This is the equation for formal charge.
What is
FC=VE-LPE-(BE)/2
or
FC=VE-(LPE+(BE)/2)
?
On its own, this bond type is stronger than the other bond type.
*Hint: we are not talking about single vs double vs triple bond.
What is the sigma bond?
This is how we determine the electron geometry and hybridization of an atom in a molecule.
What is the number of electron groups?
These are the types of intermolecular forces.
What are hydrogen bonds, dipole-dipole, dispersive forces, and 'ionic'?
*Ionic is not really and intermolecular force but at the same time it is. There are no covalent bonds in and ionic compound, therefore it isn't a molecule. It is really an electrostatic force because it is held together by opposing charges.
These are the common elements in organic chemistry.
What are carbon and hydrogen?
This is the row of elements where we can begin expanding beyond an octet.
What is row 3 on the periodic table?
This is the number of sigma and pi bonds in a single bond, a double bond, and a triple bond.
How many is 1 sigma in a single bond, 1 sigma and 1 pi in a double, and 1 sigma and two pi in a triple.
This is the number of lone pairs and bonds in a seesaw molecular geometry.
What is the geometry with one lone pair and four bonds?
These are the elements that hydrogen must bond to for hydrogen bonding to occur between molecules.
What are N, O, and F?
*Hydrogen bonding is really just an intense dipole-dipole.
With your partner(s), come up with as many functional groups as you can. The group with the most functional groups gets the points. DOUBLE JEOPARDY if you can correctly draw them. No need to buzz in!
-ane, -ene, -yne, alcohol, ether, aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, ester, amine, amide, halide, phenyl, methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl, butyl, t-butyl, s-butyl, iso-butyl
*YOU DON'T NEED TO KNOW ALL OF THESE->JUST THE ONES YOU LEARNED IN CLASS!!!!!!
