"living" components of an ecosystem
biotic
What is the ultimate source of energy for the ecosystems here on earth?
the SUN
biogeochemical cycles
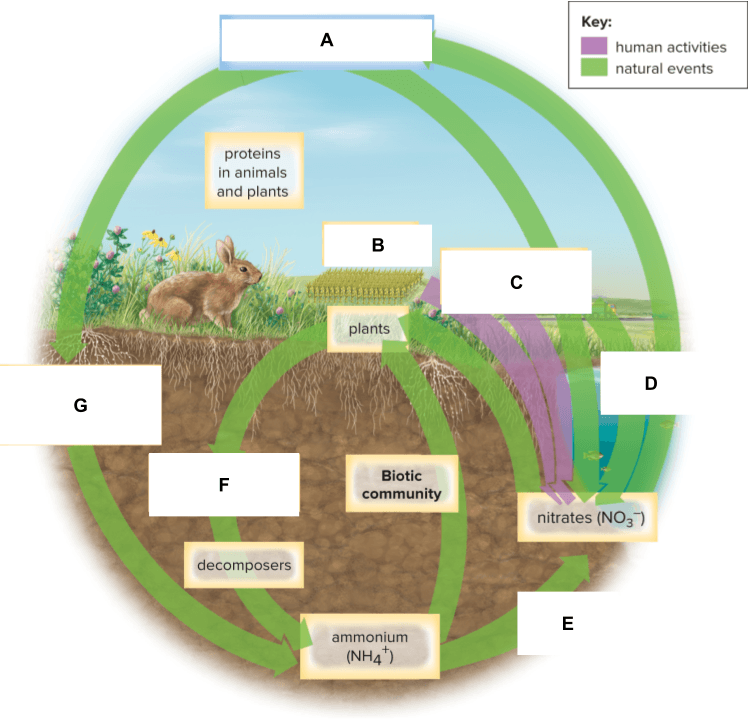
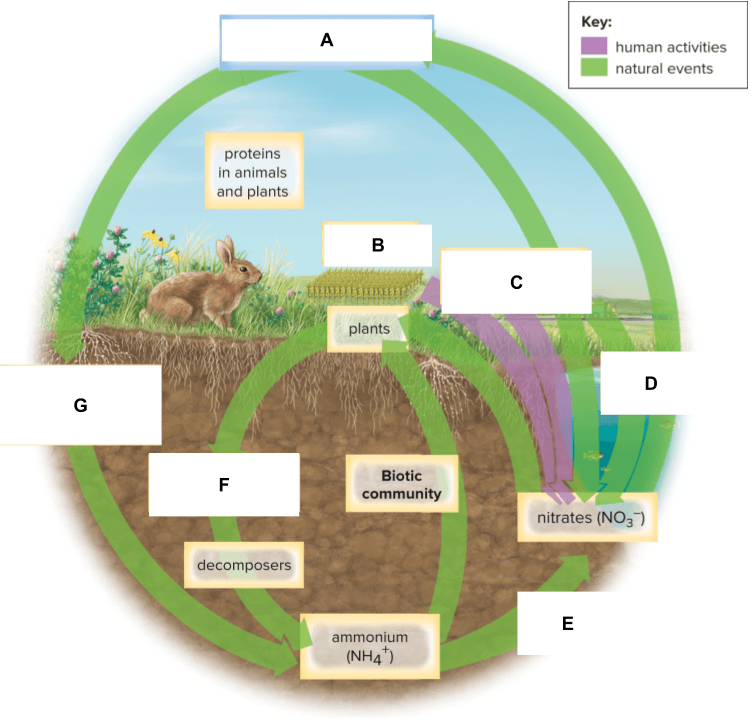
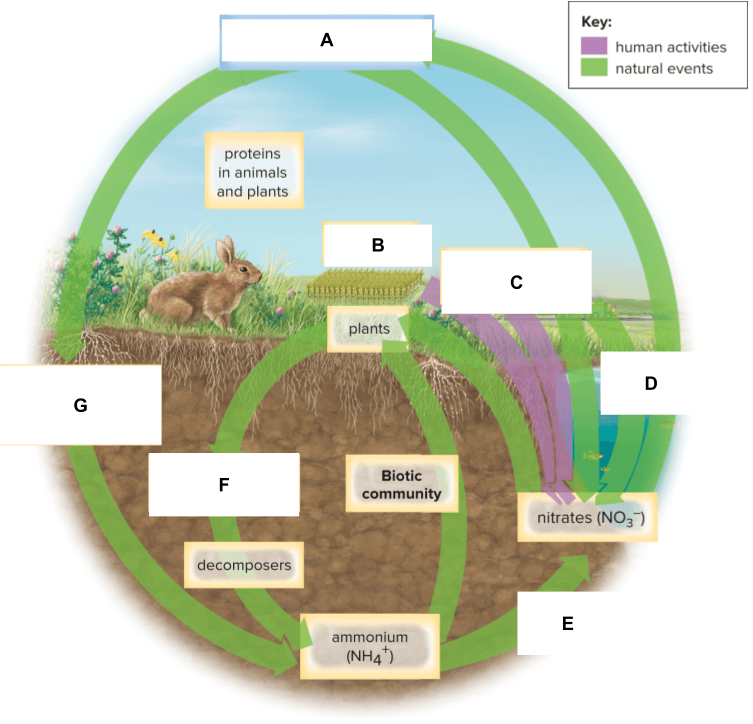
What is labeled B below?
