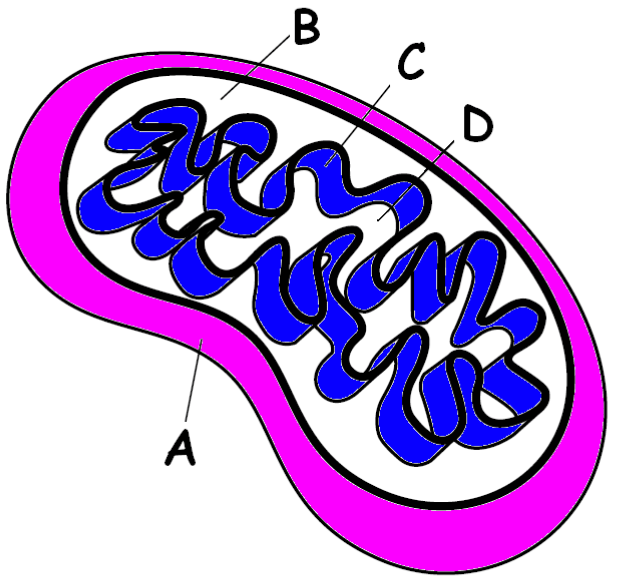
Name what D is.
Matrix
It means "not in air"
Process that happens without oxygen
Anaerobic respiration
3C molecule formed when glucose splits in half
Name this pathway:
Pyruvic acid + NADH --> alcohol + CO2 + NAD+
First step in the breakdown of glucose.
Glycolysis
Name the place in the mitochondria where the Electron Transport Chain is located.
Inner membrane (cristae)
Process that happens with oxygen
Aerobic Respiration
Enzyme that produces ATP as H+ ions pass through it.
ATP Synthase
Name the three stages of aerobic respiration.
Glycolysis
Krebs Cycle
ETC & Chemiosmosis
Number of ATP produced from one molecule of glucose in aerobic respiration.
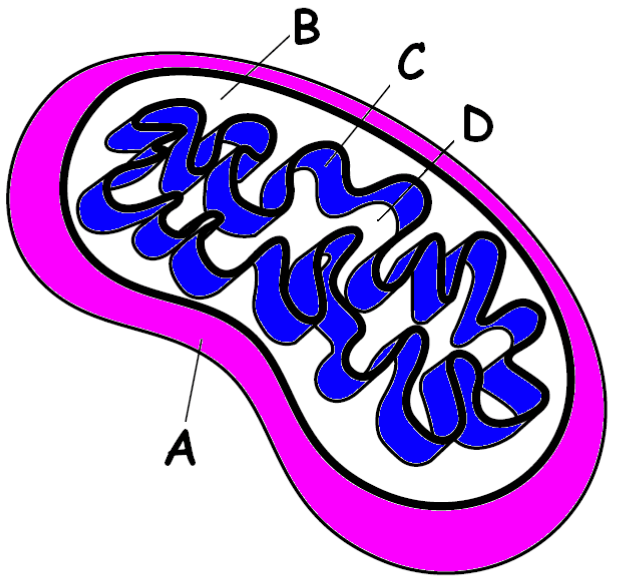
Name what B is.
Intermembrane space
Another name for the Krebs cycle.
Citric Acid Cycle
Molecule that forms when Acetyl-CoA adds its acetyl group to a 4C molecule during the first step of the Krebs cycle.
Citric Acid
Write the chemical equation for cellular respiration.
C6H12O6 + O2 --> H2O + CO2 + ATP
What happens to the carbons in aerobic respiration?
They become CO2 and are released into the atmosphere
Name the place in the mitochondria where the Krebs cycle happens.
Matrix
3C compound before it turns into pyruvic acid in glycolysis
G3P
Molecule that builds up in muscles during intense exercise that forms when cells run out of oxygen.
Lactic Acid
Number of ATP that must be added to get glycolysis started.
2
Molecule that is the final electron acceptor at the end of the ETC to form water
Oxygen
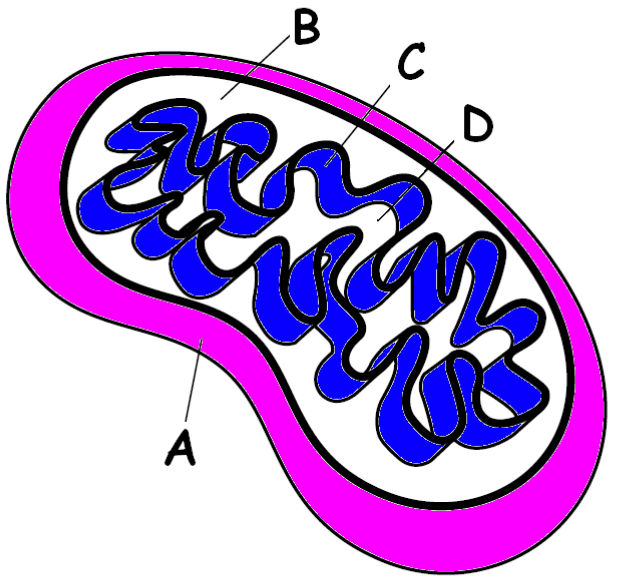
Place where H+ ions build up as electrons move down the ETC.
Intermembrane space
Process by which cells release energy by creating lactic acid or ethyl alcohol and more NAD+ as a byproduct to be returned to glycolysis.
Fermentation
Molecules that act as high energy electron carriers during cellular respiration.
NAD+ and FAD
What happens to pyruvic acid after it leaves glycolysis?
Binds with CoA and enters the Krebs cycle
Where do the electrons come from that enter the ETC?
NADH and FADH2