Rank the following in size: Cl- Ca2+ Ar K
Cl- > K > Ar > Ca2+
What is the geometry of the carbon in CH4?
Tetrahedral
Does CH2Cl2 have a net dipole?
Yes!
If the volume of a gas is doubled at constant pressure, what can we say about the absolute temperature?
it will double
For the reaction of chlorine and nitric oxide, 2NO(g) + Cl2(g) ----> 2NOCl(g) doubling the concentration of chlorine doubles the rate of reaction, and doubling the concentration of NO has no effect on the rate.
What are the respective orders?
NO- zero order
Cl- first order
Name the compound: CH3CH2CH2COOH
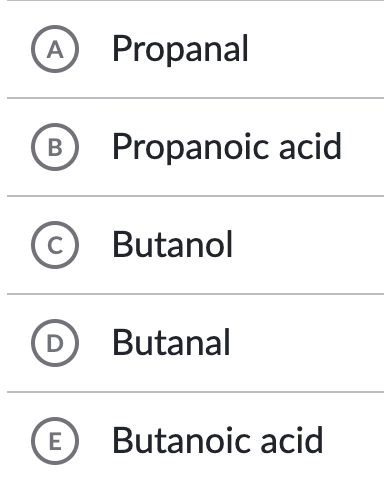
e. Butanoic acid
What is the hybridization around each carbon C2H4?
2sp2
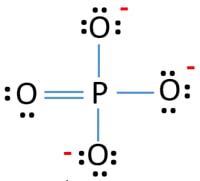
Draw a lewis structure for Phosphate (PO43-)
Which of the following is polar: CF4, CO2, SF4
SF4
What does a triple point represent?
Plots are shown for the reaction NO2(g) ----> NO(g) + 1/2 O2(g) What is the rate law for the reaction?
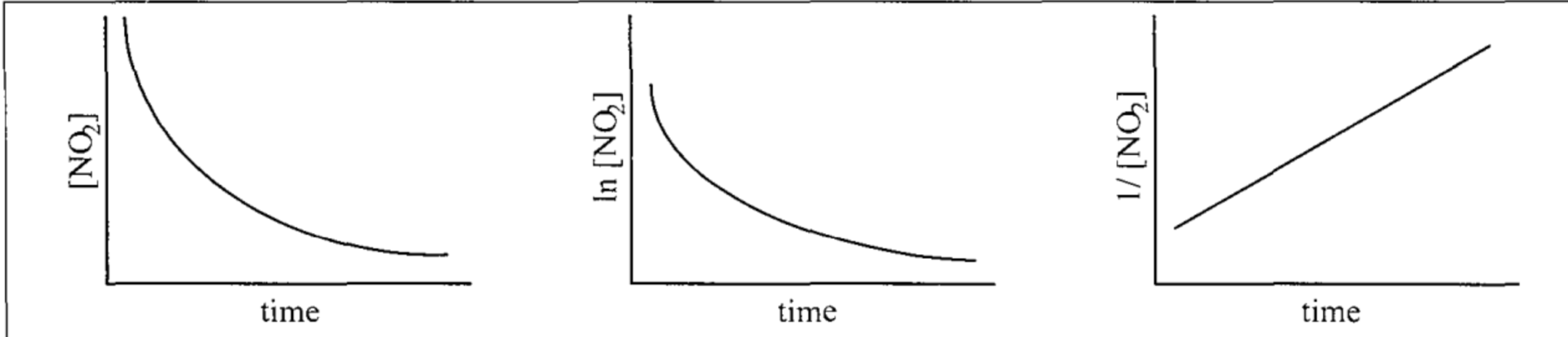
rate = k[NO2]2
*second order
The structure of propanol is
e. 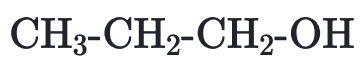
The radii of the ions in this series decreases because
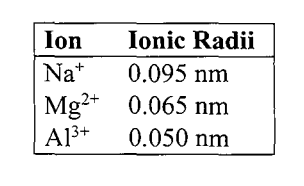
(A) the elements are in the same period.