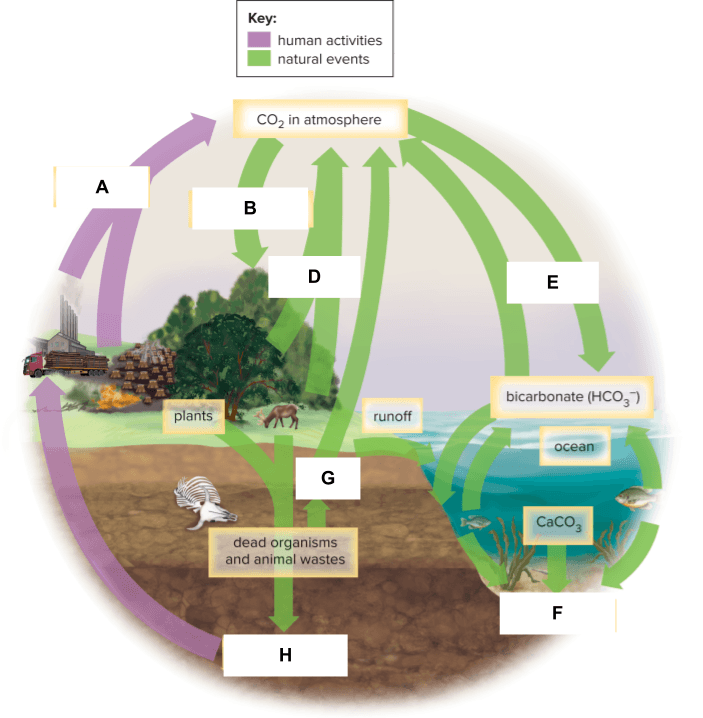
photosynthesis
What is labeled G below?
ice
Name 2 abiotic components of an ecosystem:
sunlight, water, soil, temperature, wind/weather
Diagram that shows a single path of energy flow through and ecosystem.
The part of the biogeochemical cycle that includes the food chains the chemicals move through.
biotic community
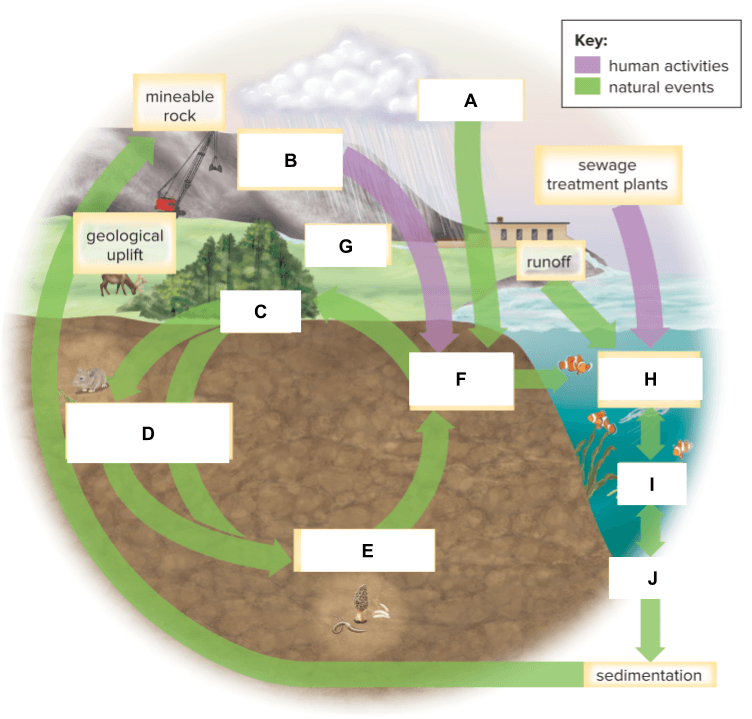
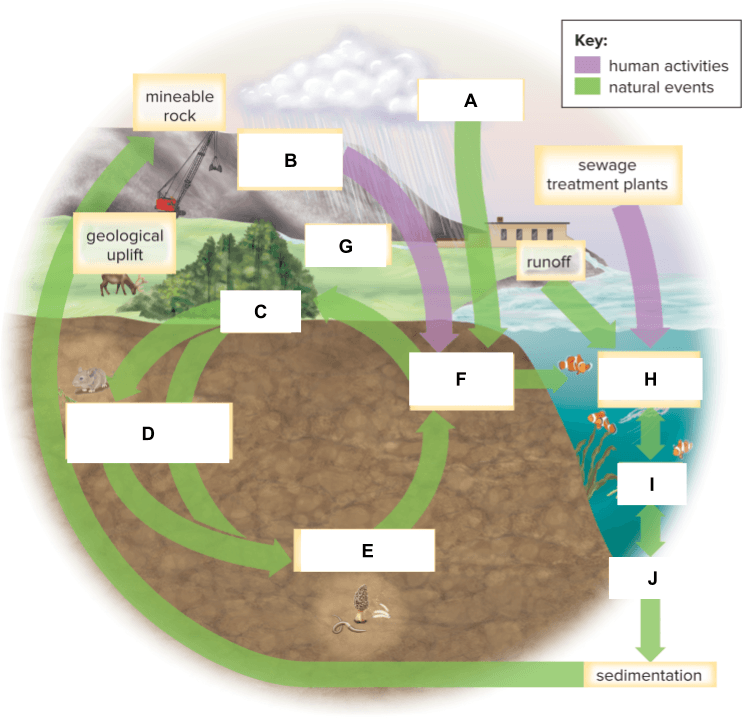
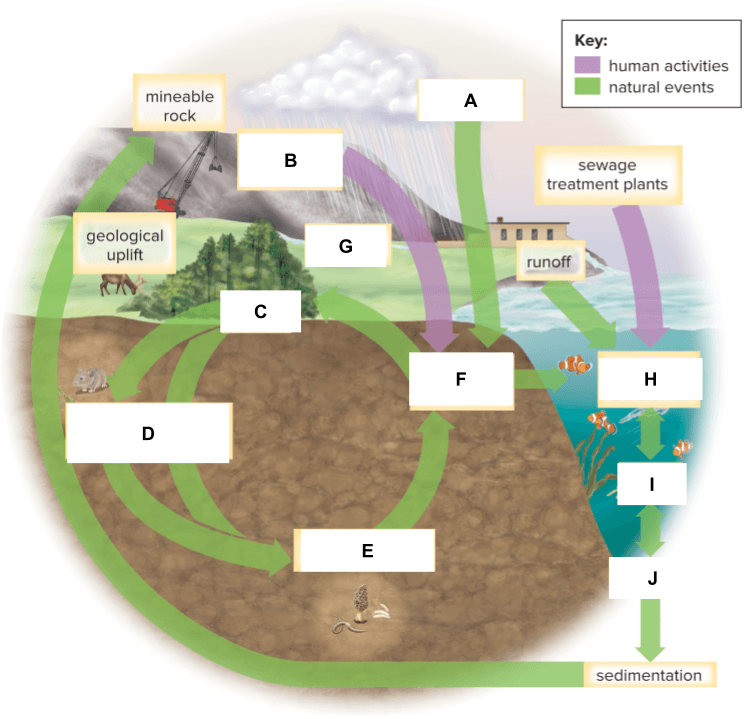
What is labeled H below?
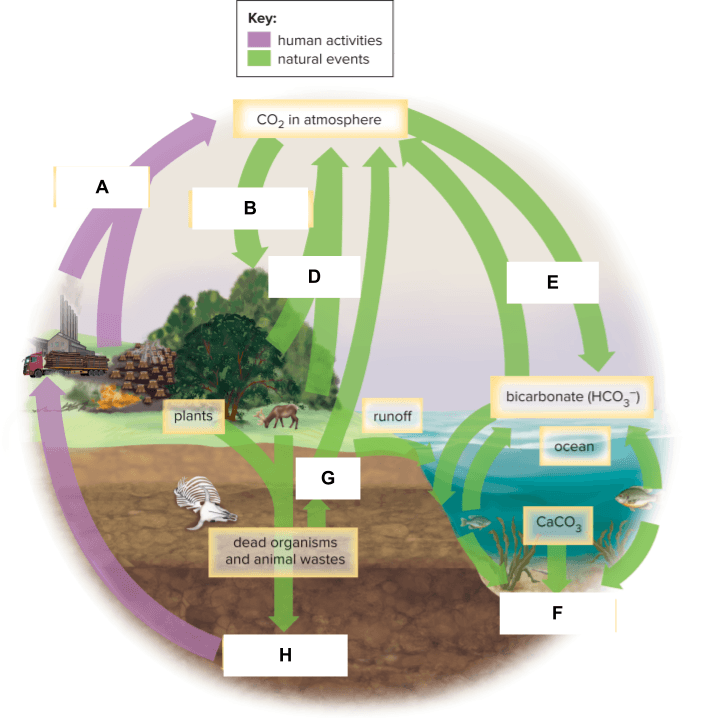
