What is the purpose of Aerobic Cellular Respiration
To generate ATP by oxidizing high-energy molecules (ie Glucose) in oxic (oxygen-containing environments)
Glycolysis
Glyco meaning:
Lysis meaning:
Glyco = Sugar (Glucose)
Lysis = Breakdown/Split
Where does the Krebs Cycle occur?
What compound needs to be regenerated for the Krebs Cycle to occur?
The Krebs Cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria
A 4C compound (OAA) needs to be regenerated for the cycle to continue
What is the purpose of Anaerobic Cellular Respiration
What are the steps of Anaerobic Cellular Respiration
To generate ATP by oxidizing high-energy molecules (ie Glucose) in anoxic (No oxygen-containing environments)
1. Glycolysis
2. Fermentation
What is the longest river in the world?
The Nile river in Egypt!
What are the Four Stages of Aerobic Cellular Respiration?
1. Glycolysis
2. The Intermediate Step/Pre Krebs
3. The Krebs Cycle
4. The Electron Transport Chain
Define Glycolysis
The oxidation (loss of hydrogen ion & electron) of glucose (6C) into two molecules of pyruvate (3C)
Why is the Electron Transport chain referred to as a Staircase?
Bonus 50 points if you can tell me the actual name of the "staircase"
Because electrons that bounce down the staircase produce energy!
in the staircase analogy:
-Electrons (our foot) are passed down the electron transport chain (the staircase) and a small amount of energy is released each time!
--> the actual name of the staircase is the cytochrome complex
1. Bacteria (like Lactobacillus bulgaricus) undergo what type of fermentation?
2. Yeasts undergo what type of fermentation?
3. Explain the role Yeasts play in the production of beer
1. Lactate/Lactic Acid Fermentation
2. Ethanol
