What principle does this violate?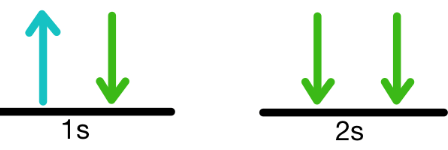
Pauli exclusion principle
What is Zeff? What is the periodic trend?
Zeff (effective nuclear charge) is the net charge experienced by an outer electron after experiencing shielding from the inner electrons. The pull on outer electrons is weaker due to this shielding. Zeff increases from left to right across a period because the number of valence electron increases while inner electrons (shielding) stays the same. It decreases down a group because of increasing electron shields. The value of Zeff is approximately equal to the number of valence electrons.
Identify the following as ionic or covalent:
LiBr
SF6
CaF2
LiBr: ionic
SF6: covalent
CaF2: ionic
Draw the lewis structure for ICl3.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ICl3_LD-56a12a2b3df78cf77268034c.png)
What is the electron geometry and molecular geometry of the following compound: 
EG: octahedral
MG: square planar
What is the condensed electron configuration for the zinc ion?
[Ar] 3d10
The neutral atom of zinc has this electron configuration: [Ar] 4s2 3d10. Remember with transition metals, the electrons are pulled from the s subshell first, as that is the outermost orbital.
Nitrogen, Oxygen, and Fluorine are all in the same row of the periodic table. Knowing what you do about atomic radius, ionization energy, and electron affinity, rank these three elements in increasing order for the 3 different trends.
Atomic radius (decreases across a row): F < O < N (biggest)
Ionization energy (increases across a row): N < O < F (biggest)
Electron affinity (increases across a row): N < O < F (biggest)
Provide the formula for the following names:
sulfate
strontium chloride
diphosphorus pentoxide
Sulfate: SO32-
Strontium chloride: SrCl2
Diphosphorus pentoxide: P2O5
What is the octet rule? What are the exceptions?
The octet rule states that atoms want a full outer shell with 8 valence electrons to be most stable. The exceptions are electron deficiency (Boron), hydrogen (only has 2 electrons), an odd number of electrons, and an expanded shell (anything with a d subshell)
For each of the 5 ELECTRON geometry names we know, provide the hybridization orbitals.
linear: sp
trigonal planar: sp2
tetrahedral: sp3
trigonal bipyramidal: sp3d
octahedral: sp3d2
What is the full electron configuration for the oxygen ion? What is the charge on this ion?
1s22s22p6
Charge is -2.O2-
Rank these in order of increasing size:
F+, F, F-
F+ (smallest) < F < F- (biggest)
Cations are smaller than their parent atom and anions are larger than the parent atom.
What is the charge of iron in the following compound, and how would you write the name of this compound:
Fe2O3
The charge is 3+. Oxygen has a likely charge of 2-, so it is contributing 6-. Iron needs to balance that out, and there are two iron atoms present. 6/2 = 3.
Iron (III) oxide
Draw the Lewis structure for SCN-, including any resonance structures. Identify which structure is best using formal charges.
Hint: the electronegativity of both S & N is 2.5.
There is no preferred structure, both 1 & 2 work. Since the electronegativity values are the same, the -1 formal charge can be on either. Structure 3 isn't ideal because 2 elements have a non-zero formal charge.

For the following compound, provide the electron geometry, molecular geometry, and hybridization around the central molecule. 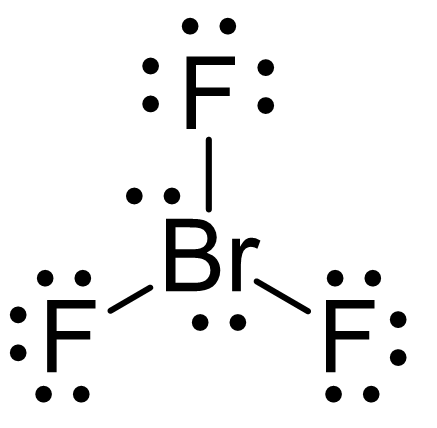
EG: trigonal bypyramidal
MG: t-shaped
Hybridization: sp3d
Draw the full orbital diagram for gallium.
Calcium's 3rd ionization energy is much larger than it's first and second. Why?
Calcium has two valence electrons. Valence electrons are much easier to remove than core electrons, so these come off way easier. The third electron removed from calcium is a core electron, so the ionization energy is much larger.
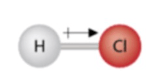
What is the bond type in this compound? Is this compound polar?
EN values: F = 4.0, Br = 2.8 
4.0 - 2.8 = 1.2
This is a polar covalent bond. This is polar because the lone pairs create t-shaped geometry and the polar bonds do not cancel out.
Why do bonds and lone pairs cause deviation from ideal bond angles?
Lone pairs repel the surrounding bonds / electron groups. They take up more space, so they push the other bonds closer together, and alter the ideal bond angle. Multiple bonds cause stronger repulsions than single bonds because they encompass more electrons.
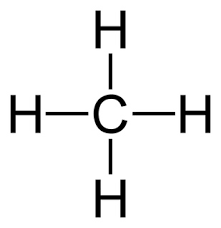
Draw the lewis structure for CH4 and provide the electron geometry, molecular geometry, and hybridization of the central atom.
EG: tetrahedral
MG: tetrahedral (the same because there are no lone pairs)
Hybridization of C: sp3
Why do s orbitals fill before d orbitals? Provide the name of this law, and explain it in your own words.
This is due to the Aufbau principle, which states that electrons fill orbitals by energy level--so lower energy levels fill first. 4s has lower energy than 3d, 5s has lower energy than 4d, etc. so these s subshells are filled first.
Provide the likely charge for the ions of these elements:
Br, Sr, Na
What elements are these ions isoelectronic with?
Br- , isoelectronic with Kr
Sr2+, isoelectronic with Kr
Na+, isoelectronic with Ar
Draw the polarity arrow for this compound, based on your knowledge of electronegativity trends.
Is this compound polar? 
What is the electron geometry, molecular geometry, and hybridization of the central atom in SF4? Draw the lewis structure!
EG: trigonal bipyramidal
MG: seesaw
Hybridization around S: sp3d