As the temperature of a substance increases, particles move ___.
Faster
As temperature increases, pressure _____.
increases.
 The state of matter represented in the image
The state of matter represented in the image
Solid
The phase change from solid to liquid
Melting
Draw a feature of a model representing particle speed / velocity.
arrows
As the temperature of a substance decreases, particles move ___.
Slower.
As temperature increases, volume increases because
The state of matter with no definite volume or definite shape.
The phase change from liquid to gas
Vaporization
Draw a particle model of a ice melting.
Includes:
- labels
- pictures
- arrows
- vibration lines
As particles of a substance gain energy and move farther apart, the _____ increases.
Volume
This is the temperature where a liquid is converted into a gas.
Boiling Point
Draw the particle diagram of a liquid.
Includes:
- vibration lines
- particles slightly spaced apart but relatively close
- not organized in neat rows
Draw 2 particles with differing speeds.
demonstrated by two particles with different sized arrows
Definition: The amount of force per square meter. Described as the collision between molecules of different substances.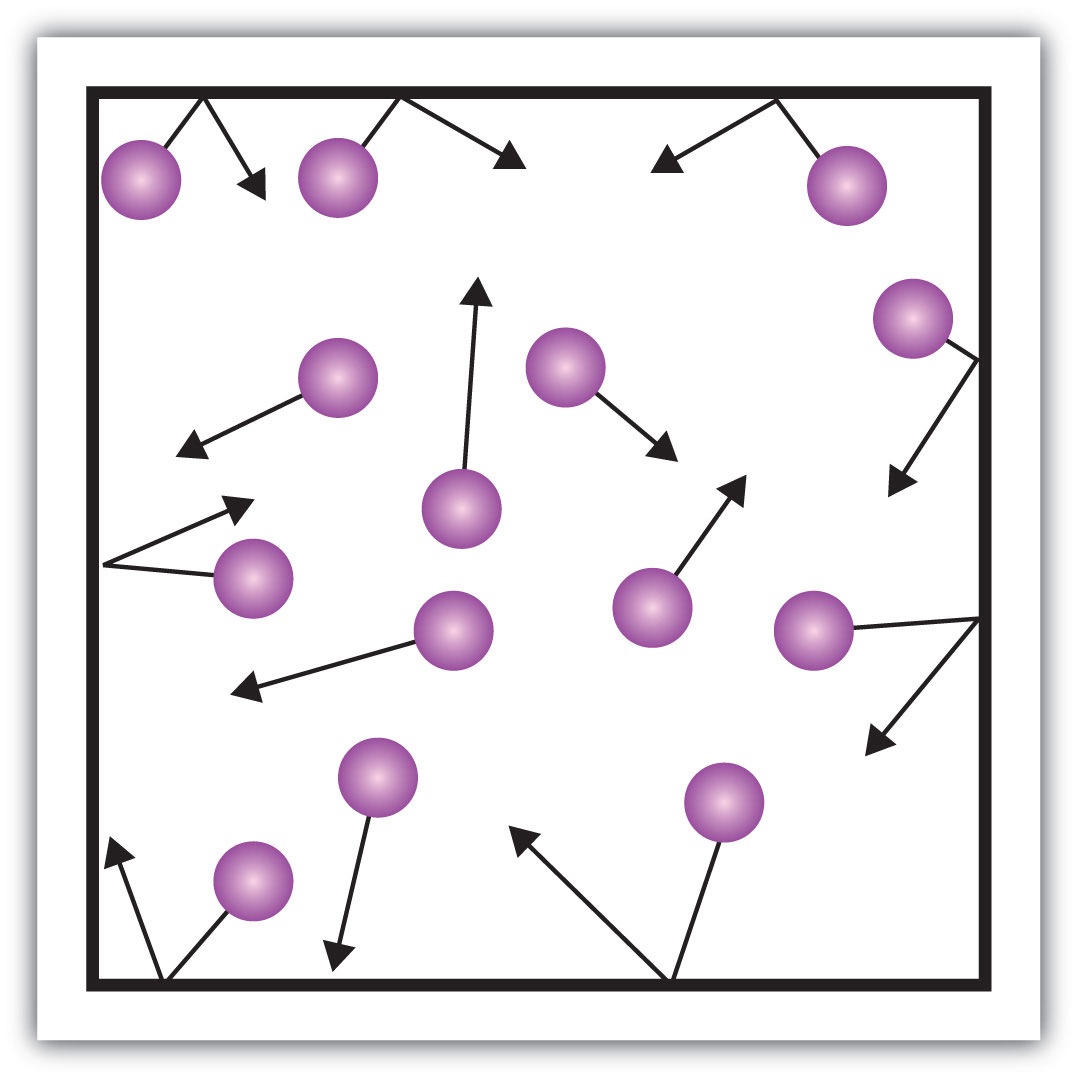
Pressure
In terms of force, why does heating a substance convert a liquid into a gas?
The increased temperature is caused by increasing thermal energy and particle velocity. The increased energy allows the particles to overcome attractive forces between them causing them to spread out and form a gas.
True or False. Thermal expansion only occurs in gases. Explain.
False. Increasing the temperature of a substance in any state of matter also increases its volume because the increasing thermal energy spreads the molecules farther apart.
Icebergs are breaking apart due to what phase change? Why?
Icebergs break apart due to melting caused by the increasing global temperatures. The ice converts into liquid water causing the iceberg to no longer hold a definite form and break apart.
Create a model depicting all covered phase changes.
includes:
- melting
- freezing
- boiling
- condensation
Why does the water in the straw stay in the straw despite gravity pulling all substances down?
Closing the top of the straw makes the air pressure above and below the water equal cancelling out the force of gravity.
Both occur at the same temperature, however, they occur in opposite directions.
- FP: from liquid to solid
- MP: from solid to liquid
Correctly sequence the events causing water vapor to condense into liquid water at the molecular level:
1) The temperature continues to drop.
2) Temperature remains at the condensation point until all water molecules form a liquid.
3) The temperature of the molecules decrease.
4) Water vapor molecules lose energy to the atmosphere and move closer together.
5) The molecules gain increased attraction between them.
6) The water vapor becomes liquid water.
4) Water vapor molecules lose energy to the atmosphere and move closer together.
3) The temperature of the molecules decrease.
5) The molecules gain increased attraction between them.
2) Temperature remains at the condensation point until all water molecules form a liquid.
6) The water vapor becomes liquid water.
1) The temperature continues to drop.
Draw a model depicting sublimation.
depicts a solid converting into a gas