The skin is the second largest organ in the body
True or False?
FALSE! Largest organ of the
body
How does our skin change with age?
Changes all throughout the lifespan
Changes denoting senescence
Aging process
Cumulative effects of exposure to sunlight
Environmental factors
Structural and functional changes
Diminished pain perception
Increased vulnerability to injury
Decreased vascularity (slower healing)
Weakened inflammatory response (slowing healing)
What are some common skin disorders
Atopic dermatitis
Contact dermatitis
Eczema and dermatitis
Stasis dermatitis
Environmental dermatoses
Rosacea
Name some common skin infections
Bacterial infections
Impetigo
Cellulitis
Viral infections
Fungal infections
Parasitic infections
What are some common skin disorders associated with immune dysfunction?
Psoriasis
Cutaneous lupus erythematous
Systemic sclerosis
Polymyositis and dermatomyositis
Name two types of cold injuries?
Localized- frostbite
Systemic- hypothermia
what IS THE SKINS PRIMARY FUNCTION?
Protect underlying structures
External injury
Harmful substances
What are some visible indications of aging?
Lax skin Vascular changes: decreased elasticity of blood
vessel walls
Dermal or epidermal degenerative changes
Wrinkling
Blood vessels within the reticular dermis
decreased in number and thinner walls
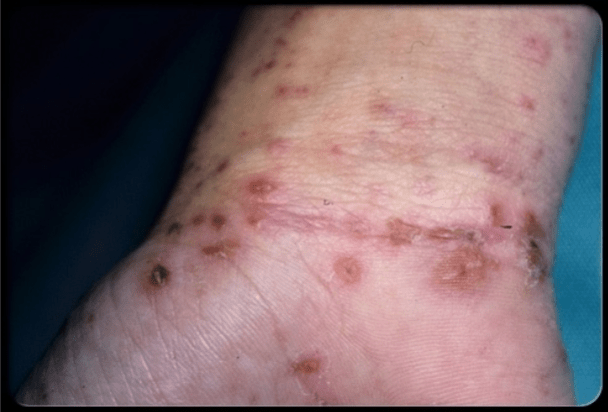
Chronic inflammatory skin disease
Most common type of eczema
Affects more than 10% of children
Common in a group of associated allergic
disorders: asthma, allergic rhinitis
Infancy: red, oozing, crusting rash
Chronic: dry, thickened,
Rash localized to flexor surfaces of folds of skin
Goal: stop inflammatory cycle
Also keep skin clean
Atopic dermatitis
Describe a bacterial infections
Skin harbors a variety of bacterial flora
Degree of pathogenicity depends
Invasiveness and toxigenicity
Integrity of the skin
Barrier of the host
Immune and cellular defenses
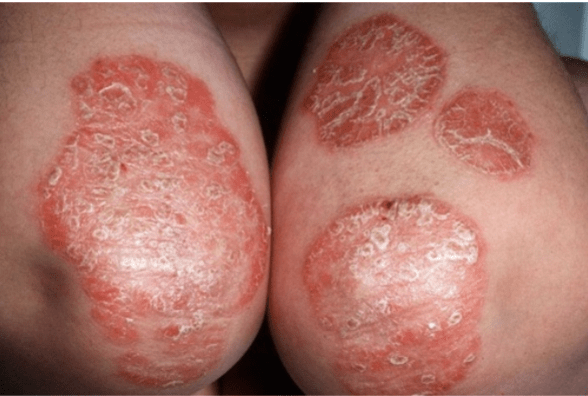
Chronic, inherited, recurrent inflammatory but
noninfectious dermatosis
Well defined erythematous plaques
Scalp, knees, skin folds, lower back
Flare ups in winter due to dry skin
Cause is unknown- appears to be hereditary and
may have a possible immune component
Once present becomes chronic that may go in
and out of remission
Psoriasis
True or false :
Severe cold affects all organs: especially the
CNS and cardiovascular system
TRUE!!
