What are the four macromolecules?
Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, & Nucleic Acids
______________ describes what happens and _______________ describes why something happens
Law describes what happens and theory describes why something happens
What are the 2 main differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex because they have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
Prokaryotic cells are smaller and simpler
What is the main difference between passive and active transport?
Give an example of each
Active requires energy (ATP) and passive is no energy
Passive: water molecules entering a cell through the pores in the membrane
Active: potassium ions entering a cell through proteins in the membrane requiring the use of ATP
How old is my son?
3
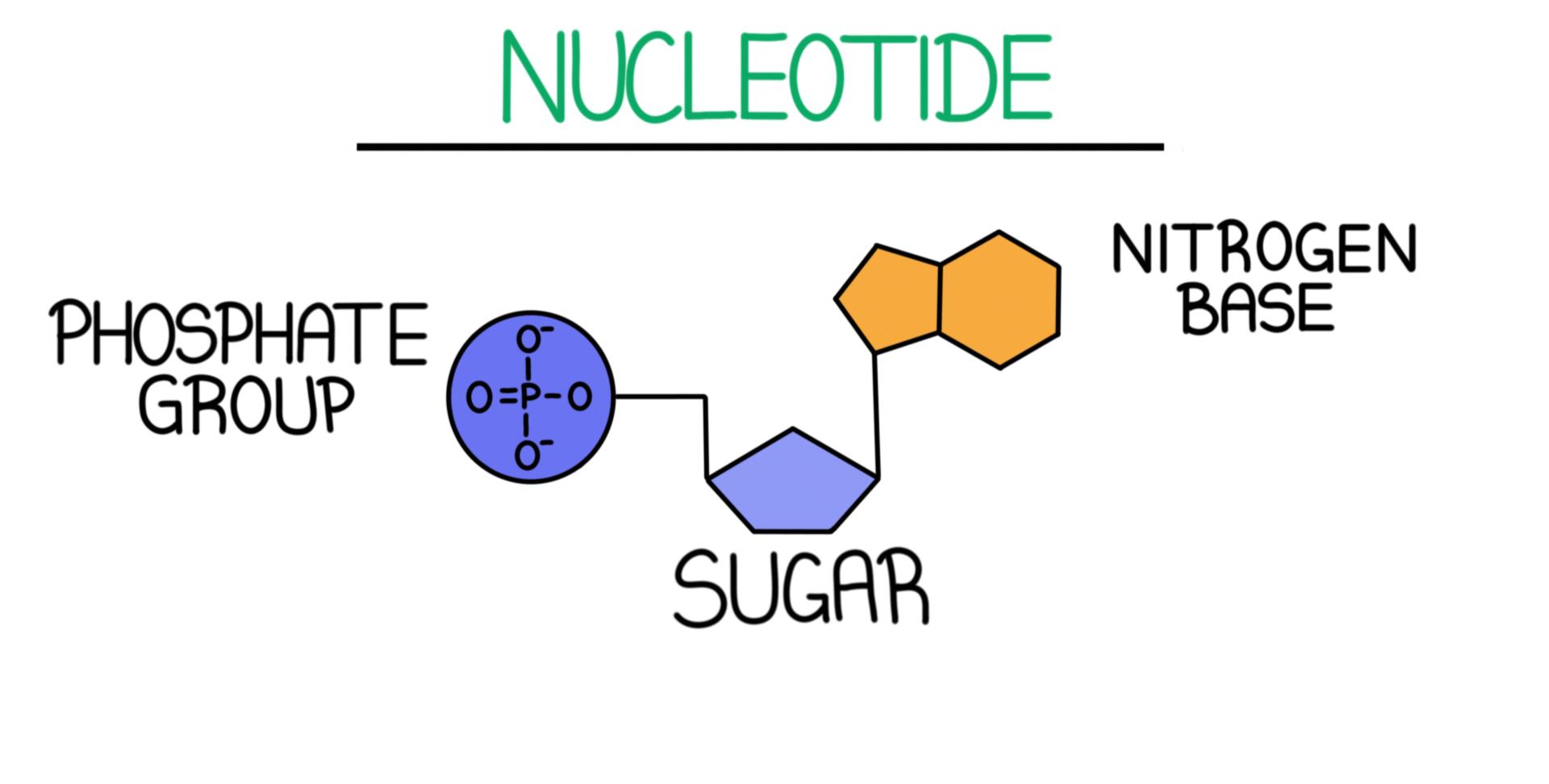
What are the three components of a nucleotide?
Phosphate group
Pentose sugar (ribose or deoxyribose)
Nitrogenous base (A, T, G, C)
What does a theory need to be widely supported amongst most scientisits?
Scientific theories are the culmination of many scientific investigations drawing together all current evidence
Why is the vacuole larger in plant cells?
To store more and exert pressure onto the cell wall to provide structural support
Briefly define endocytosis and exocytosis.
Both are bulk transport - moving large molecules (active transport)
Endocytosis - taking in
Exocytosis - moving out
What's my favorite animal?
Tiger
Give one example of each macromolecule.
Carbohydrate: glucose, cellulose, lactose, glycogen, starch, fructose
Protein: hemoglobin, lactase, insulin, keratin, myoglobin
Lipids: Wax, oil, fats, phospholipids, steroid hormones, triglycerides
Nucleic acids: DNA & RNA
Which microscope type would be best fit to look at a living sample collected from pond water?
Compound light microscope
Describe how the cell theory got developed.
Many different scientists worked together using their observations and evidence to create what we know today as the cell theory
What is the cell membrane made of?
Phospholipid bilayer and protein channels
What was my favorite school subject??
Science
What are the monomers for each macromolecule?
Carbohydrate: monosaccharide (one sugar unit)
Protein: amino acids
Lipid: glycerol & fatty acids
Nucleic acids: nucleotide
Which microscope would be used to view a whole specimen, such as a barnacle?
Dissection Microscope
What are the 3 major differences between plant and animal cells?
Plants have chloroplasts, cell walls, and a larger vacuole
Also, plant cells are fixed shape and animal cells have irregular shape
What are the three types of passive transport?
Simple diffusion, Facilitated diffusion, & Osmosis
What's my favorite holiday?
Christmas
Name one function for each of the 4 macromolecules.
Carbohydrates: short term energy (immediate use)
Proteins: transport of materials, storage, aid in movement, enzymes, structural (hair, nails), regulatory
Lipids: long term energy storage, make up cell membranes, chemical messengers (hormones), protect/insulate
Nucleic acids: genetic information
Which microscope type can only be used if the specimen is not living (dead)?
Transmission Electron Microscope / Scanning Electron Microscope
What are the 3 components of the cell theory?
1. All cells come from pre-existing cells
2. All living things are composed of cells (or single cell)
3. Cells are the basic structural unit of all organisms
Ion pumps, Endocytosis, & Exocytosis
How old am I?
31