This is the rule that never changes, has no exceptions, and must always be followed no matter the molecule.
What is the number of valence electrons?
What is the difference between diamagnetic and paramagnetic?
DOESN'T NEED TO BE IN THE FORM OF A QUESTION
Diamagnetic is where all electrons are paired so the atom or molecule isn't attracted to a magnetic field. Paramagnetic is where at least one election is unpaired so the atom or molecule is attracted to a magnetic field.
This is when the bond angle is less than the expected bond angle.
What happens when the electron groups are unequal about an atom?
This is the characteristic used to determine the strength of intermolecular forces between molecules that only have dispersion forces. Why?
What is molar mass? The reason we use this is because it directly correlates with the number of electrons in a molecule. The more electrons there are, the stronger the temporary dipole, so the stronger the intermolecular force.
Certain compounds can have different structures and therefore different properties yet have the same chemical formula.
DOUBLE JEOPARDY
What are isomers?
Draw the Lewis Structure for oxalate (C2O42-). Include the formal charge on each atom.

Draw the MO diagram for NO. What is the bond order and is it paramagnetic or diamagnetic?
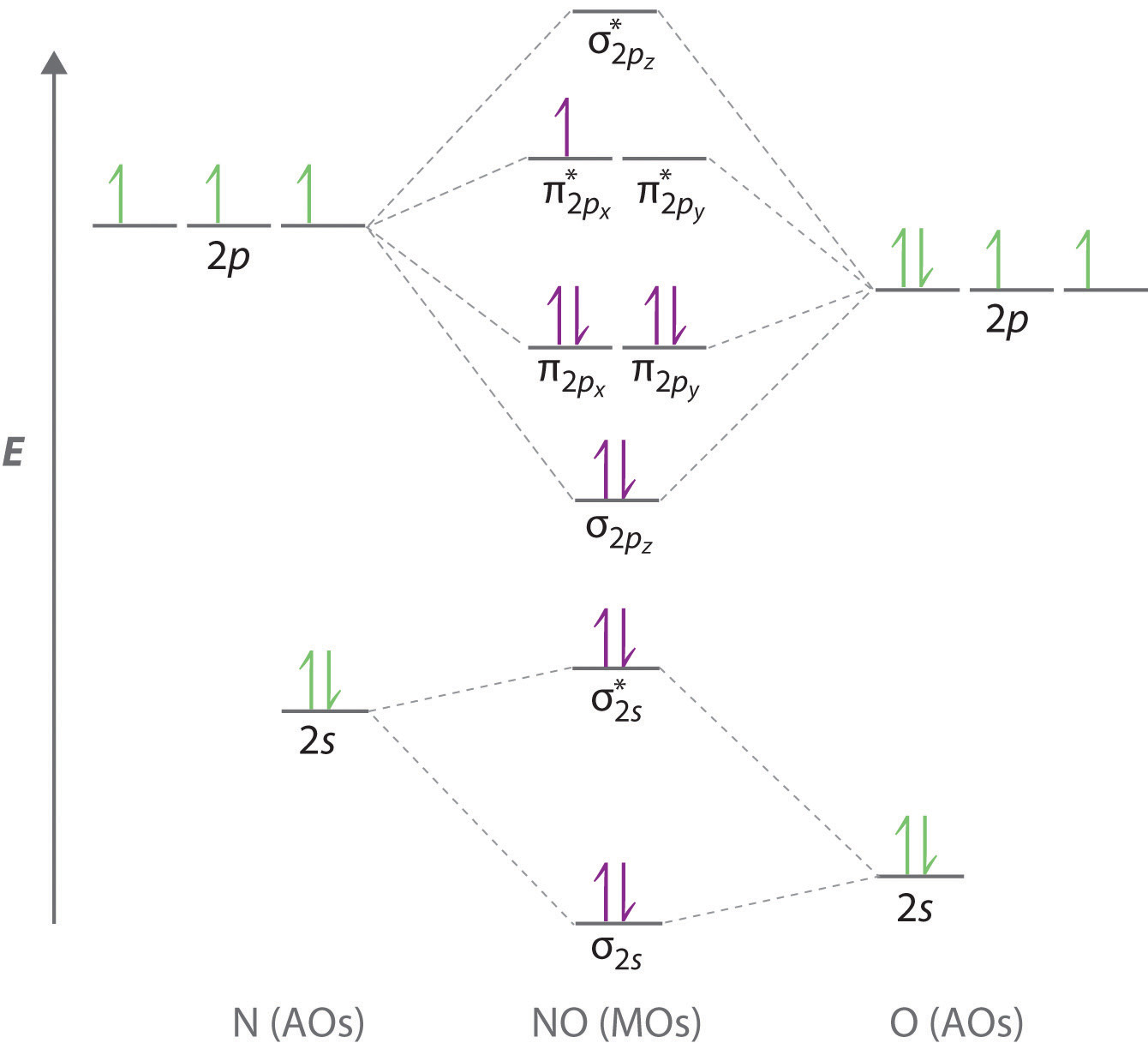
BO=2.5, paramagnetic
Determine the electron geometry, molecular geometry, hybridization, bond angle, and polarity of the following molecule: ICl4-.
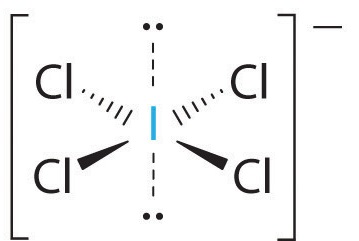
Octahedral, square planar, sp3d2, 90o, non-polar
Arrange the following in terms of increasing boiling point:
CH3OH, H2O, CH3COOH, CH3CH2OH
CH3OH<CH3CH2OH<H2O<CH3COOH
Determine the chemical formula and the functional groups in salicylic acid:
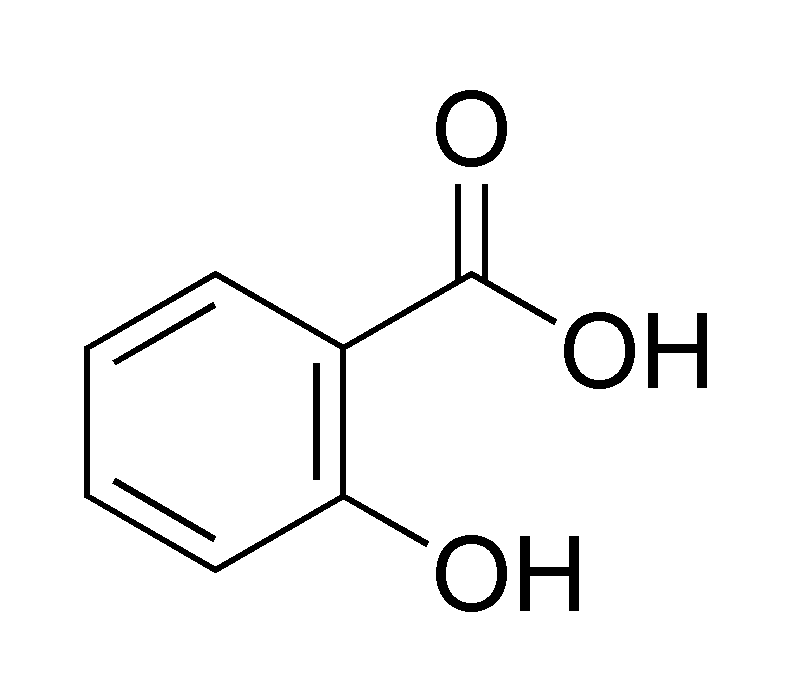
Chemical Formula: C7H6O3
Functional Groups: carboxylic acid, alcohol
BONUS: phenyl