Names the functions of the skin
Insulator
Holds organs together
Sensory perception
Contribution to fluid balance
Controlling temperature
Absorbing UV radiation and metabolizing Vit D
Synthesizing epidermal lipids
What causes wrinkles?
Loss of elastin fibers
Weakened collagen
Decreased subcutaneous fat
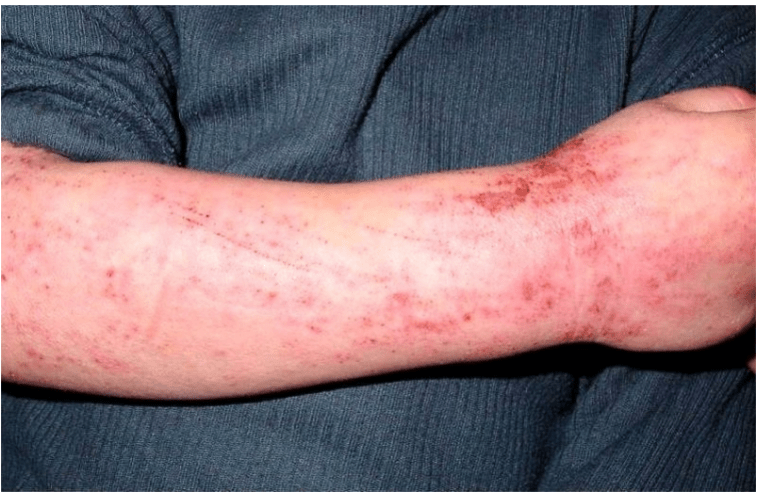
Acute or chronic inflammation
Caused by exposure to a chemical, mechanical,
physical or biologic agent
Common environmental skin disease
Common sensitizers
Nickel (jewelry)
Chromates (leathers)
Wool fats (lanolin- moistures)
Rubber additives
Topical anesthetics
Silicone (prosthetics)
Removal of offending agent then treat skin
Contact dermatitis
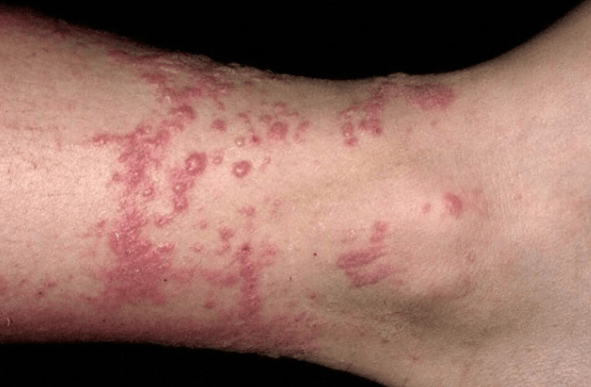
Superficial skin infection
Commonly caused by staphylococci or
streptococci
Infants and young children and older adults
Schools and overcrowded living environments
Spread by direct contact, environmental
contact or arthropod vector
Macules (flat)-> vesicles-> pus filled
Scratching spreads infection: autoinoculation
Impetigo
Chronic inflammatory autoimmune disorder of
connective tissues- which primarily affects the
skin
Chronic skin eruptions on sun-exposed skin that
can lead to scarring and permanent
disfigurement if left untreated
Discoid lesions can develop from the rash
Raised edges and sunken centers
Usually in areas exposed to sunlight
Cutaneous lupus erythematosus
Name some cold injury risk factors
Lack of insulating body fat
Older age
Drug or alcohol use
Cardiac disease
Psychiatric illness
Motor vehicle problems
Smoking
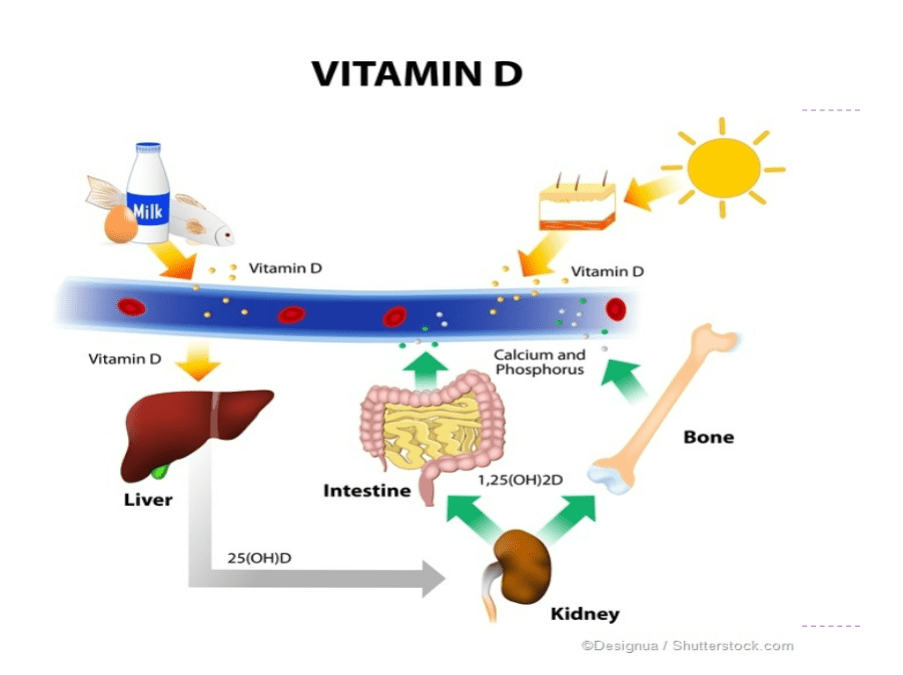
Explain how the skin helps synthesis vitamin D
What is a primary factor in loss of protective functions of skin?
Diminished barrier function of the stratum
corneum
As this layer becomes thinner- skin becomes
translucent, paper-thin-> reacting more readily to
minor changes in humidity, temperature and
irritants
Decreased protection to UV radiation- due to fewer melanocytes
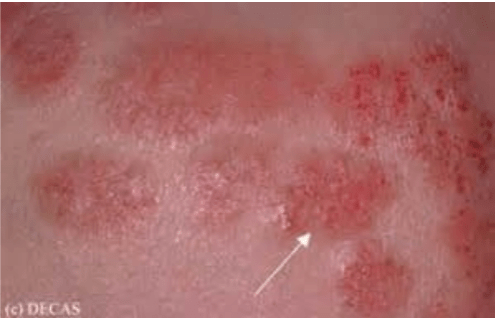
