What type of relationship exist between wavelength and frequency?
Inverse relationship. If one goes up, the other must go down. (in terms of multiplication & Division)
The dots in the Lewis Dot structure represent what?
The valence Electrons
What is ground state configuration for Boron?
1s2 2s2 2p1
Copper produced a green flame, while potassium produced a violet flame, which metal had electrons that traveled further from the nucleus?
Potassium's violet flame had more energy.
Due to having more energy, Potassium's electrons could travel further from the nucleus, and as it returned it released the large amount of energy is the form of violet light.
the arrangement of electrons in an atom
electron configuration
What is the type of radiation for an electron that produces 4.219 x 10-2 m
Microwaves
What is the noble gas configuration for Radium (Ra)?
[Rn] 7s2
What is ground state configuration for Bromine?
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3s10 4p5
What type of radiation occurs when an electron produces a wavelength of 3.8 x 10-5?
Infrared light
the number of waves that pass a given point per second
frequency
If the frequency of a wave is adjusted from 15 Hz to 105 Hz, what will the new wavelength be if the original wavelength was 56 meters?
8 meters
Freq and wavelength have an inverse relationship. Frequency increases x7 to go from 15 Hz to 105 Hz. This means wavelength must be divided by 7.
What is the dot structure for Chlorine?

Draw the orbital notation for Cobalt
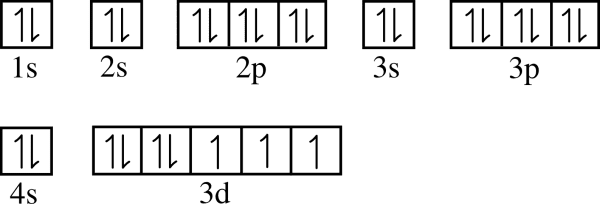
How many electrons can be held in each sublevel?
S? p? d? f?
S - 2 electrons
P - 6 electrons
D - 10 Electrons
F - 14 electrons
a three-dimensional region around the nucleus of an atom that describes an electron’s probable location
atomic orbital
What is the wavelength of a wave that travels from n=5 to n=2? What type of radiation occurs (infared, visible [be specific], or ultraviolet.)
434 nanometers of blue visible light.
Look on the back page of your yellow reference table and use the Bohr Model. 434 nanometers is the same as 4.34 x 10-7 m. This range falls under blue visible light.
Give the noble gas notation and dot structure for Bismuth (Bi)
[Xe] 6s2 4f14 5d10 6p3
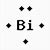
Give the ground state configuration for Yttrium
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2 4d1
Draw the orbital notation for Selenium (Se)

the minimum amount of energy that can be gained or lost by an atom
quantum
The frequency of a wave is altered from 56.7 Hz to 8.10 Hz. If the original wavelength was 124 nanometers, what will be the new wavelength?
868 nanometers.
Due to the inverse relationship that exist between frequency and wavelength, when frequency is divided by 7, wavelength must be multiplied by 7.
What is the noble Gas notation and dot structure for Berklium (Bk)?
[Rn] 7s2 5f9
Dot structure would have Bk surrounded with two dots that are on different sides of the symbol.
Give the ground state for Tungsten (W)
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p6 6s2 4f14 5d4
How many electrons can be held in the third energy level?
18 electrons
3rd energy level includes 3s, 3p, and 3d. S = 2 electrons, p=6 electrons, d =10 electrons. Add them all up to get 18 electrons.
electrons are emitted from a metal’s surface when light of a certain frequency shines on the surface
photoelectric effect