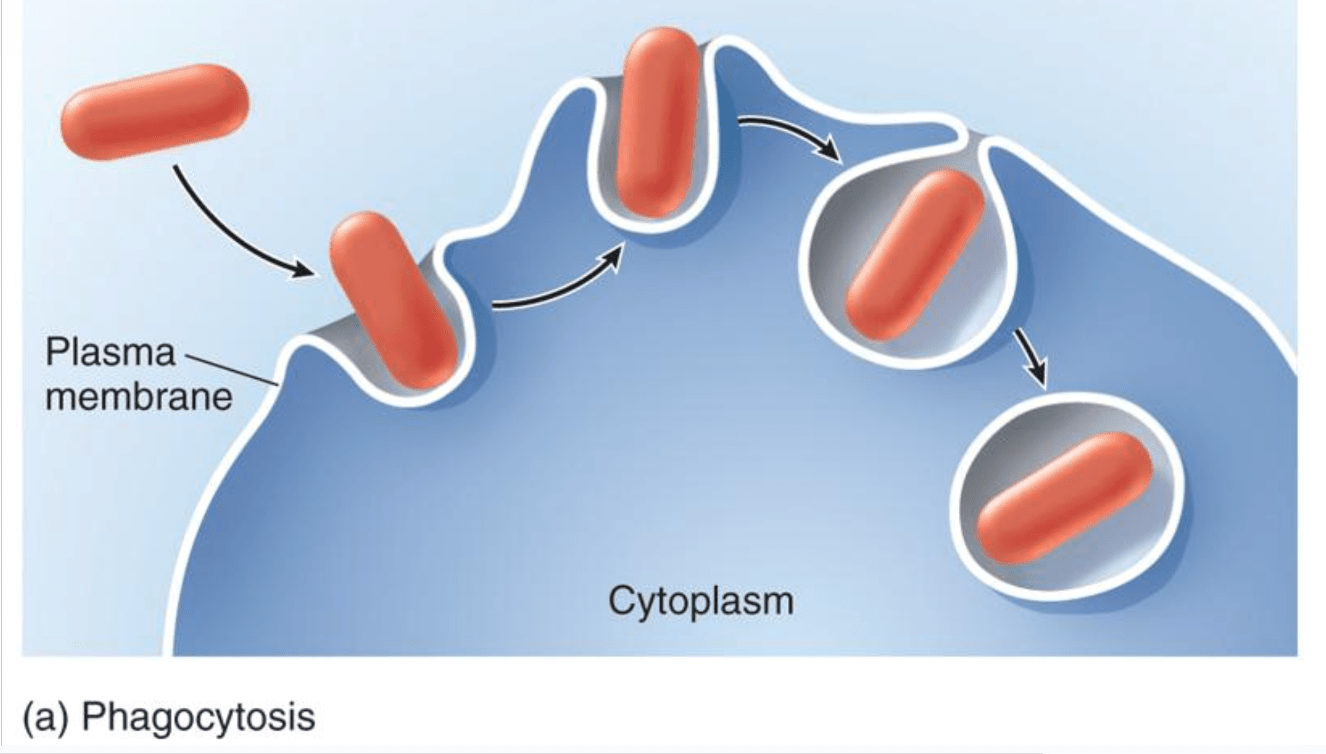
phagocytosis
During transport water will move in what direction?
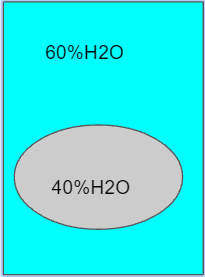
INTO the cell
Anton van Leewenhoek saw these under his microscope
What is animalcules/tiny animals/microorganisms
Which of the following cells would have the highest surface area to volume ratio?
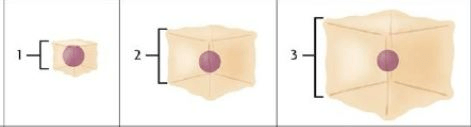
1
This organelle modifies, sorts, and packages different substances for secretion of the cell, or for use within the cell.