Group of disorders of superficial inflammation
3 stages
Acute dermatitis: erosions with serous exudate,
intensively pruritic
Subacute dermatitis: erythematous, excoriated
scaling papules
Chronic dermatitis: thickened skin
Common in older population
Can be medication related
Eczema and dermatitis
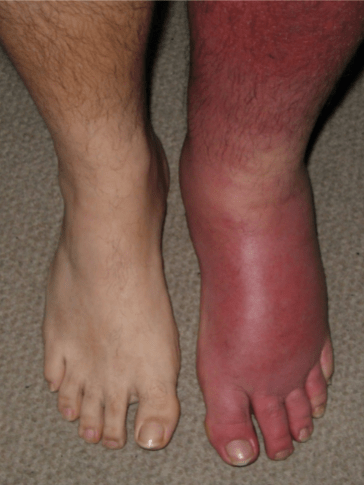
Rapidly spreading acute inflammation with
infection of the skin and subcutaneous tissue
Spreads widely through tissue spaces
Affects the extremities most often
Requires IV antibiotic treatment
Cellulitis
Diffuse connective tissue disease – causing fibrosis of the skin, joints, blood vessels and internal organs
Idiopathic origin
Distinctive widespread vascular changes
Known in past as scleroderma- although this just refers to the thickening of the skin
Systemic sclerosis
Injuries that result from direct contact with or
exposure to any thermal, chemical, electrical
or radiation source
Burns
S&S of skin pathology's
Pruritus- itching
Urticaria- hives
Rash- generalized term for eruption on the skin
Blisters- fluid-containing elevated lesions
Xeroderma- excessive dryness of the skin
What is the body’s principal supplier of Vit D
Epidermis
When 7-dehydrocholesterol is exposed to
sunlight= Vit D- decreased hormone after age 65
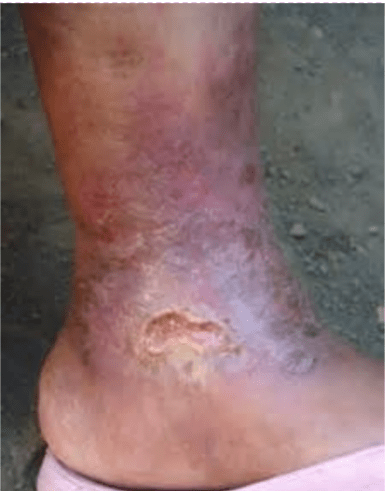
Areas of very dry, thin skin and sometimes
shallow ulcers of the lower legs
Primary due to venous insufficiency
Commonly hx of vericose veins or DVT
Slowed venous return-> leg edema -> hypoxic
tissue-> poorly nourished tissue begins to necrose
Compression and walking important
Stasis Dermatitis
an infection that uses intracellular substances of the host cells and are unable to provide for their own
metabolic needs or reproduce themselves
Viral infections
What are the 3 stages of Systemic sclerosis ?
Edematous- bilateral non-pitting edema- mostly fingers and
hands-> up the arm
Sclerotic- replacement of edema by thick hard skin
Decreased flexibility
Atrophic – thinning of the skin- especially over contractures
