& Trends
The density of helium is 0.164 kg·m-3 What is this density in lb·ft-3? 1 kg= 2.20 lb and 1 m = 3.28 ft
A. 0.0102 B. 0.110 C. 1.18 D. 12.7
A. 0.0102
What is the ground-state electron configuration of the manganese atom, Mn?
(A) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 4d5
(B) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d7
(C) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 4p5
(D) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d5 4s2
D
Which of these molecules are non-polar, but contain polar bonds?
a) CO2
b) SO2
c) O2
d) CH2Cl2
a)CO2
A 14.0 g sample of N2(g) occupies what volume at 0°C and 1 atm?
a) 5.6 L
b) 11.2 L
c) 14.0 L
d) 22.4 L
b) 11.2 L
What is the rate law of this reaction?
2H2 + 2NO --> N2 + H2O

rate = k[H2][NO]2
What is the correctly reported mass of water?
 A. 1.3 g B. 1.30 g C. 1.298 g D. 1.2980 g
A. 1.3 g B. 1.30 g C. 1.298 g D. 1.2980 g
B. 1.30 g
Which electron configuration is impossible?
(A) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 4d5
(B) 1s2 2s2 2p6 2d2
(C) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6
(D) 1s2 2s2 2p5 3s1
How many sigma and pi bonds are in the following
molecule?
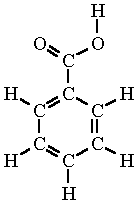
Sigma: 15
Pi- 4
Suppose a gas mixture contains equal moles of He(g) and O2(g). Which is true?
a) The partial pressure of each gas is the same?
b) The partial pressure of He(g) is 4 times the partial pressure of O2(g)
c)The partial pressure of O2(g) is 2 times the partial pressure of He(g)
d)The partial pressure of O2(g) is 8 times the partial pressure of He(g)
a) The partial pressure of each gas is the same
Plots are shown for the reaction NO2(g) ----> NO(g) + 1/2 O2(g) What is the rate law for the reaction?
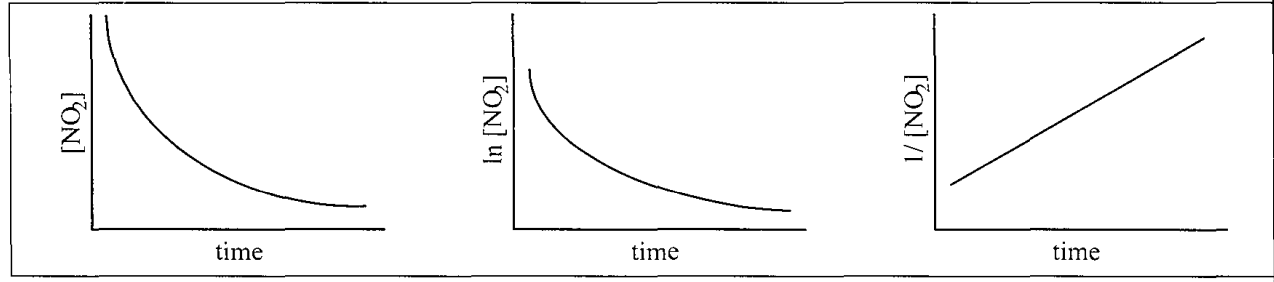
rate = k[NO2]2
If a palladium nanoparticle has a density of 12.0 g·cm3, what is the mass of a nanoparticle with a volume of 1.84 x 10-21 cm3?
A. 2.21 E-20 g B. 1.63 E-20 g C. 6.52 E-21 g
D. 1.53E-22 g
A. 2.21 E-20 g
What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy an orbital labeled dxy?
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4
(B) 2
Arrange CsBr, NaCl, and RbBr in increasing magnitude of lattice energy.
CsBr<RbBr<NaCl
What is the density of F2(g) at 1 atm and 25°C?
a) 0.776 g/L
b) 0.850 g/L
c) 1.55 g/L
d) 1.70 g/L
c) 1.55 g/L
What values does a catalyst change according to this graph?
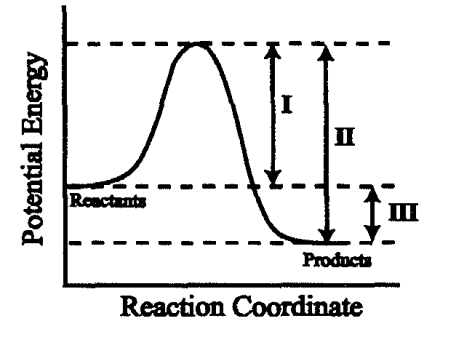
I and II
The speed of light is 3.0x 108 m·s-1. What is this speed in nm·ms-1?
(A) 3.0 x 10-4 (B) 3.0 x 102 (C) 3.0 x 1014
(D) 3.0 x 1020
C) 3.0 E14 nm/ms
Which of these species (is/are) paramagnetic?
Ti4+ Zn Fe2+
Fe2+ only
What is the bond order in the C-O bond in the acetate ion below? (The top C-O bond)

1
Which of the following has the lowest boiling point?
a) CH4
b) CCl4
c) CBr4
d) CI4
a) CH4
When the reaction: CH3Cl(g) + H2O(g) ----> CH3OH(g) + HCl(g) was studied, the tabulated data were obtained Based on these data, what are the reaction orders?

CH3Cl first order
H2O second order
A 4.08 g sample of a compound of nitrogen and oxygen contains 3.02 g of oxygen. What is the empirical formula?
(A) NO2 (B) NO3 (C) N3O2 (D) N2O5
(D) N2O5
The radii of the ions in this series decreases because
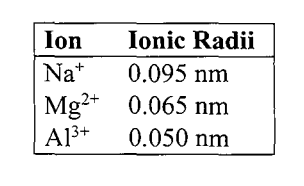
(A) the elements are in the same period.
(B) the effective nuclear charge is increasing.
(C) the atomic radius of Na decreases from Na to Al.
(D) the first ionization energies increase from Na to Al.
(B) the effective nuclear charge is increasing.
How many covalent bonds are in NH4Cl?
4 Covalent Bonds
Under the same conditions of temperature and pressure, hydrogen (H2) diffuses ______ than oxygen (O2).
a) two times slower
b) eight times slower
c) four times faster
d) sixteen times faster
c) four times faster
For the reaction of chlorine and nitric oxide, 2NO(g) + Cl2(g) ----> 2NOCl(g) doubling the concentration of chlorine doubles the rate of reaction. Doubling the concentration of both reactants increases the rate of reaction by a factor of eight. The reaction is...