The DNA is in the nucleus of this type of cell.
The protective, semi-permeable layer protecting the cell.
Cell membrane
Nucleus
The brain of the cell.
Directs the cell's activities.
Contains the genetic material (DNA, Chromosomes)
If the cell were a business, this organelle would be the CEO.
Nucleus
What is #9?
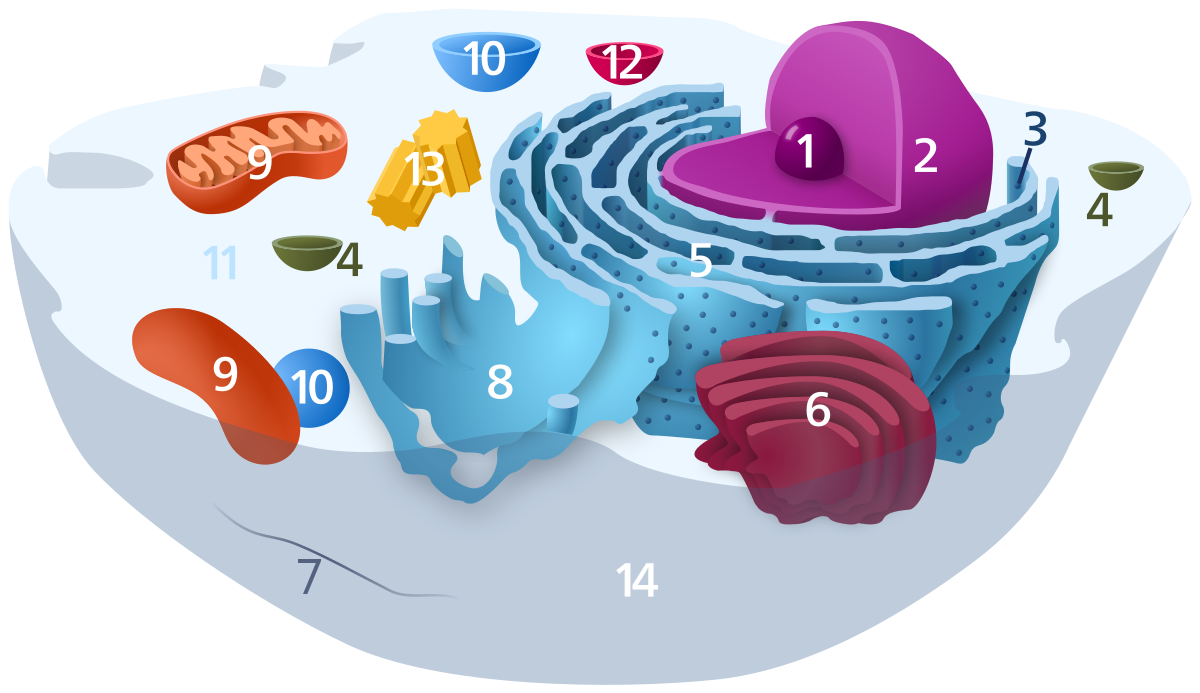
Mitochondrion
This type of cell has no membrane-bound organelles.
Prokaryotes
This organelle traps sunlight for photosynthesis.
Chloroplasts
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell.
Convert food into energy that the cell can use.
If the cell were a school, these organelles would be janitors.
Lysosomes
What is #6?

Golgi apparatus
In this type of cell the DNA is in the cytoplasm.
Prokaryotes
This is where proteins are made.
Ribosomes
Vacuoles
Stores food, water, wastes, etc.
Much larger in plants.
If the cell were an amusement park, this organelle would be the gates/fences.
Cell membrane
What is #8?

Smooth ER
This is the largest group of prokaryotes.
Bacteria
Site of lipid synthesis
Smooth ER (endoplasmic reticulum)
Golgi apparatus
Make, process, and package proteins.
Receives proteins and materials from the Endoplasmic Reticulum.
If the cell were a city, this organelle would be the post office.
Golgi apparatus
What is #10?

Vacuole
Ribosomes are in this type of cell.
Both Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
Structure found in plant cells that is made of cellulose.
Cell wall
Peroxisome
Detoxifies and metabolizes lipids.
If the cell were a construction site, this structure would be the scaffolding.
cytoskeleton
What is #13?

Centrioles