Structures in cells that perform specific functions are called
Organelles
What is the function of the nucleus?
Store DNA
/golgi-apparatus-566ef5873df78ce161a41124.jpg)
Golgi Body / Apparatus
The cell membrane is a double layer of fats. What terms describes this?
phospholipid bilayer
The type of transport that requires energy.
Active transport
A cell that contains no membrane bound organelles
Prokaryotic
Which of the following breaks down organelles that are no longer useful?
Lysosome

Chloroplast
Some things can move through the membrane and some things cannot. This is called
Semipermeable or Selectively Permeable
A type of passive transport that requires the help of a membrane protein.
facilitated diffusion
The picture below is an eukaryotic cell because it contains a
Nucleus or membrane bound organelles
Which structure helps an animal cell maintain its shape?
Cytoskeleton

Endoplasmic Reticulum
The cell membrane contains channels and pumps that help move materials from one side to the other. What are these channels and pumps made of?
To get large particles/molecules from outside the cell membrane to inside, the cell must use
endocytosis
Give one example of a prokaryotic cell.
Bacteria
Which organelle is responsible for cellular respiration? (Break down sugar)
Mitochondria
Centrioles
This part of a cell membrane keeps phospholipids from getting too close together or spreading too far apart.
cholesterol
If a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, it will
shrink
What are the three different parts of the cell theory?
1. Cells come from cells
2. Cells are the basic unit of life
3. All living things are made of cells.
What organelle is a protective barrier found in plant cells.
Cell Wall
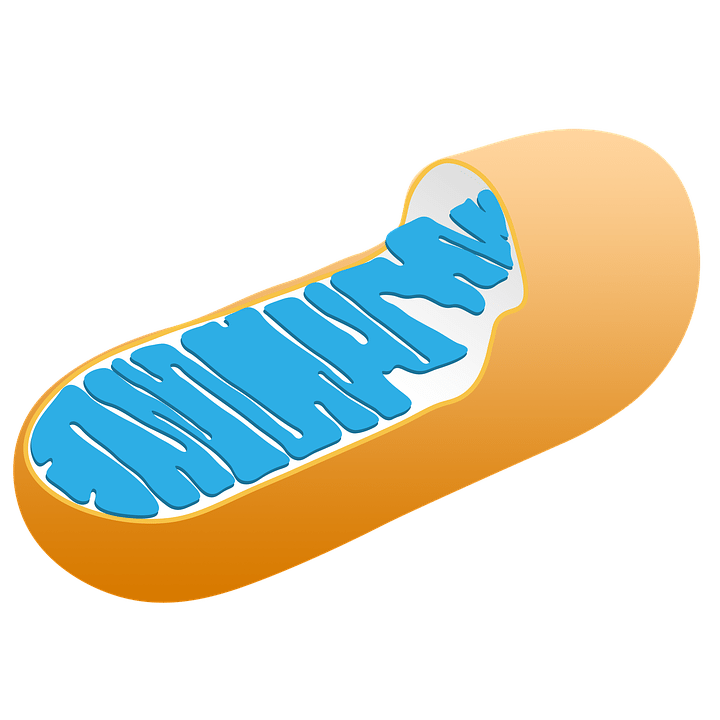

Mitochondria
What happens to the movement of molecules, once dynamic equilibrium is met?
Movement continues at equal rates in both directions.
A cell placed in a hypotonic solution would swell. This is because more ___________ are found _________ the cell.
solutes
inside