This layer of parenchyma cells is covered by a waxy Casparian strip
Endodermis
Compound leaf
This organelle contains chlorophyll
Chloroplast
This metabolic process breaks down sugars like glucose so cells can access & use the energy they contain
Cellular respiration
The term for a negatively charged ion
Anion
This parenchyma layer is responsible for production of lateral roots
Pericycle
This is a type of phyllotaxy in which there are 2 leaves at each node
Opposite leaves
This tissue moves water up the stem, from roots to leaves
Xylem
This process produces all of the oxygen in Earth's atmosphere
Photosynthesis
Magnesium
This organelle in plant roots is responsible for storing starch
Amyloplast
This is the waxy covering of the leaf epidermis
Cuticle
This organelle regulates cell water pressure & pH and is used to store wastes
Vacuole
Along with ATP and H2O, this is a product of cellular respiration
CO2 (carbon dioxide)
The term for molecules with partially charged ends that dissolve easily in water
Polar molecules
In this type of plant, the xylem forms an "X" at the center of the root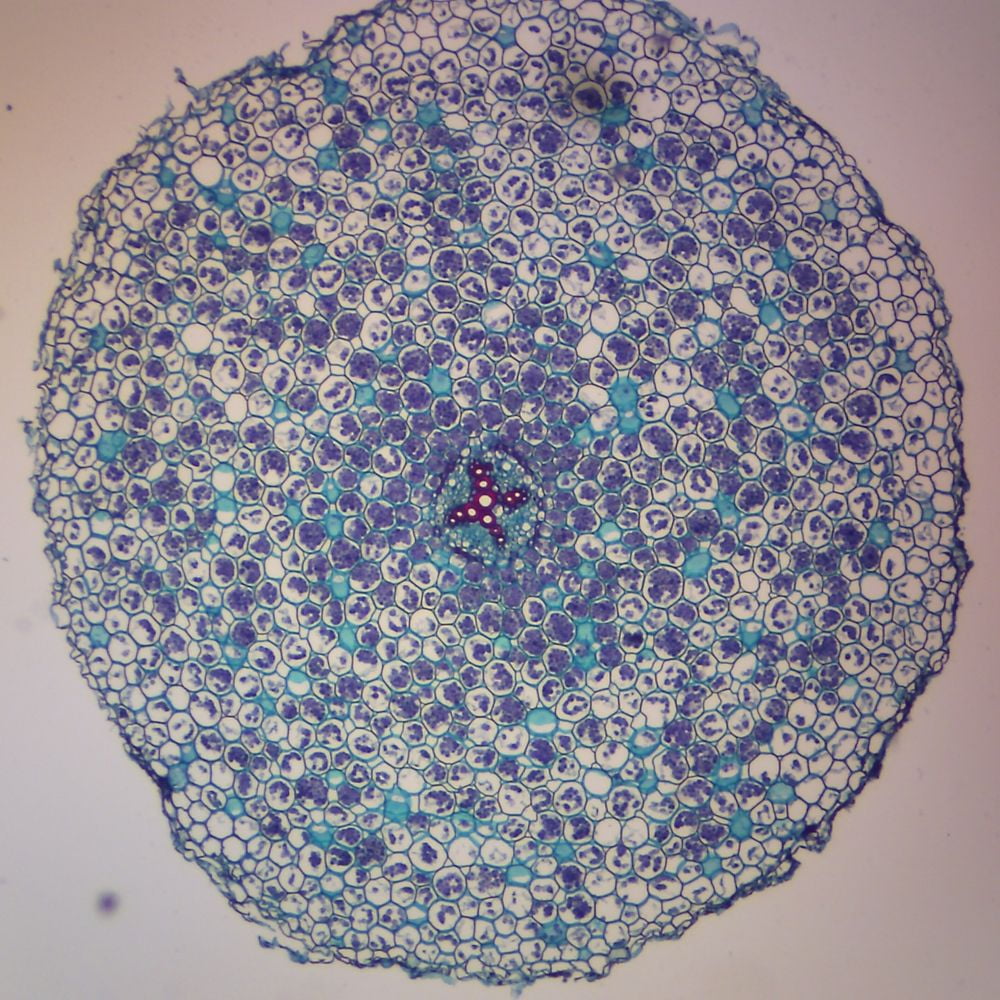
Dicot
These are openings in the underside of leaves that allow for gas exchange
Stomata
This tissue type forms the outer surface of leaves, stems, and roots and provides protection
Epidermis
Along with CO2 and light, this is an input for photosynthesis
H2O
The term for chemical bonds formed by the sharing of electrons
Covalent bonding
This is the smallest mineral particle type in soils
Clay
This is a layer of parenchyma cells surrounding the xylem & phloem in a leaf
Bundle sheath cells
This tissue type has slightly thickened cell walls and makes up the strands in a celery stem
Collenchyma
This type of photosynthesis functions well at high temperatures and high light and is common in monocots from tropical & sub-tropical environments
C4 photosynthesis
A biological molecule that is comprised of a chain of amino acids
Protein