What is the weakest IMF?
London Dispersion Forces (LDFs)
How is viscosity related to IMF strength?
As IMF strength goes up, viscosity also goes up. (Direct Relationship)
What is a common saying that can most of the time predict the solubility of two molecules?
Like dissolves like
What is the phase change from a solid to a liquid called? What is the phase change from a liquid to a gas called?
Solid to liquid is called melting and liquid to gas is vaporization.
Rank all the IMFs from weakest to strongest
1. LDF
2. Dipole-induced dipole
3. Ion-induced dipole
4. Dipole-dipole
5. Ion-Dipole
6. H-Bonding
What is surface tension and how is surface tension related to IMF strength?
What type of molecules are typically soluble in water? Which type of molecules are typically insoluble in water?
Polar molecules are typically soluble in water and non-polar molecules are typically insoluble in water.
What is the phase change from a solid to a gas?
Sublimation
What are the requirements for H-Bonding?
H-Bond donor (electron deficient H)
H-Bond acceptor (O,N,F)
What is the relationship between volatility, vapor pressure, and IMF strength.
IMF strength is inversely related to both volatility and vapor pressure, so as IMF strength goes up both volatility and vapor pressure go down.
Is the following molecule hydrophobic, hydrophilic, amphipathic, or none of the above?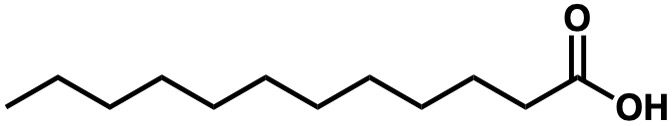
Amphipathic
Are the phase changes from solid to liquid and from liquid to gas endothermic or exothermic?
Endothermic, because you need energy in to change phase.
What is a physical property that affects the strength of LDFs?
Surface area
Out of these two compounds which has the lower viscosity?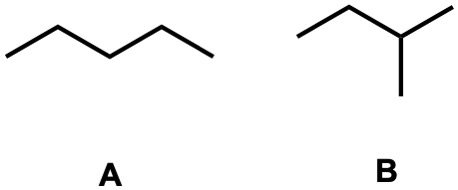
B, because they both have LDFs but the LDFs in compound B are weaker than the LDFs in compound A due to surface area
What are proteins made up of? What is an enzyme?
Amino acids, and an enzyme is a protein that catalyzed biological activity
What is the triple point? What is the critical point? Label them on the figure below. 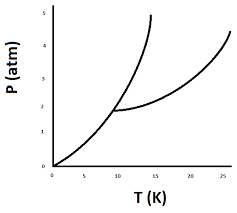
The triple point is when the solid, liquid, and gas phase are all in equilibrium with one another. The critical point is where the liquid and gas phase become indistinguishable from one another.
What are two uncommon atoms that can potentially participate in H-Bonding?
Sulfur and Chlorine
Draw out CH3(CH2)3CH3 and CH3(CH2)3CH2OH. Which will have the higher boiling point and why?
CH3(CH2)3CH2OH will have the higher boiling point because it has stronger IMFs.
What is a hydrophobic pocket?
A hydrophobic pocket within an enzyme is an area of non-polar interactions where there is no strong interaction with water.
You are taking 1.25 L of H2O from -5°C to 122°C. Calculate the energy required to do so.
ΔHfus= 3.5 kJ/mol
ΔHvap= 42.0 kJ/mol
cH2O(s)= 12.25 J/g*K
cH2O(l)= 4.184 J/g*K
cH2O(g)= 3.2 J/g*K
You would need 3,847.28 kJ of energy