smallest unit of life
the cell
This organelle is essential in a plant cell. It has a rigid outer layer that that protects the cell and helps it stand up.
Cell wall
Are Animal cells prokaryotic or Eukaryotic?
Eukaryotic
This organelle is found in both plant and animal cells. They are the powerhouses of the cell. They are responsible for making carbon dioxide, water, and lots of energy.
Mitochondria
3 phosphates
This type of cell transport does not require energy
passive transport
Identify the organelle(s) that are only found in plant cells.
chloroplasts, cell wall
How is a scientific theory accepted?
needs to be supported by evidence collected by many scientists.
This organelle takes in sunlight in a plant cell and aids in photosynthesis.
chloroplasts
This organelle is found in all animal cells and plant cells. It is a thin outer covering that lets food, water, and gases enter the cell while letting wastes leave.
cell membrane
Daily Double: Explain the difference between the vacuoles in plant and animal cells.
Plant cells have one large vacuole, while animal cells have many small vacuoles.
What ATP stand for?
adenosine triphosphate
In active transport, molecules move from ______ to _______ concentrations.
low to high
Which organelle is called the powerhouse of the cell and does the energy conversions?
The mitochondria
all organisms are composed of
cells
Are plant cells prokaryotic or Eukaryotic?
Eukaryotic
This organelle has one of the most important functions in a cell. It holds DNA which is what makes you have the traits you have.
Nucleus
What type of cell does not have a nucleus?
Prokaryotic cell
Molecule that doesn't have any energy left after energy was released.
adenosine diphosphate
This term means that the cell membrane lets some things in while keeping other things out.
selective or semi permeability
What organelle makes proteins for the cell?
Ribosomes
Scientists A agree that a rock is a non living thing. However, the students don’t believe there is evidence to support the rocks are considered a living thing.
Which cell theory support the scientists?
All living things are made of cells.
Explain the role of the vacuole in a plant cell.
The vacuole stores water, food, and waste. When it is full it keeps the plant standing upright, when it is not the plant may wilt.
Explain the job of the cytoplasm.
Cytoplasm helps hold the floating organelles in place.
Where is DNA stored inside the cell?
The nucleus
What is the process that transforms glucose into ATP?
Cellular respiration
The term used when cells get rid of large molecules like fatty acids and sugars in active transport.
exocytosis
Identify two organelles that are in both plant and animal cells.
mitochondria, vacuoles, cell membranes, nucleus, etc.
Name the 3 points of the cell theory
1. All living things are made of cells
2. The cell is the smallest unit of life
3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells.
How is the food making process different in plant than in animal cells?
Plant cells have chloroplasts to help make their food and animals?
Are animal cells multicellular? True or False
True
Explain the function of the nucleus.
The nucleus is the brain of the cell. It controls all the cells functions and it contains the DNA .
How is this setup called?
If it's just one, what is it called? 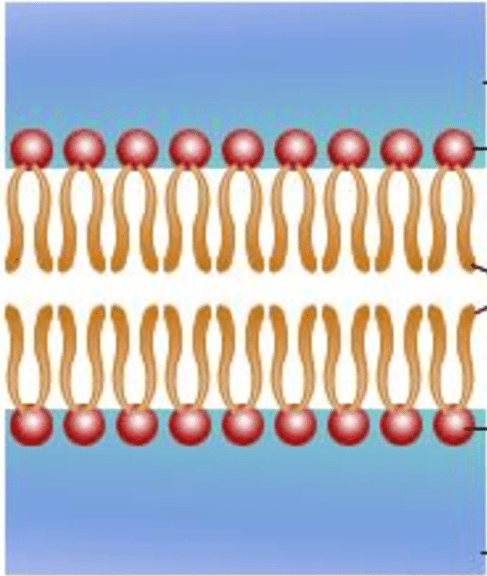
Bilayer
Phospholipid
Mention the three types of passive transport and one example of what they transport through the cell membrane.
diffusion: oxygen or co2
facilitated diffusion: carbohydrates, amino acids or ions
osmosis: water
What type of energy is released during cellular respiration?
ATP Energy