3. Beer is usually made from some type of grain (like barley), these grains contain glucose. Yeasts are added to a barrel of boiled barley & spices, this allows the yeasts to undergo Ethanol fermentation.
In the yeast:
Glucose from the barley is converted to pyruvate during glycolysis
Pyruvate is converted to an intermediate 2C compound
- during this process a carbon is cleaved off (produces energy, so NAD+ picks up the H and the electron), which is released in the form of CO2 (this is the gas that builds up inside beer barrel)
The 2C compound is reduced (gains the H+ and electron back from the NADH molecule --> NAD+) into ethanol. This is the alcoholic ingredient in beer that results in drunkenness
- The NAD + is regenerated so glycolysis can happen again!
What's black when you get it, red when you use it, and white when you're all through with it?
HINT: heat
Charcoal! 
How many ATP are produced per molecule of glucose
36 ATP are produced per molecule of glucose, depending on your source you will also see 38.
Draw a flowchart of Glycolysis (Include Net Gain)
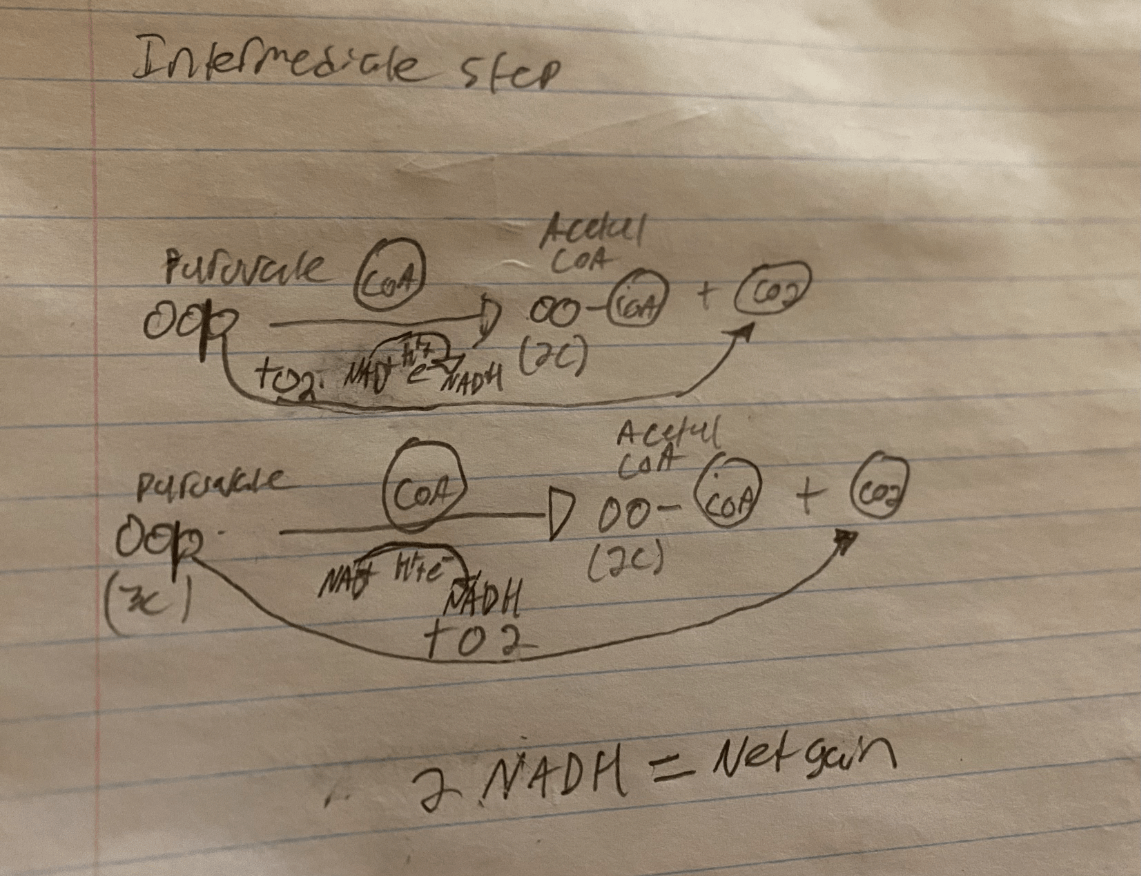
Draw a flowchart of the Intermediate step (Include Net Gain)
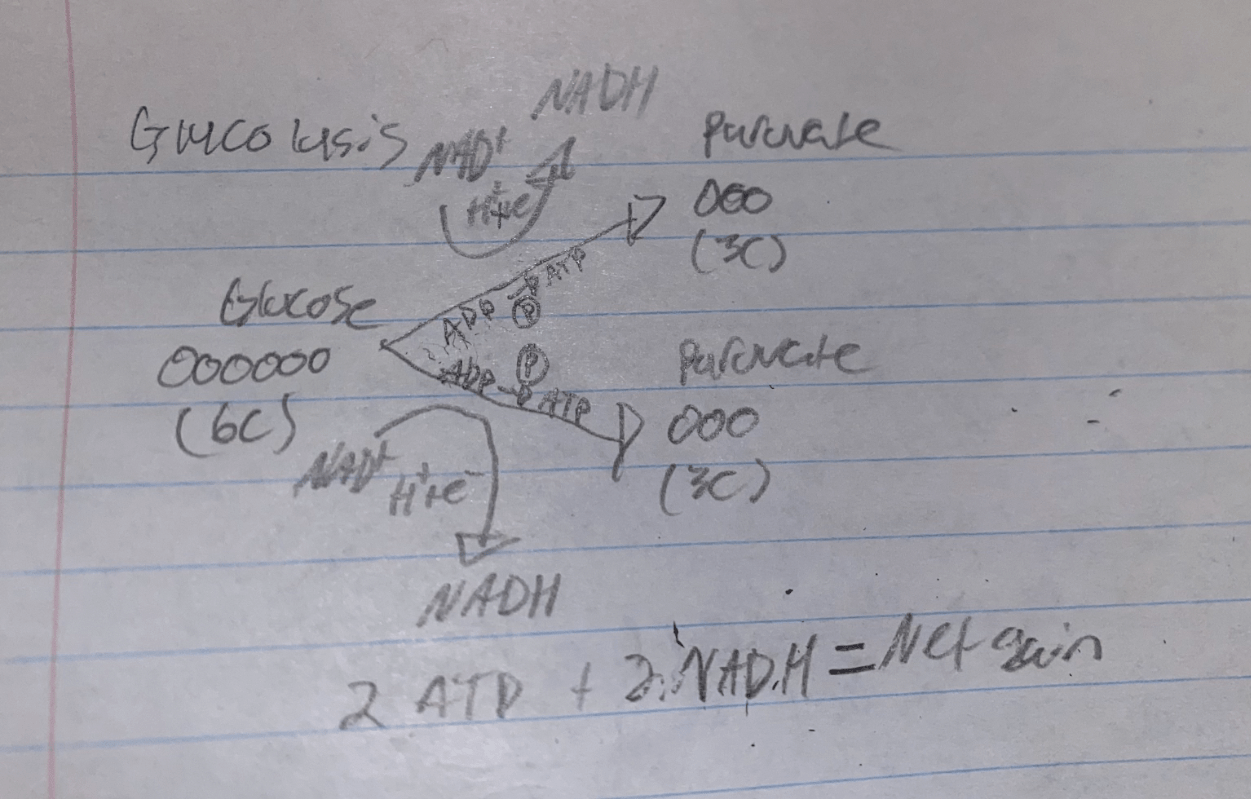
Draw, Label & Explain the stages of the Krebs Cycle (there are 7)
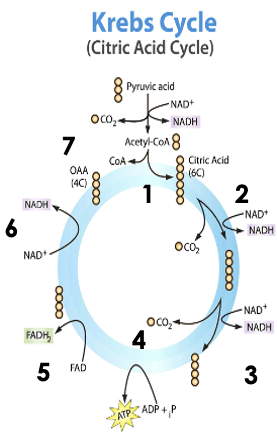
Note this process happens twice (two molecules of Acetyl CoA)
Step 1: Acetyl (2C) + 4C compound from the Krebs cycle → Citric Acid (6C)
Step 2: the 6 carbon compound is stripped of one carbon, a hydrogen and an electron
-The carbon binds to two oxygen atoms to form one molecule of CO2
-The energy in the form of the electron & hydrogen is picked up by a NAD+ molecule → NADH (reducing power)
Step 3: the 5 carbon compound is stripped of another carbon, hydrogen and an electron
