Cells are ________.
A) only found in pairs, because single cells cannot exist independently
B) limited in size to 200 and 500 micrometers in diameter
C) characteristic of eukaryotic but not prokaryotic organisms
D) characteristic of prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms
D) characteristic of prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms
A localized group of organisms that belong to the same species is called a ________.
A) community
B) population
C) ecosystem
D) family
B) population
Following a scientific method, which of the following is the correct order of steps?
A) Observation → Analysis → Hypothesis → Conclusion → Communicate results → Experiment
B) Observation → Hypothesis → Experiment → Communicate results → Analysis → Conclusion
C) Experiment → Hypothesis → Observation → Analysis → Conclusion → Communicate results
D) Observation → Hypothesis → Experiment → Analysis → Conclusion → Communicate results
D) Observation → Hypothesis → Experiment → Analysis → Conclusion → Communicate results
Characters are transmitted from parents to offspring. ________ are the units of inheritance.
A) Genes
B) Proteins
C) RNA
D) DNA
A) Genes
To understand the chemical basis of inheritance, we must understand the molecular structure of DNA. This is an example of the application of which concept to the study of biology?
A) evolution
B) emergent properties
C) reductionism
D) feedback regulation
C) reductionism
In comparison to eukaryotes, prokaryotes ________.
A) are more structurally complex
B) are larger
C) are smaller
D) do not have membranes
C) are smaller
Which of the following order is correct in terms of the hierarchy of the organization?
A) Ecosystem → Biosphere → Population → Community → Organism
B) Biosphere → Ecosystem → Population → Community → Organism
C) Ecosystem → Community → Biosphere → Population → Organism
D) Biosphere → Ecosystem →Community → Population → Organism
D) Biosphere → Ecosystem →Community → Population → Organism
How does a scientific theory differ from a scientific hypothesis?
A) Theories are proposed to test scientific hypotheses.
B) Theories are usually an explanation for a more general phenomenon; hypotheses typically address more specific issues.
C) Hypotheses are usually an explanation for a more general phenomenon; theories typically address more specific issues.
D) Confirmed theories become scientific laws; hypotheses become theories.
B) Theories are usually an explanation for a more general phenomenon; hypotheses typically address more specific issues.
As letters are to English language, ________ is/are to genetic information.
A) proteins
B) nucleotides
C) DNA double helix
D) A and B
B) nucleotides
13) Plants convert ________.
A) chemical energy to mechanical energy.
B) sunlight to mechanical energy.
C) sunlight to chemical energy.
D) mechanical energy to chemical energy.
C) sunlight to chemical energy.
3) Which of the following types of cells utilize deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) as their genetic material but do not have their DNA encased within a nuclear envelope?
A) animal
B) plant
C) archaean
D) fungi
C) archaean
Which branch of biology is concerned with the naming and classifying of organisms?
A) informatics
B) taxonomy
C) genomics
D) evolution
B) taxonomy
A controlled experiment ________.
A) is repeated many times to ensure that the results are accurate
B) includes at least two groups, one of which does not receive the experimental treatment
C) includes at least two groups, one differing from the other by two or more variables
D) includes one group for which the scientist controls all variables
B) includes at least two groups, one of which does not receive the experimental treatment
The process by which the information in a gene directs the synthesis of a protein is called ________.
A) gene expression
B) replication
C) post translation modification
D) cloning
A) gene expression
When your body temperature rises on a hot day, the neural and hormonal mechanisms activate sweating. Evaporation of sweat leads to cooling of the body surface. This is an example of ________.
A) positive feedback regulation
B) negative feedback regulation
C) chemical cycling
D) emergent properties
B) negative feedback regulation
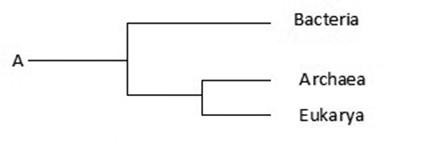
The phylogenetic tree ________.
A) depicts that Archaea is closer to Bacteria than Eukarya
B) depicts that Eukarya is closer to Bacteria than Archaea
C) includes unicellular and some forms of multicellular life, but not complex animals and plants
D) includes every single life form on this earth
D) includes every single life form on this earth
16) The evolution of one species into two or more species as a result of different populations becoming reproductively isolated from each other is best termed as ________.
A) adaptive radiation
B) creationism
C) natural selection
D) prototype
A) adaptive radiation
Why is a scientific topic best discussed by people of varying points of view, from different sub disciplines, and representing diverse cultures?
A) Robust and critical discussion between diverse groups improves scientific thinking.
B) Scientists can coordinate with others to conduct experiments in similar ways.
C) This is a way of ensuring that everyone gets the same results.
D) People need to exchange their ideas with other disciplines and cultures because everyone has a right to an opinion in science.
A) Robust and critical discussion between diverse groups improves scientific thinking.
Which of the following statements is true?
A) mRNA is the only type of RNA found in the living system
B) All forms of life employ the same genetic code
C) A typical human liver cell has one set of chromosomes
D) Organisms interact but do not affect their environment
B) All forms of life employ the same genetic code
Which of the following statements is true regarding the complexity of biological systems?
A) An understanding of the interactions between different components within a living system is an approach towards understanding reductionism.
B) Knowing the function of a component of a living system can provide insights into the structure and organization of the living system.
C) Understanding the chemical structure of DNA reveals how it directs the functioning of a living cell.
D) An ecosystem displays complex properties of the biotic component only.
B) Knowing the function of a component of a living system can provide insights into the structure and organization of the living system.
You are suffering from Streptococcus throat infection. You share the following with the bacteria that is responsible for your condition.
A) You both belong to the same domain.
B) You both are made up of cells.
C) You both have genetic material in your nucleus.
D) You and Streptococcus have nothing in common.
B) You both are made up of cells.
Which of the following is not one of Charles Darwin's observations?
A) Individuals in a population vary in their traits.
B) Many of the traits in an individual are heritable.
C) A population avoids competition by producing only as many offspring as can successfully
reproduce on their own.
D) Species generally are adapted to their environments.
C) A population avoids competition by producing only as many offspring as can successfully
The application of scientific knowledge for some specific purpose is known as ________.
A) technology
B) deductive science
C) inductive science
D) pure science
A) technology
Which of the following is true of natural selection?
A) It requires genetic variation.
B) It results in descent with modification.
C) It involves differential reproductive success.
D) It requires genetic variation, results in descent with modification, and involves differential
reproductive success.
D) It requires genetic variation, results in descent with modification, and involves differential
reproductive success.
14) Which of these provides evidence of the common ancestry of all life?
A) near universality of the genetic code
B) structure of the nucleus
C) structure of cilia
D) structure of chloroplasts
A) near universality of the genetic code