(B) the effective nuclear charge is increasing.
(C) the atomic radius of Na decreases from Na to Al.
(D) the first ionization energies increase from Na to Al.
(B) the effective nuclear charge is increasing.
What is the geometry of the Oxygen in
CH3CH2OH? What is the shape?
Geometry: Tetrahedral
Shape: Bent
Rank the following from weakest intermolecular forces to strongest.
H2Se H2S H2Po H2Te
H2S < H2Se < H2Te < H2Po
If an amount of some gas has a volume of 22.4L at STP, what will the temperature be if pressure is held constant when the volume is 11.2L?
136 K
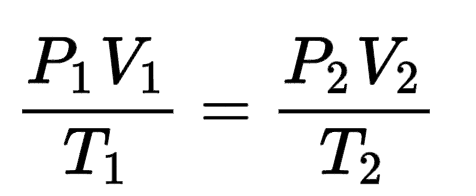
What is the rate law of this reaction?
2H2 + 2NO --> N2 + H2O

rate = k[H2][NO]2
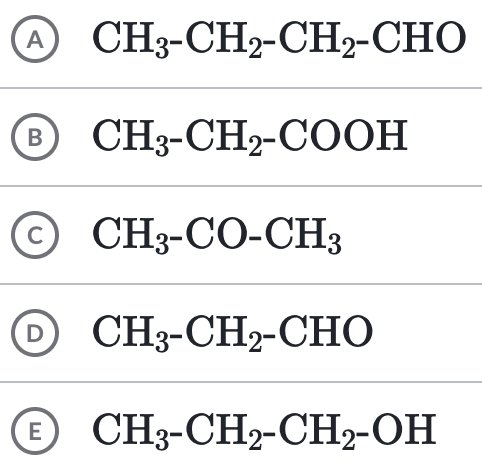
Which of the following functional groups does this compound identify as:
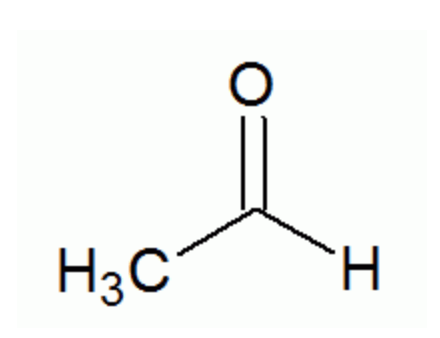
a. Keytone
b. Aldehyde
c. Carboxylic acid
e. Ester
b. Aldehyde
Draw C2H2 using the molecular orbital theory we have learned. Then identify the number of pi and sigma bonds present.
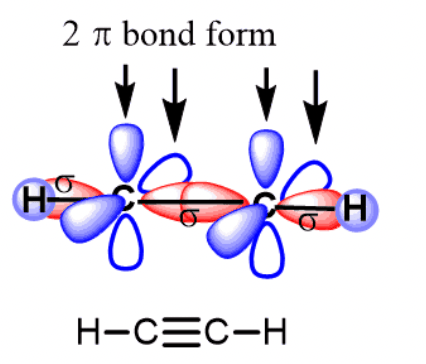
Pi:2
Sigma:3
Draw the Lewis Structure for SOCl2 and calculate the formal charges on each atom
S = 0, Cl = 0, O = 0

Consider benzene, C6H6, and phenol, C6H5OH:
Which has the lower viscosity?
Which has the higher surface tension?
Which one can H bond?
Which one has only London dispersion forces?
Which has the lower viscosity? benzene
Which has the higher surface tension? phenol
Which one can H bond? phenol
Which one has only London dispersion forces? benzene
determine the enthalpy of the reaction:
C2H4(g)+Cl2(g)→C2H3Cl(l)+HCl(g)
C-H = 413 kJ/mol, H-H 432 kJ/mol
Cl-Cl 243 kJ/mol, C-C 347 kJ/mol
C=C 614 kJ/mol, H-Cl 427 kJ/mol,
C-Cl 339 kJ/mol
(broken - formed) *remember to balance the equation
= -110 kJ/mol
What values does a catalyst change according to this graph?