-The carbon binds to two oxygen atoms to form another molecule of CO2
-The energy in the form of the electron & hydrogen is picked up by another NAD+ molecule → NADH (reducing power)
Step 4: One Molecule of ATP is Generated
-A phosphate group is attached to an ADP molecule → ATP
Step 5: the 4 carbon compound is oxidized again, however only loses a H+ ion and an electron this time
-The energy in the form of the electron & hydrogen is picked up by a FADH molecule → FADH2 (reducing power)
Step 6: the 4 carbon compound is oxidized a final time and loses one more H+ ion and an electron this time
-The energy in the form of the electron & hydrogen is picked up by one last NAD+ molecule → NADH (reducing power)
Step 7: We have regenerated the original 4C molecule, the cycle restarts!
In animal muscle cells, what happens to the lactate that builds up in the tissues?
After ~1 hour of rest & nutrition after activity, the lactate is then converted back into pyruvate & aerobic cellular respiration continues!
What is the word for the plastic thing on the end of your shoe lace?
An aglet!
What is the first part of the Aerobic Respiration process that would not function correctly if oxygen was absent (be specific)?
The transport of Pyruvate Molecules across the outer membrane of the mitochondria would not function correctly. Thus, the Pre-Krebs/Intermediate Step could not occur!
What are the products of Gycolysis & the Intermediate Step?
What is the overall energy gain from Gycolysis & the Intermediate Step?
Glycolysis
Products:
- 2 Pyruvate Molecules
Energy Gain
- 2 ATP & 2 NADH
Intermediate Step
Products:
- 2 Acetyl CoA & 2 CO2 (exhale)
Energy Gain:
- 2 NADH
Draw, Label & Explain a Diagram of the Hydrogen Ion Gradient in electron transport.
