How many parts of the cell theory are there?
3
Control center of the cell and also houses DNA
nucleus
The movement of particle from high concentration to low concentration with help
Facilitated Diffusion
Which microscopes can see ONLY non-living cells
scanning electron microscope & transmission electron microscope
All cells come from______________________
pre existing cells
The jello of the cell that keeps the organelles in place within (inside) the cell
Cytoplasm
Movement of WATER from high concentration to low concentration
Osmosis
Light/compound microscope
A cell is the ______________ unit of ___________ and ___________
A cell is the basic unit of structure and function
The protector of the nucleus. It decide what enters and leaves the nucleus
What is cell membrane
What is it called when the cell is filled with water and swells up?
Hypotonic Solution; HYPO=IN
Cell wall & chloroplast
All living things are ________________________________
made up of cells
This organelle is the Stores, modifies and packages proteins
Golgi Apparatus
What would the cell look like if placed in a hypertonic solution
The cell would shrink and shrivel up ; HYPER=GET OUT!
What is the difference between prokaryotic & eukaryotic cells
Prokaryotic cells don't have a nucleus or organelles. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and organelles.
what are the three tenets of the cell theory
All living things are composed of cells
Cells are the basic unit of structure and function
Cells come from pre-existing cells
This organelle is green. It is found in plant cells and can convert energy from the sun into food for the plant cell.
Chloroplast
What is the difference between active transport and passive transport
Active transport is the movement of particles from low concentration to high concentration using energy (ATP) Passive transport is the movement of particle from high concentration to low concentration without energy 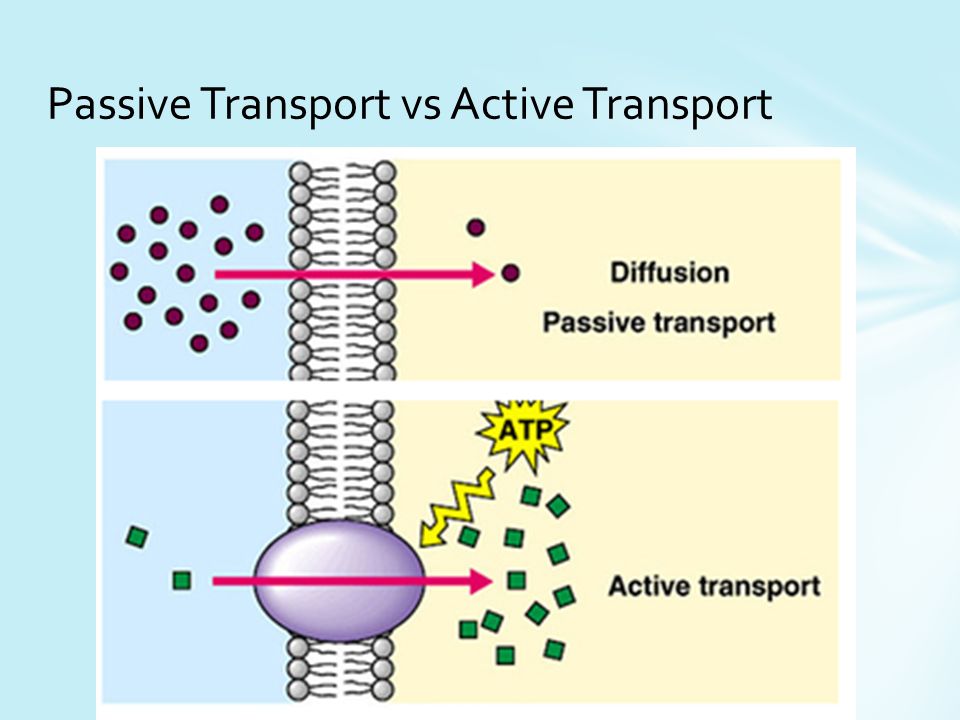
This microscope is able to see 3D images, it has a high magnification and high resolution, and it also allows you to see the inside of cells
Scanning Electron Microscope