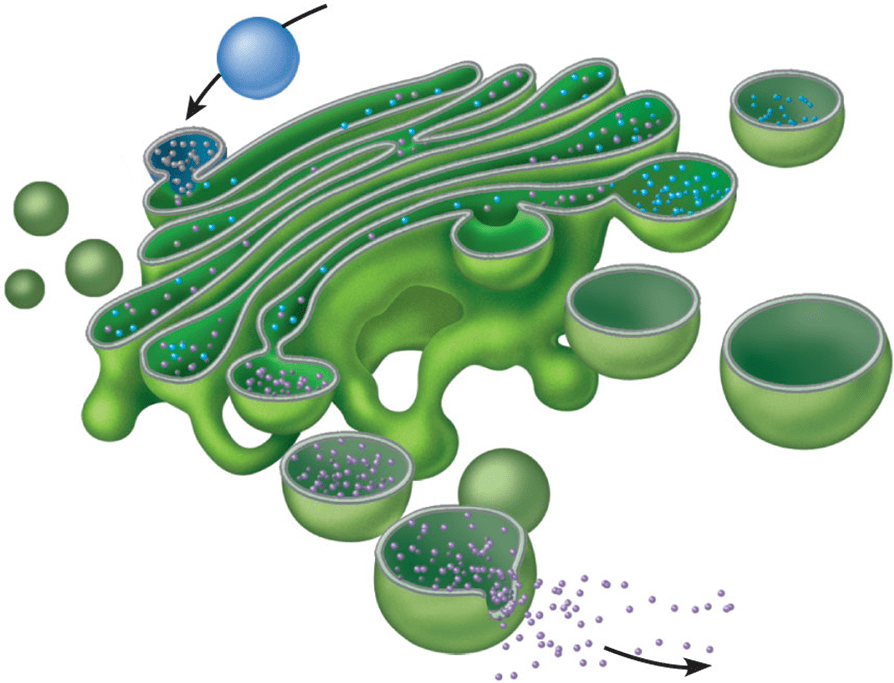
Golgi Apparatus/GolgiBody
The brain of the cell because it controls all of the cell functions
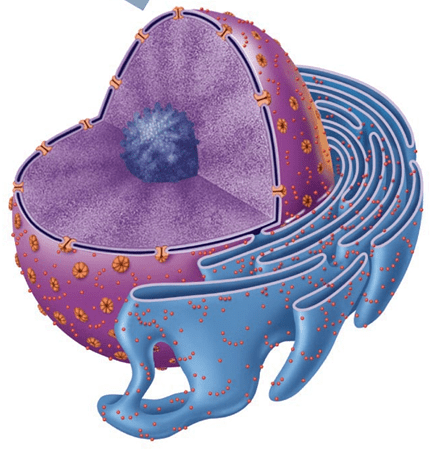
Nucleus
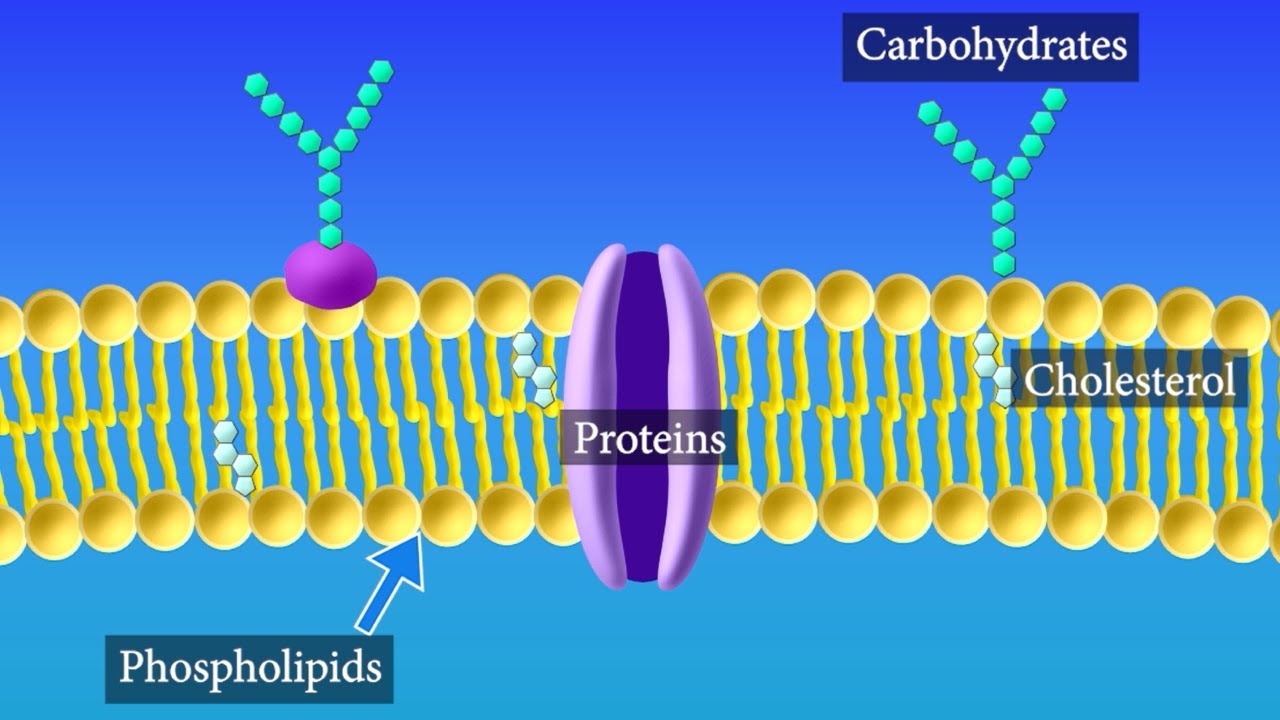
The fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane structure describes the plasma membrane as a fluid combination of
phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates.