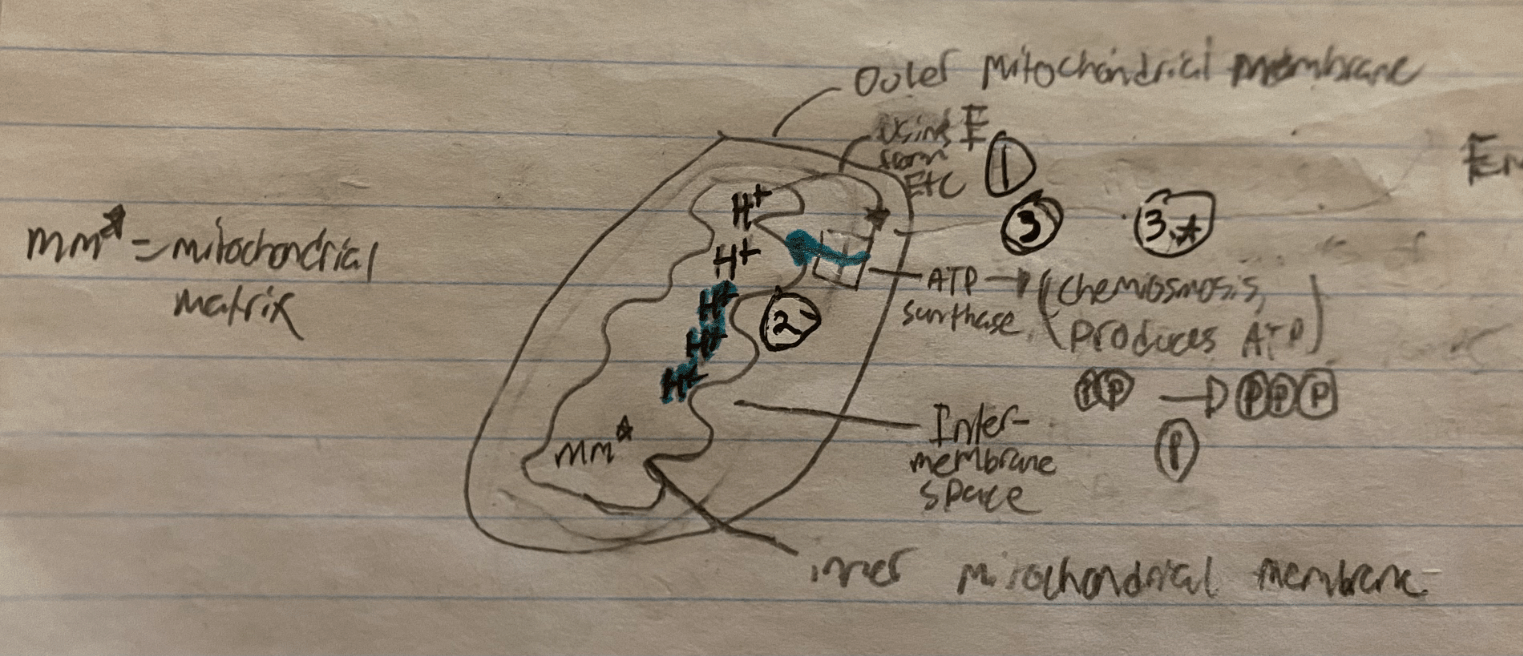
1. Energy from the ETC is used to pump H+ ions across the inner mitochondrial membrane and into the IMS
- This create a hydrogen ion gradient (IMS -->MM)
2. the buildup of H+ ions in the intermembrane space causes H+ ions to flow down the concentration gradient and back into the mitochondrial matrix!
-THEY CAN ONLY RETURN TO THE MATRIX THROUGH ATP SYNTHASE
3. ATP Synthase: Enzyme located in the inner mitochondrial membrane (mainly on the matrix side) that catalyzes the generation of ATP
3a. ATP Synthase uses the energy from H+ ions that flow back into the mitochondrial matrix. The energy from the Flow of H+ ions is used to bind a phosphate group to a molecule of ADP & ATP is produced! → Chemiosmosis
Draw, Label & Explain a flowchart of Lactate Fermentation.
