This part of an Eukaryotic cell that contains DNA and controls cell functions.
What is the nucleus?
Where is the DNA in a prokaryote cell?
Cytoplasm
This is the smallest unit of life in all living organisms.
What is a cell?
Animal cells shape
Spherical, Round or irregular
This term refers to the outer layer of a plant cell that gives it structure and support.
What is the cell wall?
The invention of _________________was important for the discovery of cells because they could not see it prior to it being made.
Microscope
This means living things can make more of their own kind. It's how life continues from generation to generation! Some organisms reproduce asexually with one parent and sexually with two parents.
Reproduction
Passive transport does not require_______________.
Something that has all the characteristics of life and is not dead is ___________________.
living
This foundational concept of science would best help solve the problem of scientific papers having lots of mistakes and typos.Scientists should check each other’s work. We checked each other's work and gave suggestions during the playdough lab.This was called a ________________________.
Peer Review
This gel-like substance inside the cell holds the organelles in place.
What is the cytoplasm?
Animal cells contain this organelle, which breaks down waste
A living thing made of one or more cells
organism
Organisms that have more than one cell are called______________________.
Multicellular
Is a virus a living thing?
NO
He gave cells their name. In 1655 he noticed chambers on a sample of cork, a plant, in a microscope which reminded him of the rooms, or cells, used by monks at a monastery.
Robert Hooke
All Living Things Respond to Their Environment. Example is a plat moving towards the sunlight.
Stimulus and Response
The movement of water from high to low concentration through the cell membrane is called _____________.
osmosis
No longer alive This is something that was once alive.
Dead
Is the following an example of a Law, Theory, or Hypothesis?: If a heavier marble is used then it will complete a track faster than a light-weight ball of the same size.
A hypothesis.
Known as the "powerhouse" of the cell, this organelle produces energy.
What is the mitochondria?
What 2 Kingdoms have Prokaryotic Cells?
Archea, Eubacteria
Two or more tissues that work together to perform a specific function form this.
What is an organ?
Bonus: give an example of an organ
This organelle transports materials throughout the cell. Its named because it is covered in ribosomes, giving it a bumpy appearance
Rough ER (Endoplasmic Reticulum)
An organism's ability to maintain stable conditions
Homeostasis
(homeo = same, stasis = status)
Proposed that all ANIMALS are made up of cells.
Theodor Schwann
This is a fancy word for keeping things stable inside! It is a self regulating process to keep your body stable. Your body shivers when it's cold to warm you up, and sweats when it's hot to cool you down. Living things work to keep their internal conditions just right. The cell membrane aids in this with regulating the amount of water in the cell.
Homeostasis
During transport water will move in what direction? Into or out of the cell?
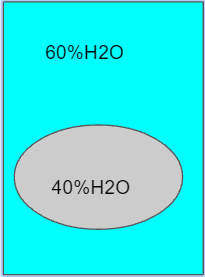
Into the cell.
Something that has never been alive like a Robot, car, or basketball are _________________.
Non living
Are a Law and a Theory equally valid
Yes, they are equally valid.
This part of the cell acts as a protective barrier, controlling what enters and exits the cell.
What is the cell membrane?
Prokaryotes are lacking this large organelle where Eukaryotes store their DNA in..
What is NUCLEUS?
Groups of Cells that work together to do the same job.
Tissue
Rectangle
Everything a living organism does requires this.
They get this by making their own food or by eating/absorbing food.
Energy
A scientist who proposed that all cells arise from pre-existing cells by Cell Division in 1855. He rejected the Spontaneous Generation Theory.
Rudolph Virchow
From a tiny seed to a giant tree, or a baby kitten to a full-grown cat – living things get bigger and change over time.
Growth and Development
Diffusion occurs because substances need to move toward__________________>
equillibrium
Provides shape and protection; found in plant cells, most fungi, bacteria.
Cell Wall
Is the following an example of a Law, Theory, or Hypothesis?: If a heavier marble is used then it will complete a track faster than a light-weight ball of the same size.
Hypothesis
What is Ribosomes?
Read messages from the nucleus to build proteins
List one part that is common between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
-DNA, ribosomes, cytoplasm, cell membrane
Multiple organs working together to do a BIG job.
Organ System
Prokaryotic cells(BACTERIA) have this structure, which acts like a tail or motor to help it move
Flagellum, Flagella
This prokaryote lives in extreme environments, like volcanoes or hot sulfur springs.
Archea
A botanist who studied plants, discovered that all PLANTS have cells in 1838.
Matthias Schleiden,
All of the interactions among molecules and the chemical reactions that occur within an organism to get the ENERGY to maintain life within the Every living thing needs ENERGY to do things like grow, move, and even think!
Metabolism
The movement of oxygen, food, or wastes into and out of the cell from high to low concentration is called_____________.
Diffusion
What is the name of the pigment inside chloroplasts that gives chloroplasts?
Chlorophyll
A team of scientists repeats an experiment several times, uses careful measurements, and shares their results with others for feedback. What is a strength of this scientific study?
It uses repetition, accuracy, and peer review to support the results.
Stores water, nutrients, and waste; large in plant cells, small in animal cells.
Vacuole
Name 3 parts that are in Prokarytoic Cells and Eukaryotic Cells
Cytoplasm, Cell Membrance, DNA, Ribosomes
A small structure within a cell that performs a specific function
What is an Organelle
Organsims that make their own food are called _______________. It means the same thing as producer.
Autotroph
What 4 kingdoms have Eukaryotic Cells
Plant
Animal
Fungi
Protist
What are the two parts of the Cell Theory
1. All living things are made up of one or more cells.
2. Cells are the basic Unit of Structure,Function organization in living things.
3. Cells come from pre-existing cells.
A state of suspended activities where organisms may appear dead or sleeping.
Dormancy
What do you call transport from low to high concentration?
Active Transport
Name all 6 kingdoms
Archea, Eubacteria, Protists, Fungi, Plant, Animal
Is the following an example of a Law, Theory, or Hypothesis?: Sir Isaac Newton found that if the forces acting upon an object are balanced, then the acceleration of that object will be 0 meters per second².
Law of Motion