This organelle helps to break down waste and old cell parts.
What is lysosome?
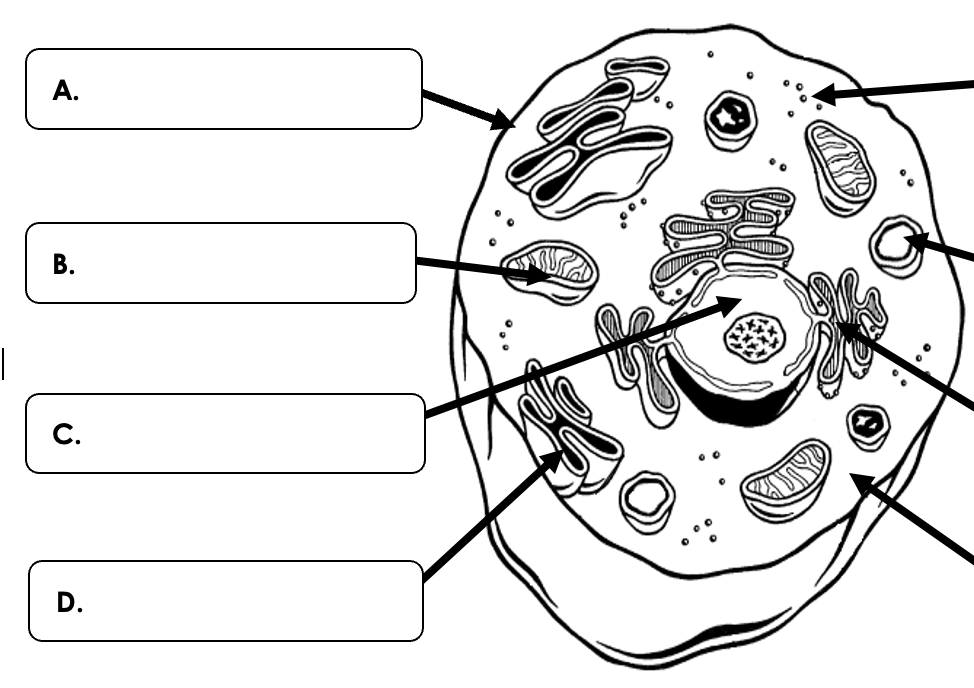
Which organelle is C pointing to?
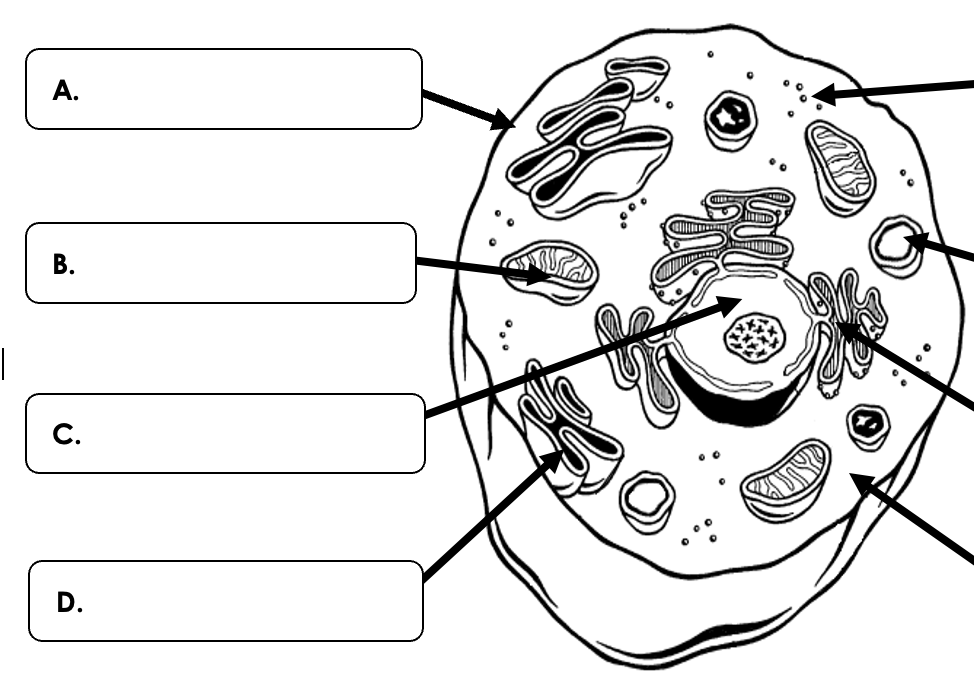
What is the nucleus?
This is a protective organelle that surrounds plant cells.
What is the cell wall?
When using a microscope the image appears to be _________ compared to the slide.
What is flipped upside down or inverted?
Name two organelles that plant cells have but animal cells do not.
What is: a cell wall, chloroplasts, or a central vacuole?
This organelle helps plants (and some other organisms) make their own food using the energy of the sun.
What are chloroplasts?
What organelle is B pointing to?
What is the mitochondria?
What organelles (three of them) could you see in the onion cell under the microscope?
What is the cell wall, nucleus, and cytoplasm?