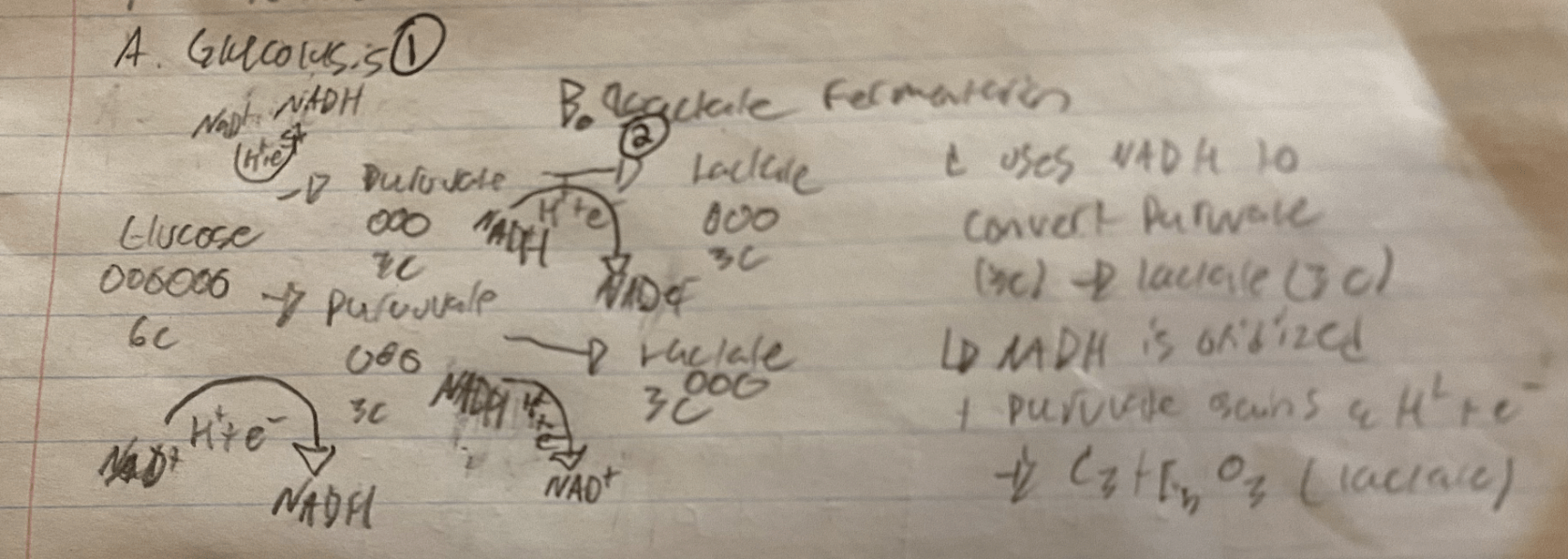
Step 1: A glucose (6C) molecule is oxidized, 2 molecules of NAD+ are reduced (gain hydrogen ion & electron) to 2 molecules of NADH. This splits the glucose molecule into two molecules of Pyruvate (3C).
Step 2: Lactate fermentation Uses NADH to convert Pyruvate (3C) into lactate (3C)
-NADH is oxidized in this process (loses a H++ e-) and Pyruvate is reduced (gains a H++ e-) to lactate
-The products are two molecules of lactate and 2 NAD+ molecules (so glycolysis can occur again!)
Which WNBA team just the WNBA championship?
Bonus 50 points if you can tell me who they played against
The New York Liberty just beat the Minnesota Lynx for the 2024 WNBA championship
Why do large multicellular organisms like humans or cows require Aerobic Cellular Respiration?
Why do certain species of single-celled bacteria only do Anaerobic Cellular Respiration
Multicellular organisms contain more and in most cases more complicated body processes (Hair Growth, Cell Division, Muscle Contraction etc.) which require the production of a lot of ATP. This means most multicellular organisms breathe in oxygen, so their mitochondria can perform their Pre Krebs, Krebs Cycle & ETC to produce enough energy to power their bodily processes.
