This organelles function is to capture usable energy from sunlight.
Chloroplast
What is the function of a carbohydrate?

What type of solutions are these?
1) Hypo
2) Iso
3) Hyper
1) Reproduction
2) Repair
3) Growth
How is energy transferred through a food web / chain? What is the "rule" to describe it?
10% rule
This organelles function is to restore homeostasis and control what enters the cell. It's very selective.
Cell Membrane
A scientist is studying sunflowers and determined that offspring receive traits and DNA from their parents from pollen. What type of macro molecule is this referring to?
Nucleic Acids
What is the job of a transport protein? What is an example of a type of transport (active or passive) that uses these?
To move ions and molecules across the membrane, that cannot diffuse through.
Examples: Facilitated (passive), NA+ / K+ pump (active)
What happens during the S-phase of interphase and why is it necessary?
What is the order of steps in cellular respiration?
Glycolysis -> Krebs Cycle -> ETC
This organelle collects and packages cell products into vesicles to be sent out of the cell.
Golgi Body
This macromolecule controls chemical processes in organisms.
Proteins
In the middle beaker, what type of osmotic solution is this? Where will the water flow and what will happen to the cell?
Hypotonic.
Water will flow into the cell because there is a higher concentration of salt inside. The cell will swell and potentially burst.
What is the product of mitosis? How many chromosomes will they have (in humans)?
2 genetically identical cells, each with 46 chromosomes.
Rhizobium bacteria interact with plant roots in the flow of nitrogen through the ecosystem. What is the role of the bacteria in moving nitrogen through the ecosystem
The bacteria convert nitrogen gas into nitrates that the plants can use to make proteins.
This organelle synthesizes proteins.
Ribosomes
What are the 3 things that affect enzyme activity?
1) Temperature (hot v cold)
2) pH (acid v base)
3) Concentration (low v high)
Active transport goes (with) or (against) the concentration gradient from a _______ to a ______ concentration.
Passive transport goes (with) or (against) the concentration gradient from a ______ to a _______ concentration.
Active transport goes AGAINST the concentration gradient from a LOW to a HIGH concentration.
Passive transport goes WITH the concentration gradient from a HIGH to a LOW concentration.
What is at least one similarity and one difference between binary fission and mitosis?
Similar = they are both forms of asexual reproduction.
Different = binary fission is only in bacteria, mitosis is all other multi-cellular organisms. Binary fission is only for reproduction, whereas mitosis is reproduction, repair, growth.
What happens during the light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle) of photosynthesis?
The plant takes energy (sunlight) stored in the light dependent and carbon dioxide to make sugar (glucose!)
Compare and contrast how plant get food/energy vs how animals get food/energy?
Plants capture sunlight and convert it into chemical energy, which becomes their food. Animals have to eat other organisms and release the energy obtained using aerobic respiration.
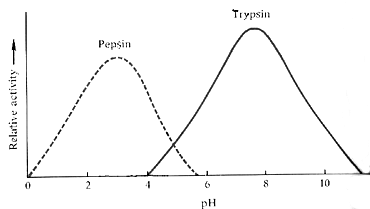 The enzymes Pepsin and Trypsin are listed on the graph above. What pH does Pepsin function best at? What pH does Trypsin function best at?
The enzymes Pepsin and Trypsin are listed on the graph above. What pH does Pepsin function best at? What pH does Trypsin function best at?
Pepsin = low pH, acidic, ~3
Trypsin = average, basic/near neutral, ~8
What is the difference between exocytosis and endocytosis? What types of materials does the cell transport?
Exo = exit
Endo = inside
Large materials, too big for carrier proteins or to diffuse through the membrane
Which organelle helps during cell division? When does it appear in mitosis?
Centrioles, which hold spindle fibers. It appears during prophase.
What does the light dependent reaction produce?
ATP (from sun) and NADPH (e- carrier)