fossil fuels
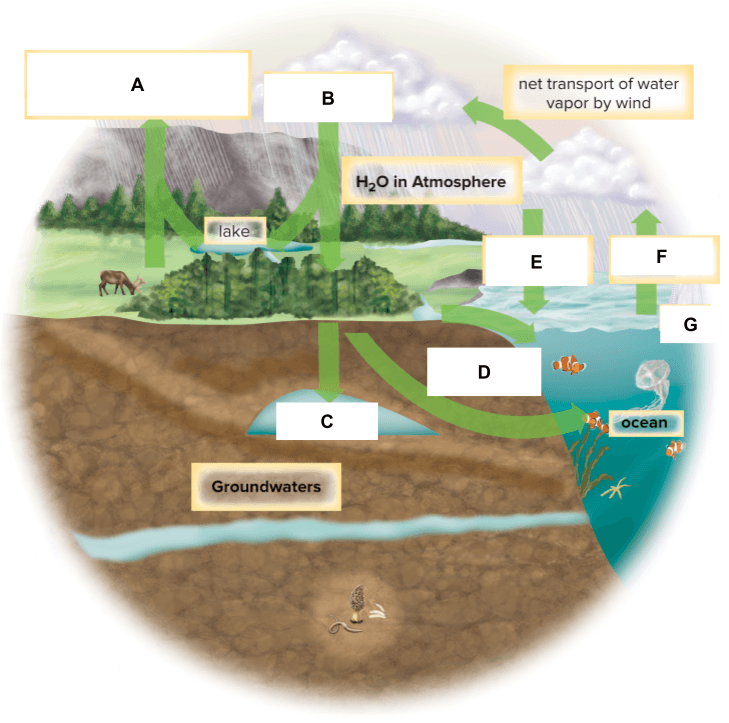
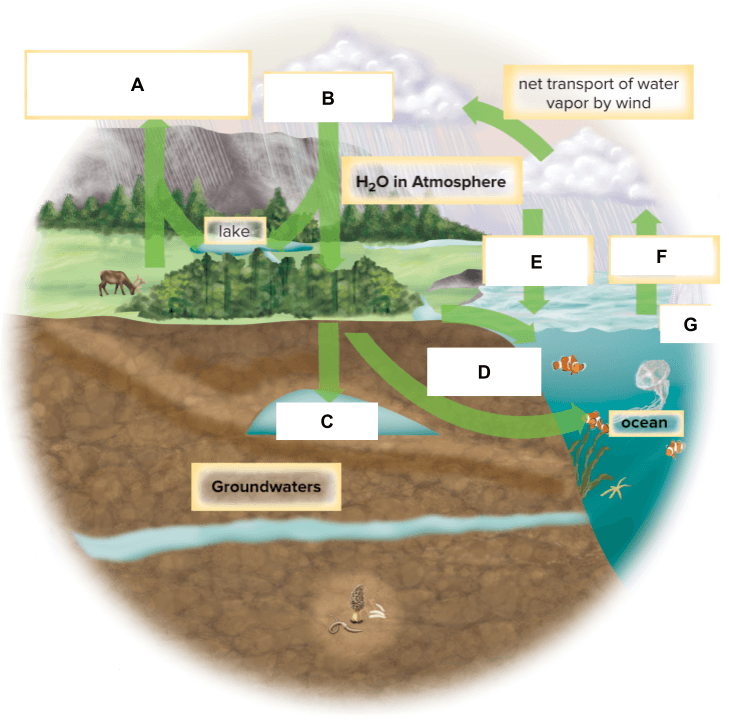
What is labeled C below?
aquifer
Organisms that are adapted to eating either plants or other consumers (meat).
omnivore
The amount of energy lost when it passes from one trophic level to the next.
90%
The source from which the living organisms (producers) take the chemicals.
What is labeled G below?
Nitrogen fixing bacteria in root nodules of legumes
What is labeled F below?
Phosphate in soil
Name the three levels of consumers found in an ecosystem:
Term for all the organisms that feed at a particular link in a food chain:
trophic level
The source of the chemical that is directly unavailable to the producers.
reservoir
What is labeled E below?
Nitrifying bacteria
What is labeled B below?
phosphate mining
Term for bacteria that can use chemicals to make sugars instead of sunlight
chemoautotrophs
Where are inverted energy pyramids located?
aquatic ecosystems
Term for the partially decomposed matter in the soil or water.
detritus
What is labeled D below?
denitrifying bacteria
What is labeled I below?
biota