Certain single-celled bacteria only have to energize processes within a single cell, which means anaerobic respiration will produce enough energy (ATP) to power these species of bacteria.
Draw, Label & Explain (out loud) a diagram of Glycolysis & The Intermediate Step
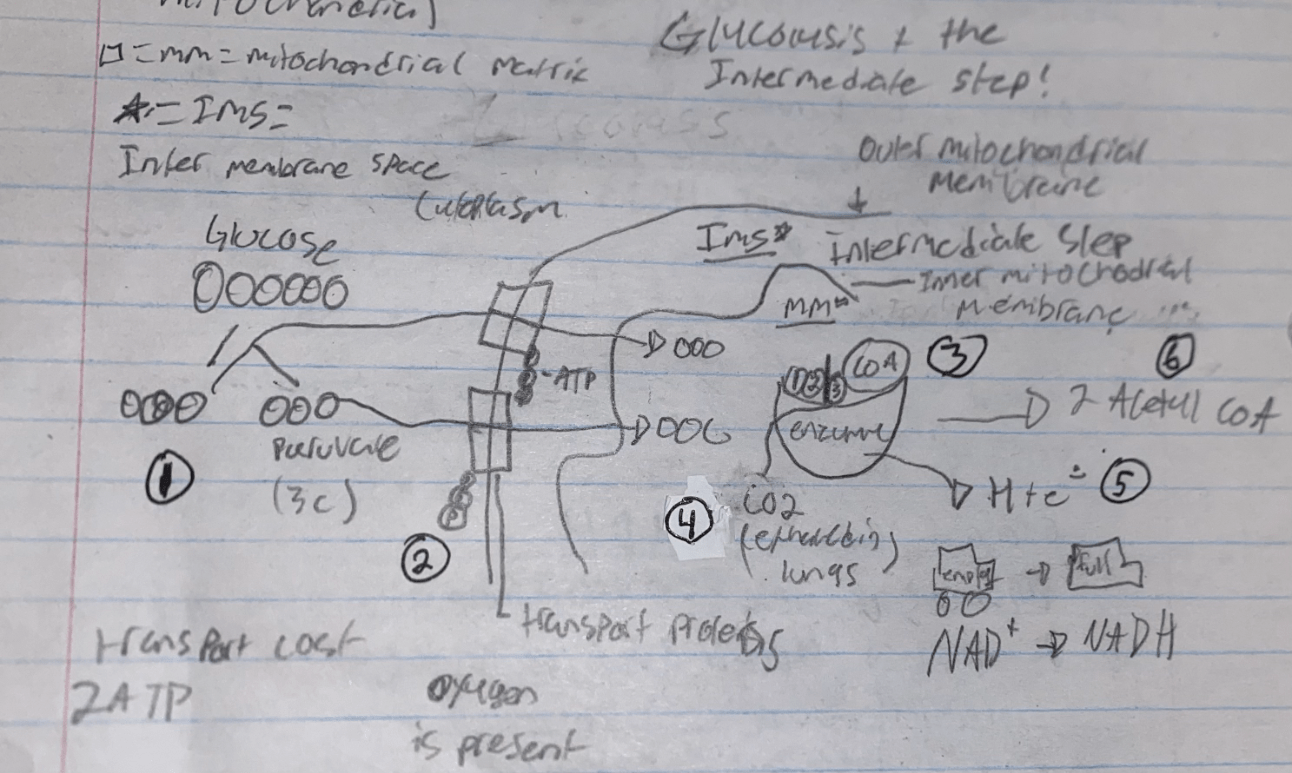
1. A glucose (6C) molecule is oxidized, 2 molecules of NAD+ are reduced (gain hydrogen ion & electron) to 2 molecules of NADH. This splits the glucose molecule into two molecules of Pyruvate (3C).
2. Two molecules of ATP are spent to transport the pyruvate molecules through transport proteins in the outer membrane and across the inner mitochondrial membrane into the mitochondrial matrix
3. Coenzyme A (CoA) attaches to the pyruvate molecules, breaking a carbon, two oxygens, a hydrogen ion & an electron off.
