The English scientist first to use the word “cells” when describing cork under the microscope.
Robert Hooke (fact: he and Newton hated each other)
This is found in all cells and contains instructions to make proteins.
DNA
This organelle is only found in eukaryotic cells. Its role is to house and protect the DNA.
nucleus
All prokaryotic cells are these types of organisms.
bacteria
What is the difference between smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum?
rough ER has ribosomes and smooth doesn't
The cell theory would not have been formed without this tool
and
what is the highest magnification in our light microscopes?
Microscope
x400
What is the difference between cytoplasm and the cytoskeleton?
cytoplasm
A jelly like substance found in all cells in which the organelles or other structures are suspended in.
A network of fibers that help the cell maintain shape and can assist with cell movement.
cytoskeleton
This organelle is responsible for packaging proteins into vesicles
AND
This organelle is a tunnel like structure that aids in the production and transportation of proteins.
golgi apparatus
rough endoplasmic reticulum
True or False: Prokaryotes have ribosomes AND a plasma membrane.
IF false, please correct the statement
true
What can be found surrounding the cell membrane of plants- what is it made out of and what is its function?
The cell wall can be found surrounding the cell membrane of plants.
It is made out of cellulose, a type of polysaccharide.
The function is to provide support, structure, and protection for the plant.
Name at least 3 scientists that played a role in the formation of the cell theory.
Hooke, Leeuwenhoek, Schleiden, Schwann, Virchow
All cells are encased in this barrier. It is an important structure because it determines what enters and leaves the cell.
Describe what this barrier is made out of
cell membrane
Name 3 examples of eukaryotic cells
Animal
Plant
Protists
How many membrane-bound organelles do prokaryotic cells have?
Prokaryotic cells have ZERO membrane-bound organelles.
These organelle structures, primarily used during cell division, can be found in animal cells but are NOT found in plant cells.
centrioles
Who discovered that cells divide to make more of themselves?
Virchow
These structures are found in all cells and are the site of protein synthesis.
ribosomes
What is the function of the chloroplasts and what molecule do they make?
To harvest energy from sunlight and use it to make glucose.
C6H12O6
Which two organelles are strikingly similar to a prokaryote and why?
Mitochondria and/or a chloroplast, because they contain their own DNA
Describe the relationship between the nucleus and the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
The nucleus contains the instructions to make proteins, which travel to the rough ER where proteins are made on its ribosomes, then transported.
What are the three parts of the cell theory?
1} All living things contain cells.
2}All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
3} Cells are the basic unit and structure of life.
What is the endosymbiotic theory and how does it relate to the origin of eukaryotic cells?
Endosymbiosis is when an organism lives inside another organism. In relation to cells, this theory describes how a large host cell ingested a bacteria to create a eukaryotic cell. Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA, showing they came from outside the host cell.
What is the orange organelle and how do you know?
What is the purple organelle and how do you know?
What is the yellow organelle and how do you know?
What is the blue organelle and how do you know?
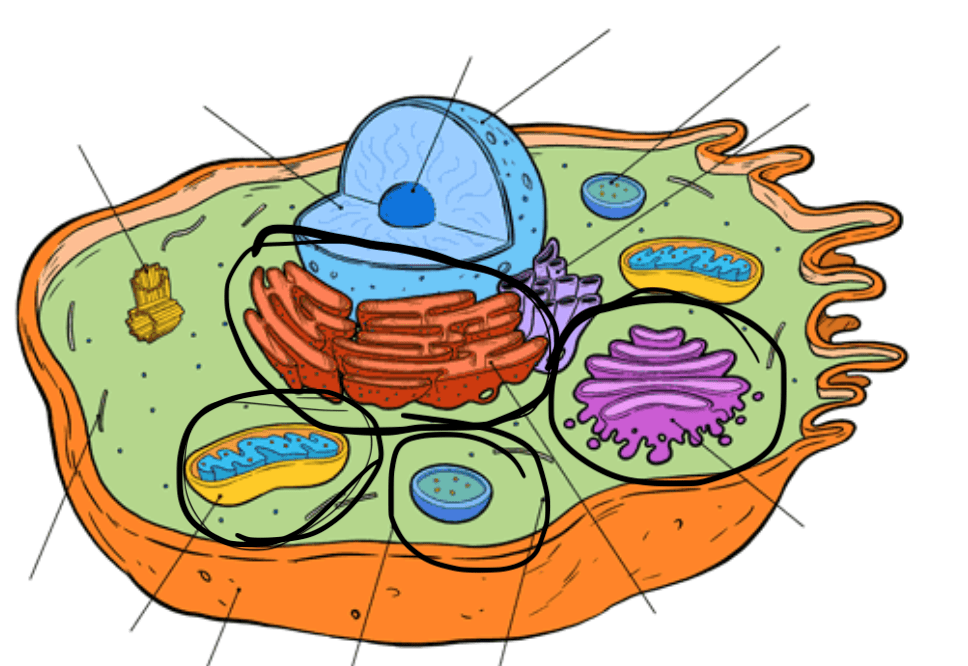
RER
Gogli Body
Mitochondria
Vacuole / Vesicle
It takes much longer for a eukaryotic cell to replicate (make copies of itself) than a prokaryotic cell.
Based on what you know, hypothesize TWO reasons why it takes bacterial cells less time.
Prokaryotic cells are smaller.
Prokaryotic cells have less “stuff”. They have less organelles and are therefore are less complex.
Describe the differences among the vacuoles of plant and animal cells.
In plant cells, the vacuole is a single, central vacuole that is large and stores water.
In animals, the vacuoles are smaller and used to store various substances.