At which phase of mitosis do the sister chromatids become daughter chromosomes?
Anaphase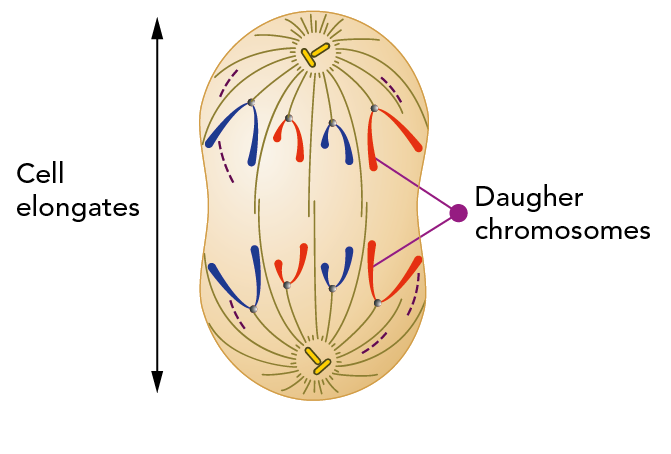
Somatic cells in elephants have 56 chromosomes. How many chromosomes would be carried by the gametes produced by elephants?
28
During mitotic interphase, most of the nucleus is filled with a complex of DNA and protein in a dispersed form called
chromatin
You have the technology necessary to measure each of the following in a sample of animal cells: carbohydrates, organelle density, picograms of DNA, cell wall components, and enzymatic activity. Which of the following cell characteristics would you expect to increase significantly between a cell in mitosis and one just beginning G1?
carbohydrates. DNA content. enzyme activity. cell wall components. organelle density
enzyme activity
Which bond or interaction is the most difficult to disrupt when compounds are put in water?
Covalent. Hydrogen. van der Waals. ionic
Covalent

