Term used to describe the cell "maintaining balance".
Homeostasis
Molecules naturally like to move from a _________ to __________ concentration.
High / Low
Type of transport that DOES require energy.
Active Transport
What is the monomer for proteins?
What macromolecule is this?

Carbohydrate
What macromolecule does this monomer belong to?
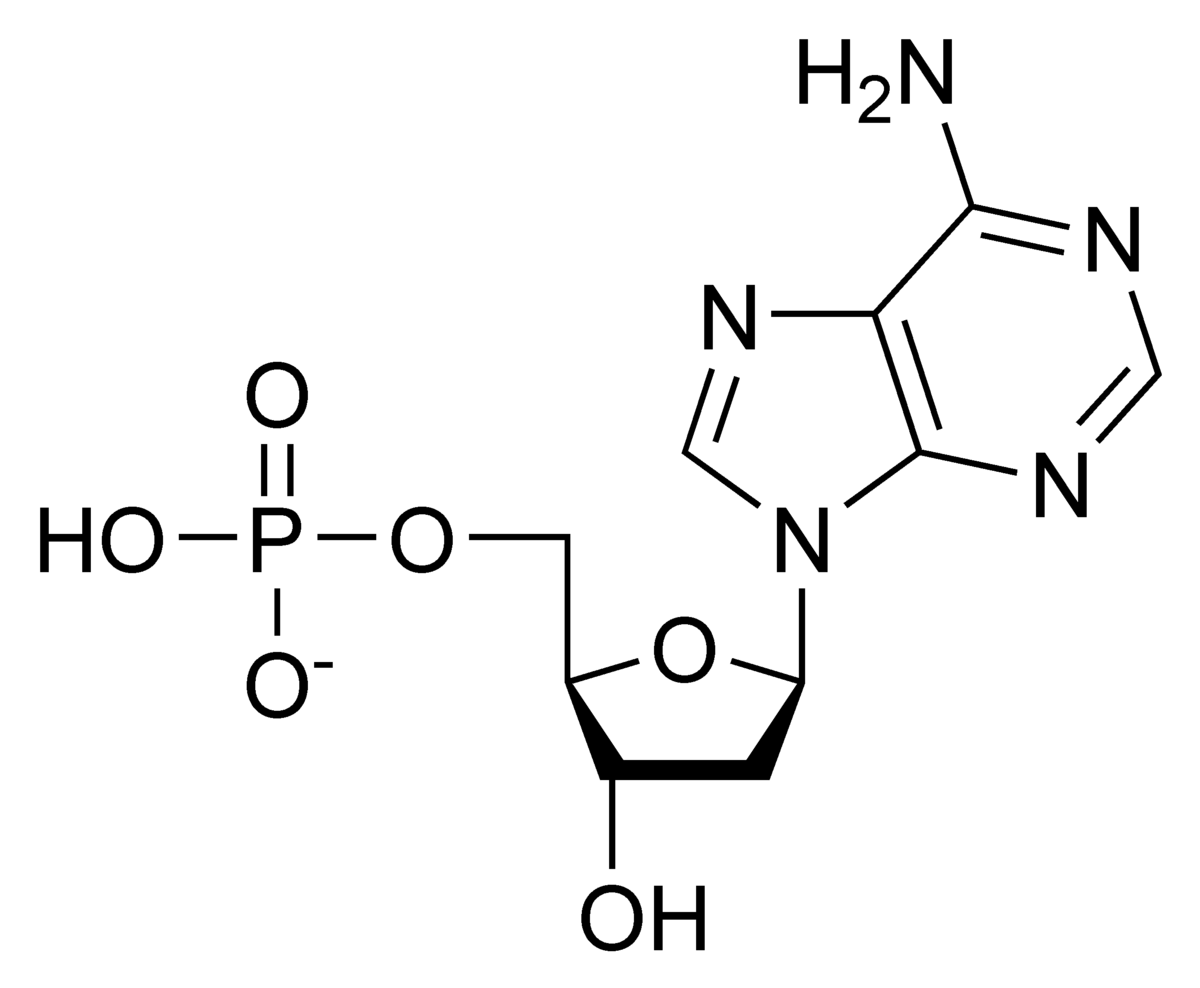
Nucleic Acids
Transport that moves molecules DOWN their concentration gradient.
Passive Transport
Type of transport that deals with water movement.
Osmosis
What type of transport is shown here?
Passive Transport
The function of this macromolecule is to provide quick energy.
Carbohydrates
This molecule serves to provide energy storage and makes up cell membranes.
[DOUBLE JEOPARDY]
Lipids
This macromolecule is only made up of the atoms: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, and Nitrogen
Protein
What type of transport is shown here?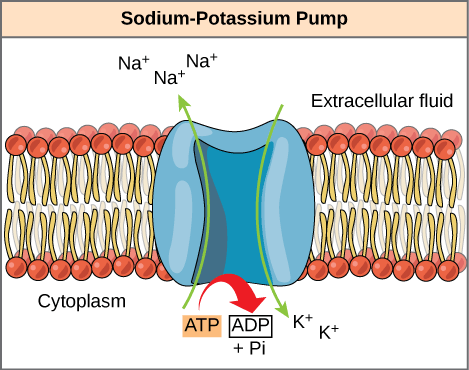
Active Transport
Process when cells get rid of waste by sending it out of the cell.
Exocytosis
Condition where there is more solutes in the cell than in the solution.
[DOUBLE JEOPARDY]
Hypotonic
This type of bond connects amino acids together.
[DOUBLE JEOPARDY]
Peptide bond
This macromolecule has an iconic "ring" structure.
Carbohydrate
The only macromolecule that contains Phosphate.
[DOUBLE JEOPARDY]
Nucleic Acid
Condition where the solute concentrations inside and outside the cell are equal.
Isotinic
Condition where there are more solutes in the solution than in the cell.
[DOUBLE JEOPARDY]
Hypertonic
What process is shown below?
[DOUBLE JEOPARDY]
Endocytosis
What part of an amino acid is interchangeable to make different amino acids?
R group
Term describing how lipids interact with water.
[DOUBLE JEOPARDY]
Hydrophobic
Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine, Thymine, and Uracil are examples of this macromolecule.
Nucleic Acids