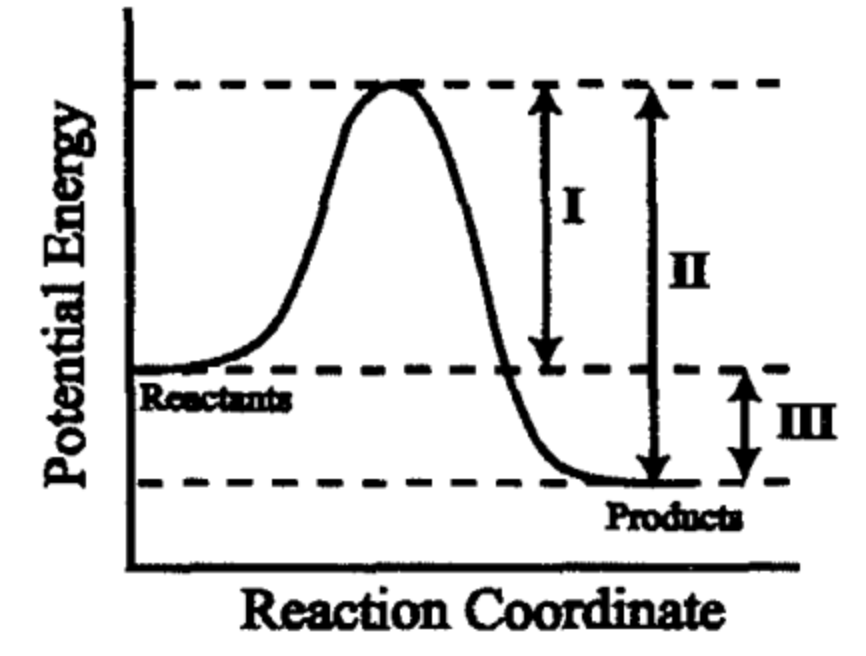
I and II
What functional groups are a part of this compound:
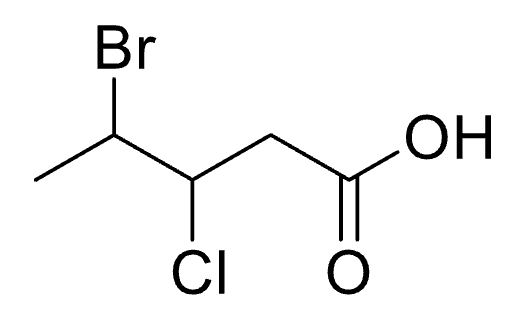
a. Ketone
b. Aldehyde
c. Carboxylic acid
d. Amine
e. Bromine
c. Carboxylic acid
Which compound has the strongest bond?
CO2, H2O, N2
*bond, not IMF
N2, Triple bond! (shortest & strongest)
What is the shape of CH3- and angle between 2 hydrogens in CH3-?
Shape: Tetrahedral
Angle: <109.5°
Which of the following compounds has the highest volatility?
a. H2O
b. CH3OH
c. CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
d. MgO2
Draw the molecular orbital for CN-
is CN paramagnetic or diamagnetic?
c. CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
A sulfuric acid solution containing 571.4 g of H2SO4 per liter of solution has a density of 1.329 g/cm3. Calculate the molality of H2SO4 in this solution
m = 7.690 mol/kg
Calculate the rate constant:

First order with respect to I-, first order with respect to S2O82-, Overall order is 2 Rate= k [I-][S2O82-]
K=36.8
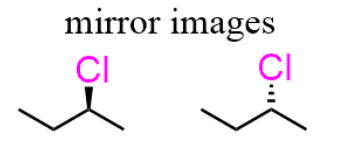
What is an enantiomer?