The movement of any substance from high concentration to low concentration, with or without a membrane
What is Simple Diffusion?
This is something active transport requires that passive transport does not.
What is energy/ATP?
The definition of osmosis.
What is the diffusion of water?
The two main phases of the cell cycle.
What are interphase and mitosis?
What is prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase?
The movement of any substance through a membrane, from high to low concentration through a membrane protein.
What is Facilitated Diffusion?
What is against the concentration gradient?
Osmosis is a type of [active/passive] transport.
What is passive?
When a cell is in interphase, DNA is in the form of [chromatin/chromosomes]. When a cell is in mitosis, DNA is in the form of [chromatin/chromosomes].
What is chromatin, chromosomes?
The stage of mitosis depicted here:

What is metaphase?
The type of diffusion demonstrated in this picture:
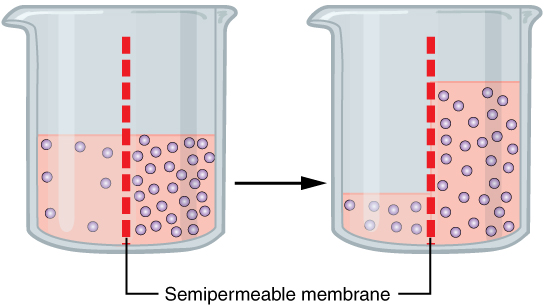
What is Osmosis?
The type of active transport demonstrated in this picture.
What is exocytosis?
Red blood cells placed in a solution with the same concentration of solutes as inside the cell will neither gain nor lose water. This solution is called...
What is isotonic?
This occurs during the G1 phase.
What is cell growth?
The stage of mitosis depicted here:
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Anaphase-58e3d5c53df78c51624bf58c.jpg)
What is anaphase?
During passive transport, particle move from ________ concentration to _______ concentration.
What is high to low concenctration?
The type of transport depicted in this image.

What is molecular transport?
When a plant cell is placed in pure water, water moves into the cell causing it to swell. This happens because the solution outside the cell is...
What is hypotonic?
Before a cell can divide into 2 cells, it must replicate its DNA. The identical copies of chromosomes that separate in mitosis are called…
What are sister chromatids?
The stage of mitosis defined by the cells genetic material condensing into chromosomes, the nuclear envelope dissolving, and spindle fibers beginning to form.
What is prophase?
Which of the following is NOT true about cell membranes?
1) It is selectively permeable
2) It is a fluid mosaic with many proteins and channels
3) Anything can pass through it
4) It controls what goes in and out of the cell
What is 3) Anything can pass through it?
What is
1) Sodium / Potassium Pump to maintain electrical gradient so nerve cells can send signals to muscles.
2) Hydrogen ion pump during photosynthesis to generate ATP
When you get a leech stuck to your leg, you add salt and then the leech will shrivel up and fall off. That is because the salt on the outside is this type of tonicity.
What is hypertonic?
The role checkpoints play in the cell cycle.
What is pauses the cell cycle until key events are completed correctly, ensuring that the cell is ready to move to the next stage. This prevents errors in DNA replication and chromosome segregation, which is crucial for maintaining genetic stability and avoiding diseases like cancer.
The two reasons cells go through division.
What are growth and repair?