The purpose of cellular respiration
What is to convert sugars/food into energy (ATP)?
What is "another substance"?
Acetyl co-A plus oxaloacetate join to form a 6-carbon compound called this.
What is citric acid (citrate)?
The organelle in which aerobic respiration occurs.
What is the mitochondrion?
The amount of energy it takes to heat up 1kg of water by 1 degree Celsius.
What is a Calorie? (kilocalorie) **Note that the C is capitalized**
Photosynthesis & cellular respiration are complementary. When energy is converted during these reactions, some is lost in this form.
What is heat?
These are the reactants of glycolysis
What are glucose, ADP, NAD+?
The citric acid cycle contains many redox reactions. This is the difference between oxidation and reduction.
What is ...
Oxidation is loss of electrons (hydrogens)
Reduction is gain of electrons (hydrogens)
The two energy-storing compounds (electron carriers) that release their electrons during the last stage of cellular respiration.
What are NADH and FADH2?
What is the 3rd/final phase/electron transport?
Multiple Choice!
During cellular respiration, energy in glucose:
a. is carried by electrons
b. is used to manufacture glucose
c. becomes stored in molecules of NH3
d. is released all at once
What is "a"? Carried by electrons
This is the term for the (non) oxygen requirement for glycolysis.
What is anaerobic?
This gas is required for cellular respiration; this gas is released.
What are O2 and CO2?
Hydrogen ions flow through this membrane protein, which phosphorylates an ADP to make ATP.
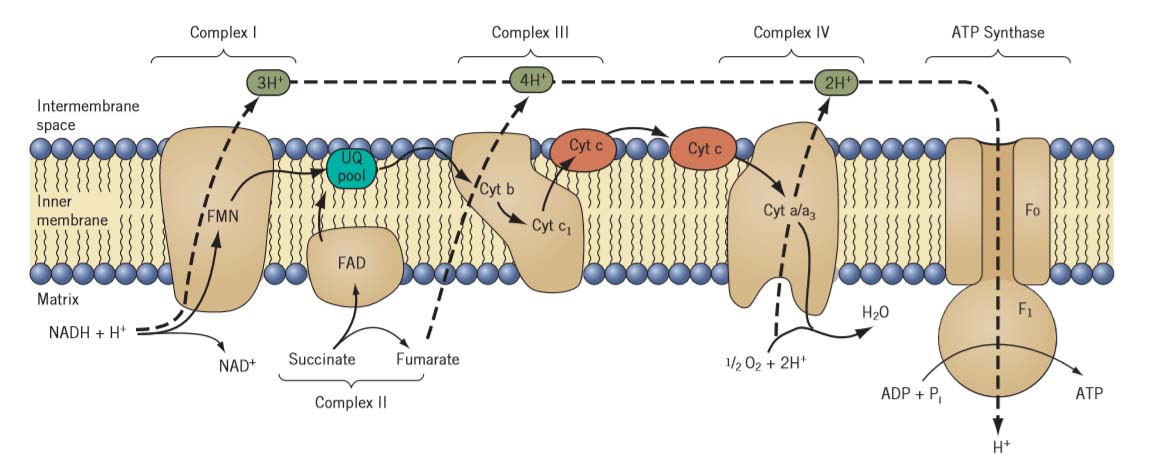
What is ATP synthase?
When H+ accumulate in the intermembrane space, they flow in through this membrane enzyme to form ATP.
What is ATP synthase?
This is the purpose of ATP.
What is an energy source for cells?
Why is aerobic respiration preferred to anaerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration releases more ATP
Pyruvate does not enter the Krebs cycle, this does.
What is acetyl-CoA?
Oxygen serves as the final electron acceptor, picks up two hydrogens and forms this compound.

What is water?
To obtain energy from a starch or glycogen, it must first be...
What is broken down into glucose?
This is the overall equation of cellular respiration
What is:
O2 + Glucose -> CO2 + H2O + ATP (+ heat)
These are the products of glycolysis.
What are pyruvate, NADH, and ATP?
These are the four different products of the citric acid cycle (Kreb's cycle).
What are ATP, FADH2, NADH, and CO2?
The approximate amount of ATP produced via glycolysis, citric acid cycle, and electron transport chain.
If acetyl-CoA failed to form, this part of cellular respiration would not occur.
What is the citric acid (Krebs) cycle?