Higher risk of ulceration
3 phases of the patient with major burns
Emergent and resuscitation phase
Begins at the time of injury and concludes with the restoration of
capillary permeability – usually 48-72 hours after injury
Resuscitation phase- initiation of fluid resuscitation measures and
ends when capillary integrity returns to near normal levels
Acute phase
When the patient is hemodynamically stable, capillary permeability
restored, diuresis has begun and continues until wound closure is
achieved
Rehabilitation phase
Gaining independence through functional achievements
What is a generalized term for a rupture on the skin?
Rash
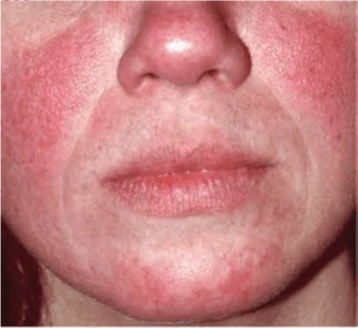
Chronic facial disorder of middle-aged and
older people
Facial blushing
Large vascular component
Rosacea
A benign viral infections of the skin
and adjacent mucous membranes caused by HPV
WARTS
What is an Ulcer?
What puts you at risk for them?
lesion caused by unrelieved pressure-> resulting
in damage to underlying tissue
Risk factors
Interface pressure
Friction
Shearing (forces in opposite direction)
Maceration
Decreased skin resilience (dehydration
Malnutrition
Decreased circulation
Blister
How to treat viral skin infections
Cryotherapy: cosmetically preferred but painful->
epidermal necrosis and peels off with wart
Acids: painted on daily
Electrodesiccation: high frequency electric current
Fungi Infections
Fungi that invade the ________, ____ and
____-> can spread without treatment
Superficial- live on- not in the skin
Confined to the dead skin keratin layers
Stratum corneum, Hair, and Nails
A type in fungi infection...
Ring shaped pigmented patches
Direct skin contact or contaminated objects
Ring worm
A type of fungi infection
Erythema, pruritus between toes-> sole
Can be an entry for other types of infection
Athlete’s foot (tinea pedis)
Mites-> highly contagious skin eruption
Easily transmitted by skin-to-skin contact or by
contact with contaminated objects
Female mite burrows into the skin and lays eggs
Scabies