4. The Carbon and Oxygen (2) atoms combine to produce CO2 which we exhale
5. The Hydrogen ion (H+) and the electron (e-) are picked up by a molecule of NAD+ which is reduced to NADH
6. CoA binding to the pyruvate produces two molecules of Acetyl CoA (2C)
Draw, Label & Explain a Diagram of the Electron Transport Chain in electron transport.
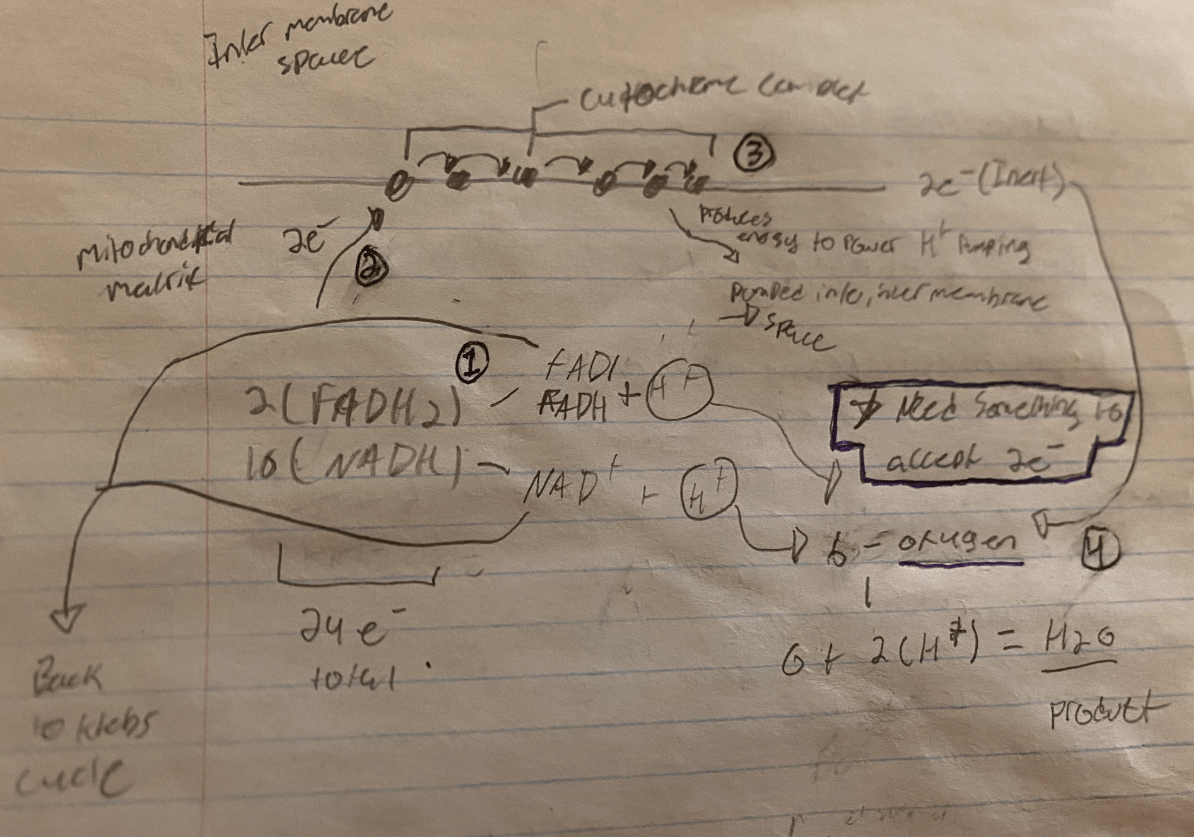
Step 1: Hydrogen & Electrons are lost by FADH2 & NADH
-The products (NAD+ & FADH are sent back the Krebs Cycle), the Hydrogen ions bond to oxygen to produce water!
Step 2: the electrons are passed along the ETC, as the electrons hit each “step” some energy is released
-The energy released is used to pump H+ ions out of the matrix and into the Intermembrane space → creates a hydrogen ion [ ] gradient!
Step 3: the electrons that went down the ETC have now lost energy (inert).