During which phase of mitosis in animal cells do centrioles begin to move apart?
Prophase

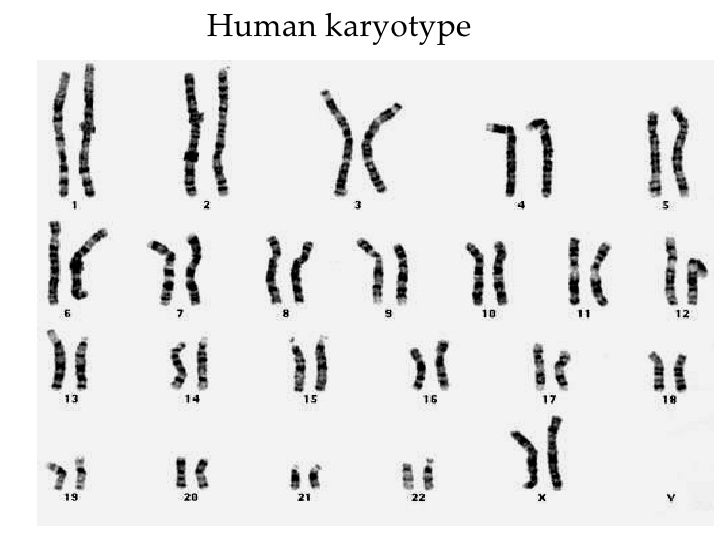
Why are cells arrested at metaphase in the preparation of a karyotype?
All of their chromosomes are highly condensed and easy to visualize.
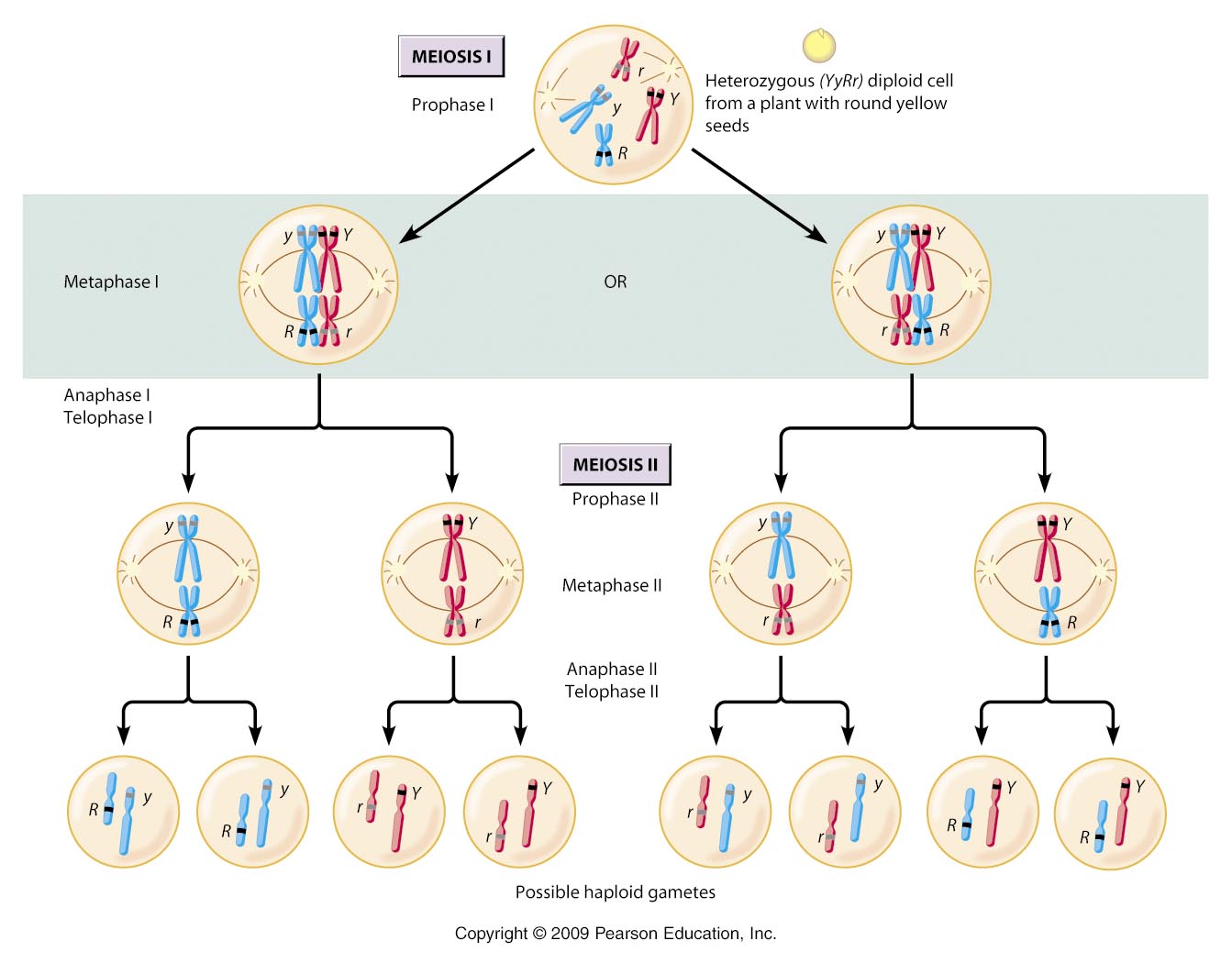
In Meoisis during which process does independent assortment of chromosomes occur?
Meiosis I
Which is the first checkpoint in the cell cycle that will cause a cell to exit the cycle if this point is not passed?
G1
A group of molecular biologists is trying to synthesize a new artificial compound to mimic the effects of a known hormone that influences sexual behavior. The biologists have turned to you for advice. Which of the following compounds is most likely to mimic the effects of the hormone? A compound with:
the same number of carbon atoms
the same molecular mass
the same 3-D shape
the same number of valence electrons
the same number of hydrogen and nitrogen
same 3-D shape