This type of transport requires energy
The type of transport is shown in the picture
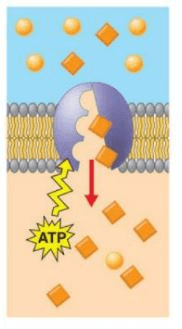
Active Transport
Which scientist created a compound microscope with multiple objective lenses?
Anton Van Leewenhoek
A cell has a volume of 64 units and total surface area of 96 units. What is the cell's surface area to volume ratio?
Volume = l x w x h
Surface Area - l x w x 6 sides
1.5:1
The cell organelle the protects the cell by controlling what goes in and out of the cell
cell membrane
The function of the chloroplast
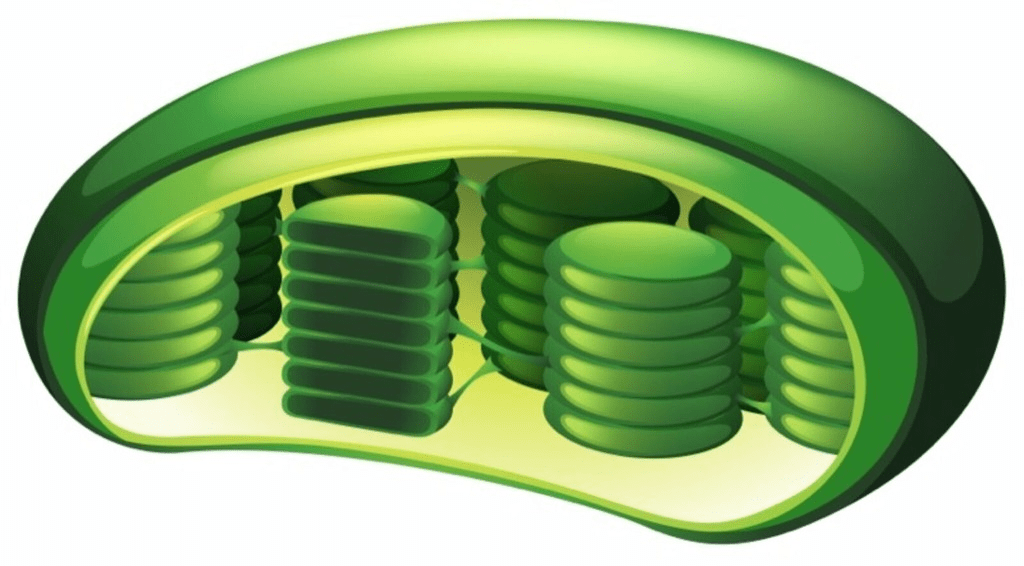
is to capture energy from the sun and use it to produce sugars for food
list atleast three proteins found within the cell membrane and describe their function.
Integral - span the cell membrane,
Peripheral - sits on top of the cell membrane.
Transport - helps transports molecules across the membrane.
Receptor - binds with other cells by communicating
Cell Recognition - identify other type of cells.
Osmosis is a type of passive transport that does this function
What are the three types of passive transport?
Osmosis
Facilitated Diffusion
Simple Diffusion