Step 4: The inert electrons are accepted by oxygen atoms (the final electron acceptor molecule in the ETC) that we breathed in! These oxygen atoms also bind to free-floating hydrogen ions and produce water!
Draw, Label & Explain a Diagram of flowchart Fermentation.
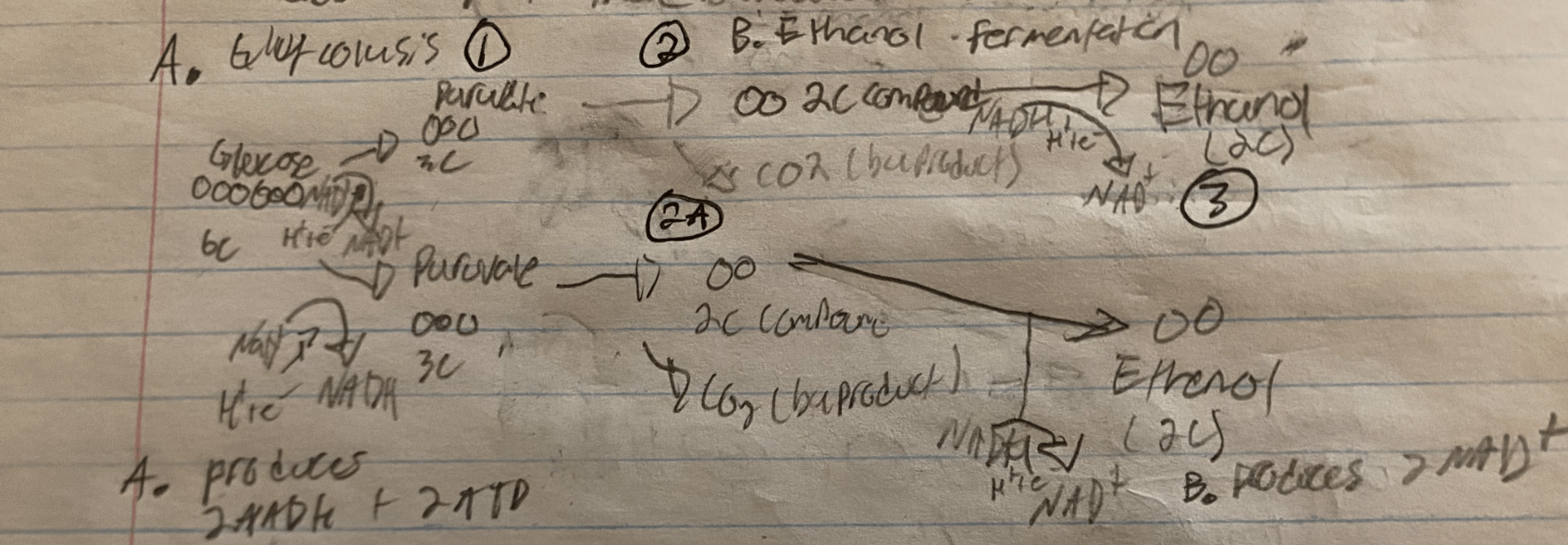 1. A glucose (6C) molecule is oxidized, 2 molecules of NAD+ are reduced (gain hydrogen ion & electron) to 2 molecules of NADH. This splits the glucose molecule into two molecules of Pyruvate (3C).
1. A glucose (6C) molecule is oxidized, 2 molecules of NAD+ are reduced (gain hydrogen ion & electron) to 2 molecules of NADH. This splits the glucose molecule into two molecules of Pyruvate (3C).
2. Pyruvate (3C) loses carbon and is converted to an intermediate two-carbon molecule (2C)
2a. CO2 is produced as a byproduct of this carbon cleaving process
3. The 2C compound is reduced (gains a H++ e- from NADH) and is converted into an Ethanol Molecule (2C)
-The products are two molecules of Ethanol and 2 NAD+ molecules (so glycolysis can occur again!)
Name at least three of the five most dangerous land animals in the world.
Lions, Hippos (Bowling ball), Elephants, Dogs (rabies), Humans