Plant cells have a large version of this organelle while animal cells have many smaller versions of this organelle.
What is the vacuole?
This organelle controls the cell.
What is the nucleus?
What organelle is D pointing to? 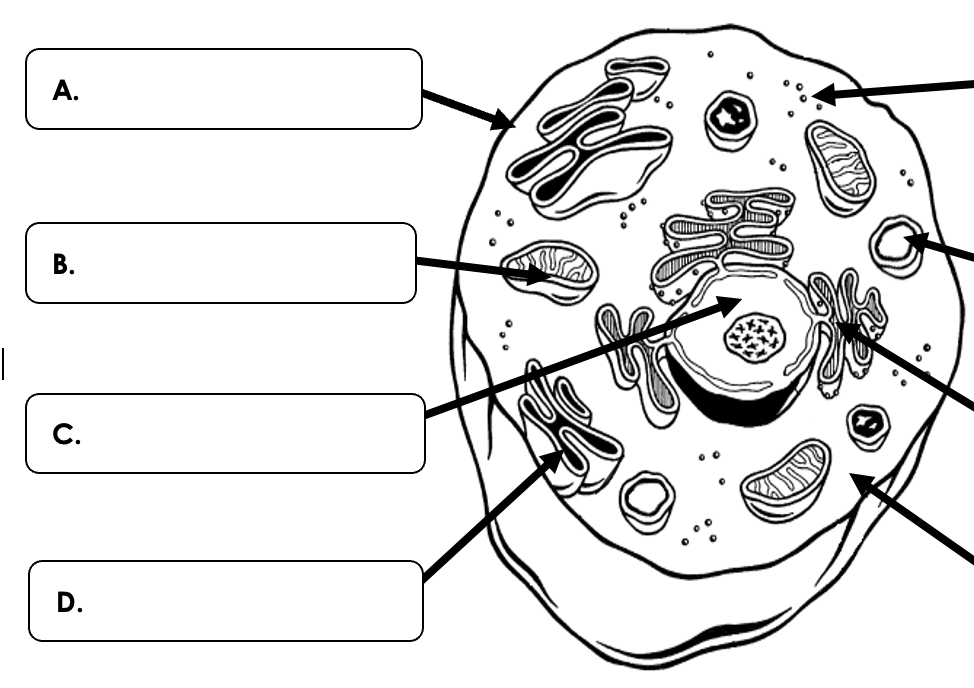
What are the Golgi bodies or Golgi apparatus?
A cell in the mouth where digestion begins would have more ___________ than a skin cell or nerve cell would. (Name the organelle)
What are lysosomes?
A cell in the leaf of a plant would have more ___________ than a root cell. (Name the organelle)
What are chloroplasts?
This organelle helps store water and other things within the cell.
What are vacuoles?
What organelle is E pointing to?
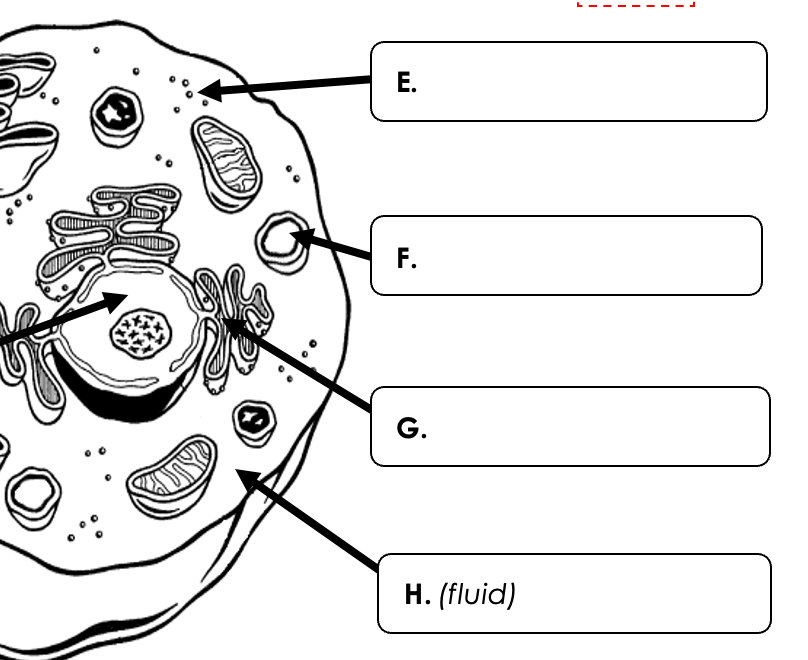
What are ribosomes?
Name the three parts of the cell theory.
What is: 1. All living things are made of cells. 2. Cells come from other cells. 3. Cells are the basic organizational unit of life.
A muscle needs a lot of energy to do its work. A muscle cell would have a lot more ______________ than a bone cell or skin cell. (Name the organelle)
What is mitochondria?
This is where ribosomes are made in the cell (be specific).
What is the nucleolus?
What organelle is G pointing to? (Notice there are ribosomes attached)

What is the endoplasmic reticulum?