What is Gel Electrophoresis?
Technique used to separate DNA fragments based on their size.
What type of chromosomal mutation is this?
Deletion, Inversion, and translocation
Explain the process of the formation of a protein?
DNA --> mRNA --> PRotein
What is the organelle that photosynthesis is taking place?
What is the organelle that cellular respiration is taking place?
Chloroplast and Mitochondria
Use the codon chart in order to find the amino acids of UGC UAC AGA ACC?
Cysteine- Tyrosine- Arginine-Threonine
Health workers collect a nasal swab from a patient to test for COVID-19. They use a machine that targets the virus's genetic material with primers and amplifies small fragments of DNA, which can then be analyzed to see if the virus is present.
What biotechnology are they using?
PCR, Polymerase Chain Reaction
What type of chromosomal mutation is being describe?
In a ____ ,a portion of a chromosome break off and reattaches to another chromosome.
Translocation
A. The rate at which the cells grow
B. The genes expressed within the cells
c. The nutrients available to the cells
d. The age of neighboring cells
The genes expressed within the cells
What is the relationship between reactants of photosynthesis and the products of cellular respiration?
The products of cellular respiration serve as the reactants of photosynthesis
What is a lytic and lysogenic cycles?
Lytic is a bacteriophage reproduces inside a host cell and releases bacteriophages when the host.
Lysogenic is a bacteriophage inserts its viral genome into a host cell's genome.
Which molecular technology are the scientist using to improve the corn crop?
Genetic Engineering
What is often the end result of a inversion mutation? TWO ANSWERS
a. Effects often lead to longevity and increased survivability for the offspring.
b. Missing or extra copies of genes can be made
c. Gametes (sex cells) may have unbalanced chromosomal arrangements.
d. Offspring with this type of mutation often have no negative effects.
b. Missing or extra copies of genes can be made
c. Gametes (sex cells) may have unbalanced chromosomal arrangements.
How the different cell types are formed from a stem cell?
Each cell type expresses different genes at different times.
What type of energy transformation occurs in photosynthesis?
Light energy to chemical energy
Waxy coating of a plant, helps to reduce water loss because if is not water-permeable. This coating is an example of what molecule?
A. Carbohydrate
b. Lipid
C. Nucleic acid
D. Protein
Lipid
A DNA mutation results in a protein that is the same as the initial protein synthesized before the mutation. Which statement BEST explains this outcome?
A. One amino acid substitution does not affect protein synthesis.
B. Different codons can be translated into the same amino acid, so some mutations do not affect protein synthesis.
C. Only mutations that occur at the chromosomal level change protein function.
D. Amino acids have similar functions, so their corresponding proteins are unaffected by mutations
Different codons can be translated into the same amino acid, so some mutations do not affect protein synthesis.
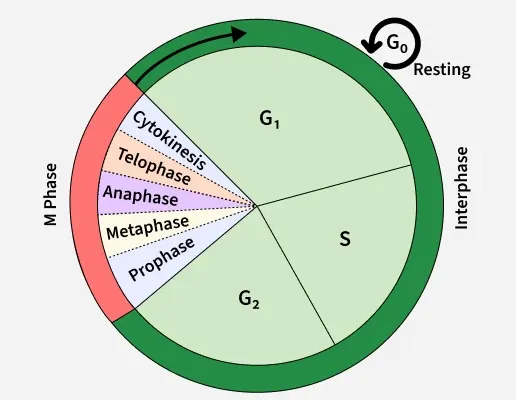 What is happening is the S Phase of the cell cycle?
What is happening is the S Phase of the cell cycle?
During this phase, the DNA is synthesized into identical pairs of DNA molecules.
Cellular Respiration Carbon Dioxide is released to the atmosphere and energy is released from carbon compounds.
Energy is stored in carbon compounds and carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere in photosynthesis.
What are the three types of RNA?
What do each do?
mRNA: Encodes genetic information from DNA during transcription
rRNA: Helps build the ribosomes that are used in translation
tRNA: Carries amino acids to ribosomes during translation.
During a substitution mutation what happens to cause this gene mutation?
During DNA replication, a nucleotide or series of nucleotides are placed in the wrong position.
Myosin is a protein that allow it to pump blood. What factor mostly directly determines the amino acids that are combined to create myosin?
A. The temperature of the cell when translation is taking place
b. The number of chromosomes in a cell
c. The amount of energy that is available in the cell
d. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA
The sequence in nucleotides in DNA
Starch in plants are use for quick energy. What type of biomolecule is this?
Carbohydrates
