Which cervical vertebrae do not have a body?
C1
What are the routine projections for C-spine?
AP axial, AP open mouth (fuch’s if patient cant open mouth), both obliques, and lateral
What are the unique characteristics of C-spine?
Transverse foramina, bifid spinous process tips, overlapping vertebral bodies
What projection is this?
AP axial projection
Why is the anterior oblique preferred over a posterior oblique?
To reduce thyroid dose
Which cervical vertebrae do not have bifid tips?
C1 and C7
Why is it important to protract the chin when doing obliques?
To prevent the mandible from superimposing the vertebrae
Which of the following is the first compensatory spinal curvature to develop in the young child?
Cervical
What is best demonstrated in this radiograph?

intervertebral foramen
Which projection is taken with a c-collar on?
Lateral
Which oblique best demonstrates the upside of the intervertebral foramina?
Posterior obliques
What type of CR angle is used for the anterior oblique projection of the cervical spine?
15- to 20-degree caudad
What two structures are aligned for the Fuchs method?
Tip of chin and mastoid processes
What is E?
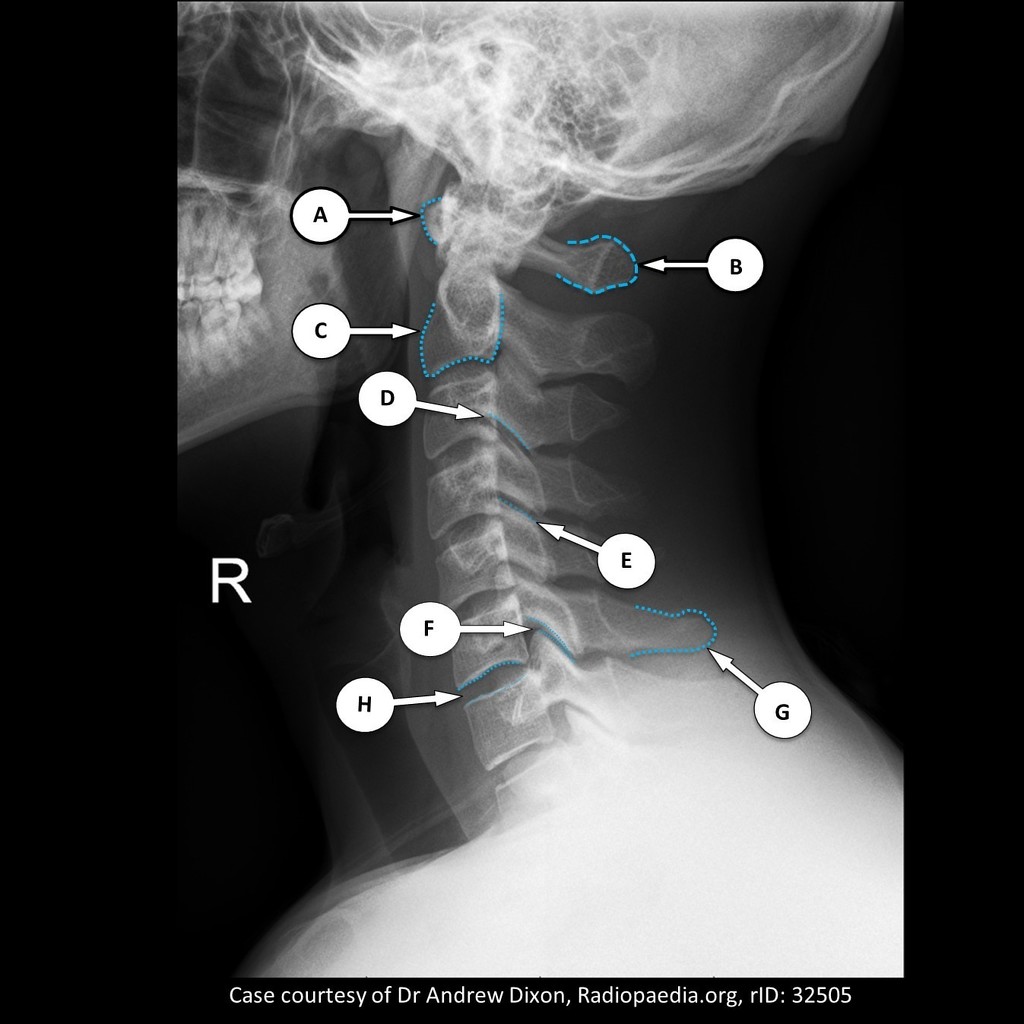
superior articular process
A patient’s radiograph demonstrates a fracture in the dens extending into the lateral masses of C1. What is the name of the fracture?
Odontoid fracture
Which foramen allows the passage of arteries, veins, and certain nerves?
Vertebral foramen
Where is the CR centered and parallel to when performing a Fuchs projection?
CR is parallel to MML and directed to inferior tip of mandible
The zygapophyseal joints are classified as?
diarthrodial
What is 7?

Right Atlanto-axial joint
A fracture that extends through the pedicles of C2, with or without subluxation of C2 on C3 due to hyperextension is termed?
Hangman’s fracture
What is the soft, semi gelatinous inner part of the intervertebral disk
Nucleus pulposus
What additional measure can be taken if the patient cannot depress the shoulders adequately for the cervicothoracic (swimmer’s) lateral projection?
Add a 3-5 caudad angle to the tube
Which projection will project the dens within the shadow of the foramen magnum?
Fuchs method
What is this fracture called?
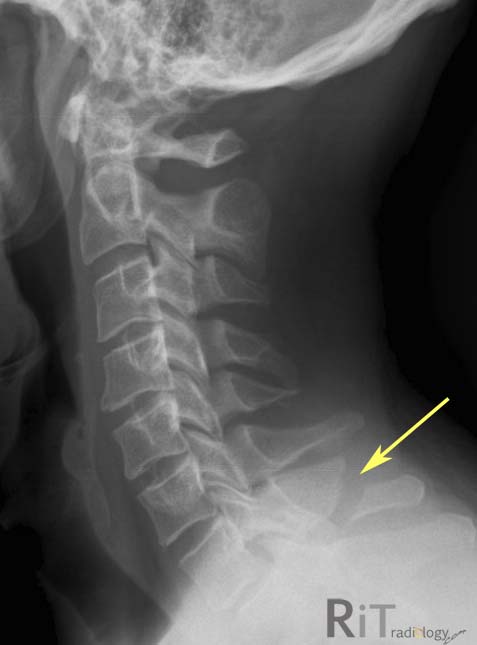
Clay Shoveler Fracture
In the image produced by the Odontoid projection, which cranial structure should be superimposed with the occlusal surface of the upper central incisors?
base of the skull
