Nucleus
How do plants get their energy?
Photosynthesis, they make their own food
Do viruses have any cells?
No
What is the first level of organization?
Cells
All living things are made of ...
Cells
What organelle can only be found in plant cells?
Chloroplast
(Cell wall is found in prokaryotic cells)
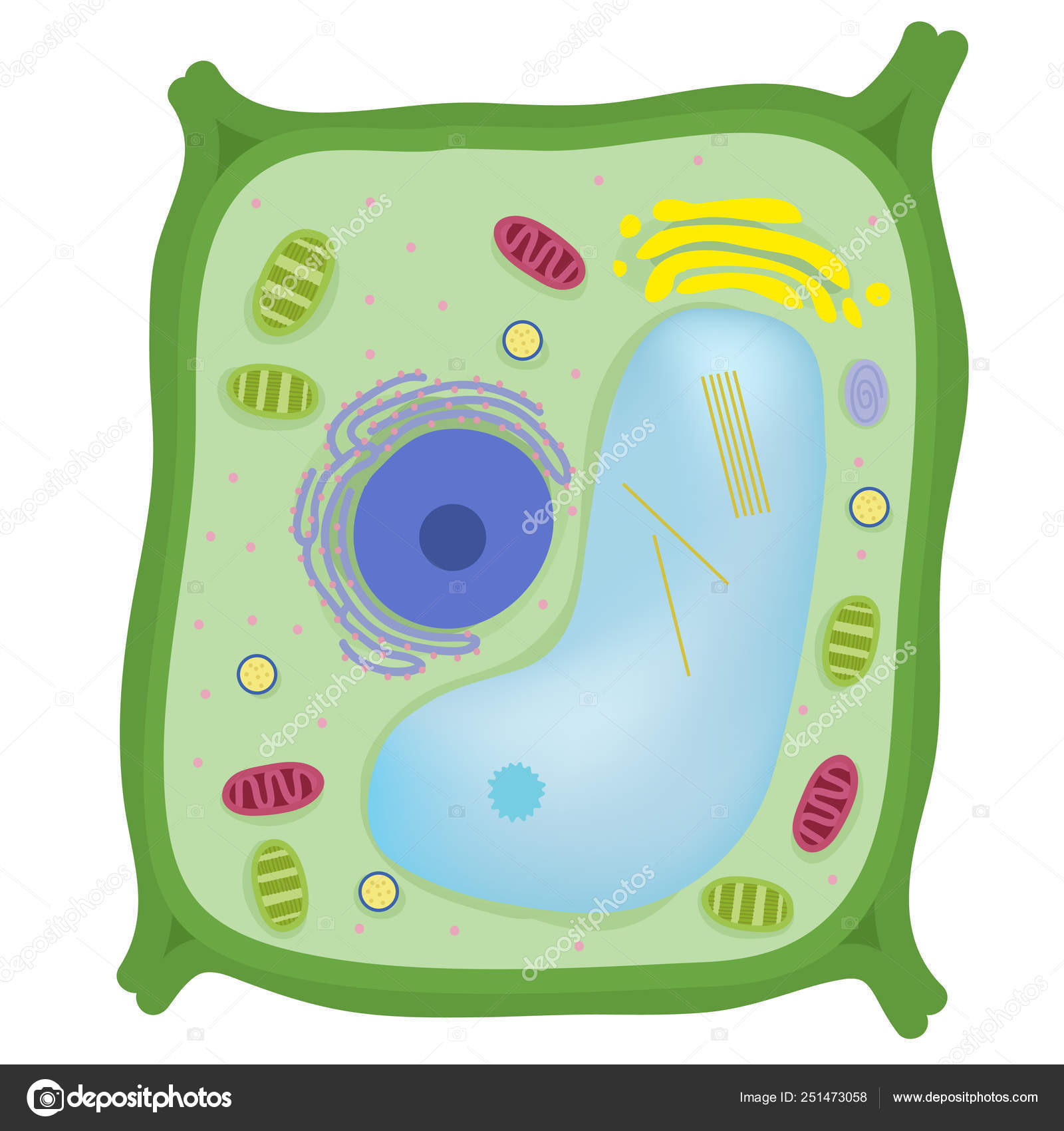
What cell is this?
a single plant cell
Are amoebas uni or multicellular?
unicellular, but are eukaryotic
What is level of organization?
Cells -> Tissue -> organ -> organ system -> organism
What is a hypothesis?
An educated guess to an experiment. That doesn't mean that will happen
What are organelles?
Different parts of the cell that have different jobs to help support the cell.
What eukaryotic cell is unicellular?
Amoebas
If you were looking at a cell, what should you look for if you want to decide if it is prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
the nucleus
Level of organization is in order of what? (complexity)
Least complex to most complex
Where is DNA stored in prokaryotic cells?
Nucleoid Region
Where does nutrients enter the cell?
the cell membrane
What is an example of a prokaryotic cell?
bacteria
If a plant cell doesn't have enough nutrients, what do you think happens to the cell wall?
It loses its ability to remain strong (rigid)
Give a human example of levels of organization
Heart cells -> Heart tissue -> Heart -> cardiovascular system -> human
What is cell theory?
1. All living things are made up of one or more cells
2. Cells are the basic unit of life
3. All cells come from other cells
Cell organelles are located within the ____ of the cell
Cytoplasm
What are the four things prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have in common?
1. DNA
2. Cell Membrane
3. Cytoplasm
4. Ribosomes
What organelle is found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Cytoplasm, cell membrane, ribosomes
Give an example of plant level of organization
Root cell -> Root tissue -> root -> root system -> plant
What is homeostasis?
the process where the organism will try to keep inside conditions the same