Where do the microtubules of the spindle originate during mitosis in animal cells?
 centrosome
centrosome
How are sister chromatids and homologous chromosomes different from each other?
Homologous chromosomes contain the same gene loci but may have different alleles of a particular gene. Sister chromatids are identical copies of each other produced during DNA replication.
In Meiosis, Homologous chromosomes move toward opposite poles of a dividing cell during
Meiosis I (anaphase I)

The cell cycle is regulated at the molecular level by a set of proteins known as
cyclins

Which of the following compounds are formed by dehydration reactions?
triacylglycerols. monosaccharides. amino acids. fatty acids
triacylglycerols

How many cells and how many nuclei would be the result if a eukaryotic cell completes mitosis but does not undergo cytokinesis?
One cell-- two nuclei

If the DNA content of a diploid cell in the G1 phase of the cell cycle is represented by x, then the DNA content of the same cell at metaphase of meiosis I would be __________.
2x

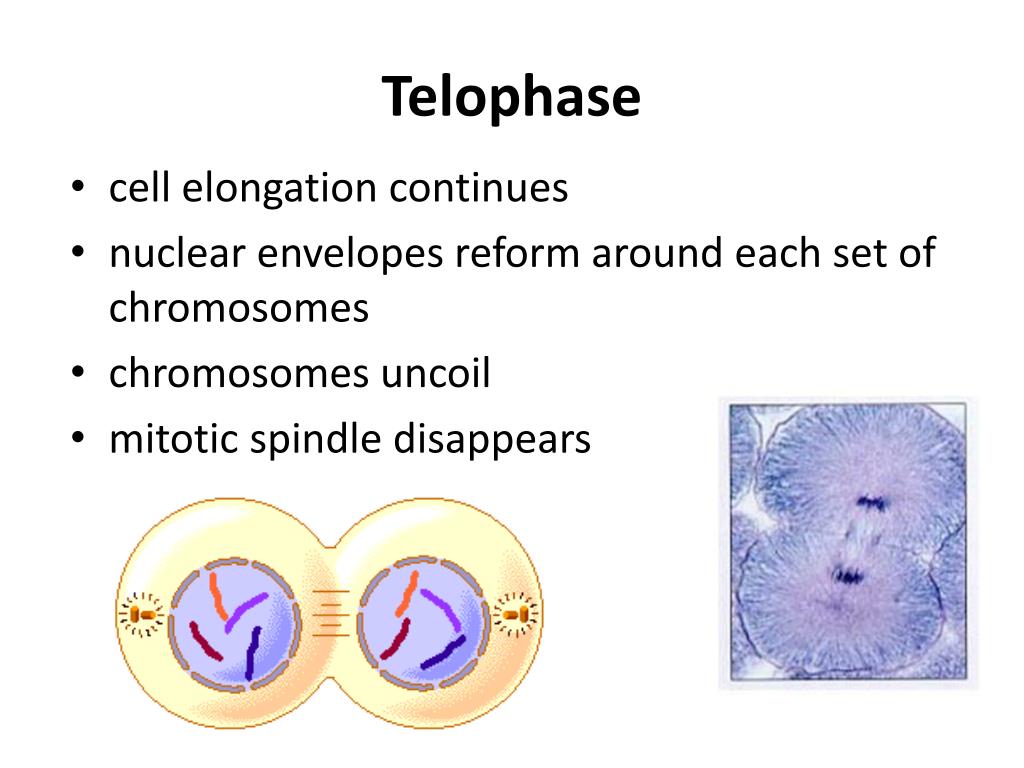
In mitosis, spindle microtubules disassemble during which step
Telophase
Cells will usually divide if they receive the proper signal at a checkpoint in which phase of the cell cycle?
In mammalian cells, the G1 checkpoint is termed the restriction point.
Interactions between side chains (R groups) in a polypeptide are most important in stabilizing which of the following structures?
primary. secondary. tertiary. quaternary
tertiary

If there are 8 centromeres in a cell at anaphase of mitosis, how many chromosomes are there in each daughter cell following cytokinesis?
4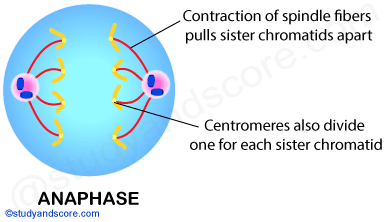
If chiasmata can be seen in a cell under a microscope, which of the following meiotic processes must have occurred?
Prophase 1

What stage of mitosis is this cell in?

Metaphase

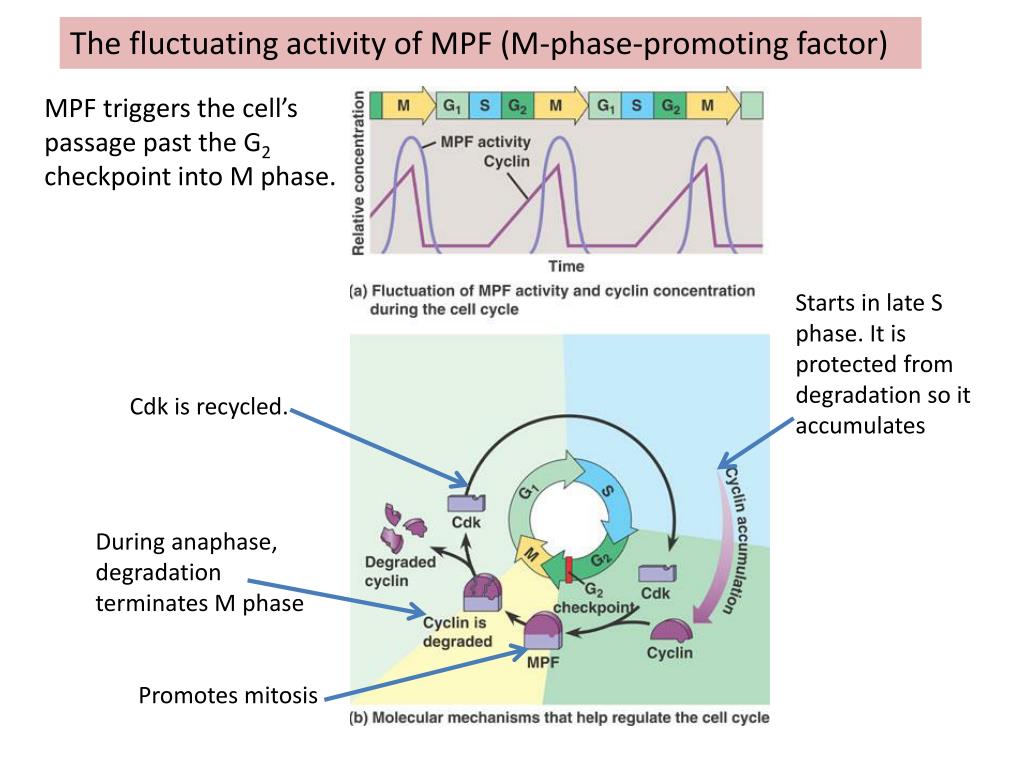
What triggers the cell's passage past the G₂ checkpoint into mitosis?
MPF: maturation-promoting factor
Biologists commonly use cell fractionation to
sort whole cells based on their size and weight
visualize the 3-D structure of cell membranes
isolate organelles to examine their biological functions
isolate organelles to examine their biological functions
