The first stage of cellular respiration. Glucose is split into two pyruvate.
Glycolysis
The gas that organisms breathe in during cell respiration
Oxygen
The main organelle responsible for cellular respiration
Mitochondria
Anaerobic
The net amount of ATP produced by Glycolysis
2 ATP
The stage where most of the energy is produced
Electron Transport Chain
The reactant that is converted into useable energy.
Glucose
The location of glycolysis in both prokaryotes and eukaroytes
Cytoplasm
When beer, wine, and bread dough is made this type of fermentation product is produced.
Ethyl Alcohol
NADH and FADH2 carry these two the ETC
Electrons
The stage in cellular respiration where water is produced.
Electron Transport Chain
The total number of ATP molecules produced during the process of aerobic cellular respiration
36
 The fluid portion of the mitochondria, site of the Krebs Cycle
The fluid portion of the mitochondria, site of the Krebs Cycle
Matrix
When cheese, buttermilk, saurkraut are made, this type of fermentation product is produced.
Lactic Acid Fermentation
The final electron acceptor of cellular respiration
Oxygen
The stage in which the electron carriers NADH and FADH2 are produced
Krebs Cycle
The product of cellular respiration that is converted by plants into sugar through photosynthesis
Carbon Dioxide
The location of the electron transport chain.
Inner Membrane of the Mitochondria
To win a 60-second footrace like a 400m dash, your body primarily uses this to make energy
In order to produce ATP, the movement of this Ion must take place
H+ (Hydrogen)
The stage where carbon dioxide is produced
Krebs cycle
The oxygen we breathe is converted into this at the end of the electron transport chain
Water
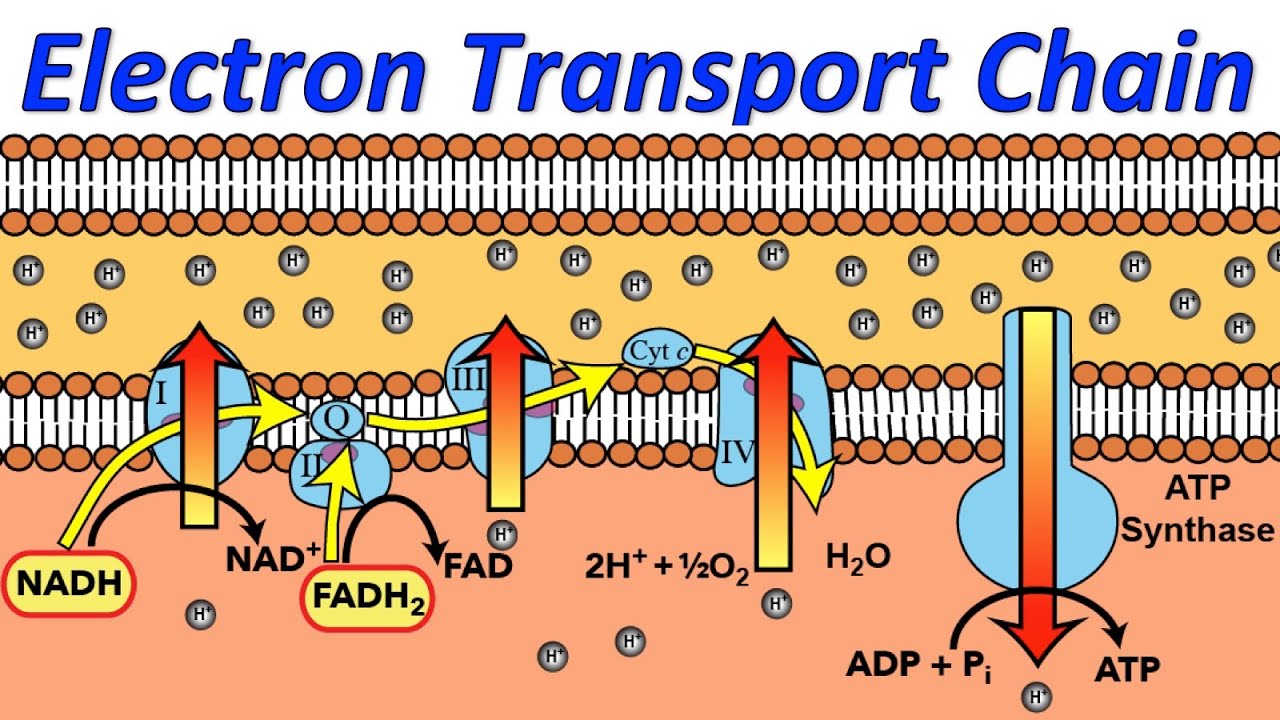
The space found between the inner and outer membrane where H+ ions are concentrated
Intermembrane Space
The purpose of fermentation is to allow for this step of cellular respiration to continue
Glycolysis
The name of the enzyme that produced ATP during the final stage of Cellular Respiration
ATP Synthase